On July 12, NASA will release the first color photos taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The day before the release of the images, the space agency published a list of celestial objects photographed by the telescope. The goals include galaxies, nebulae, and a giant planet outside our Solar system.
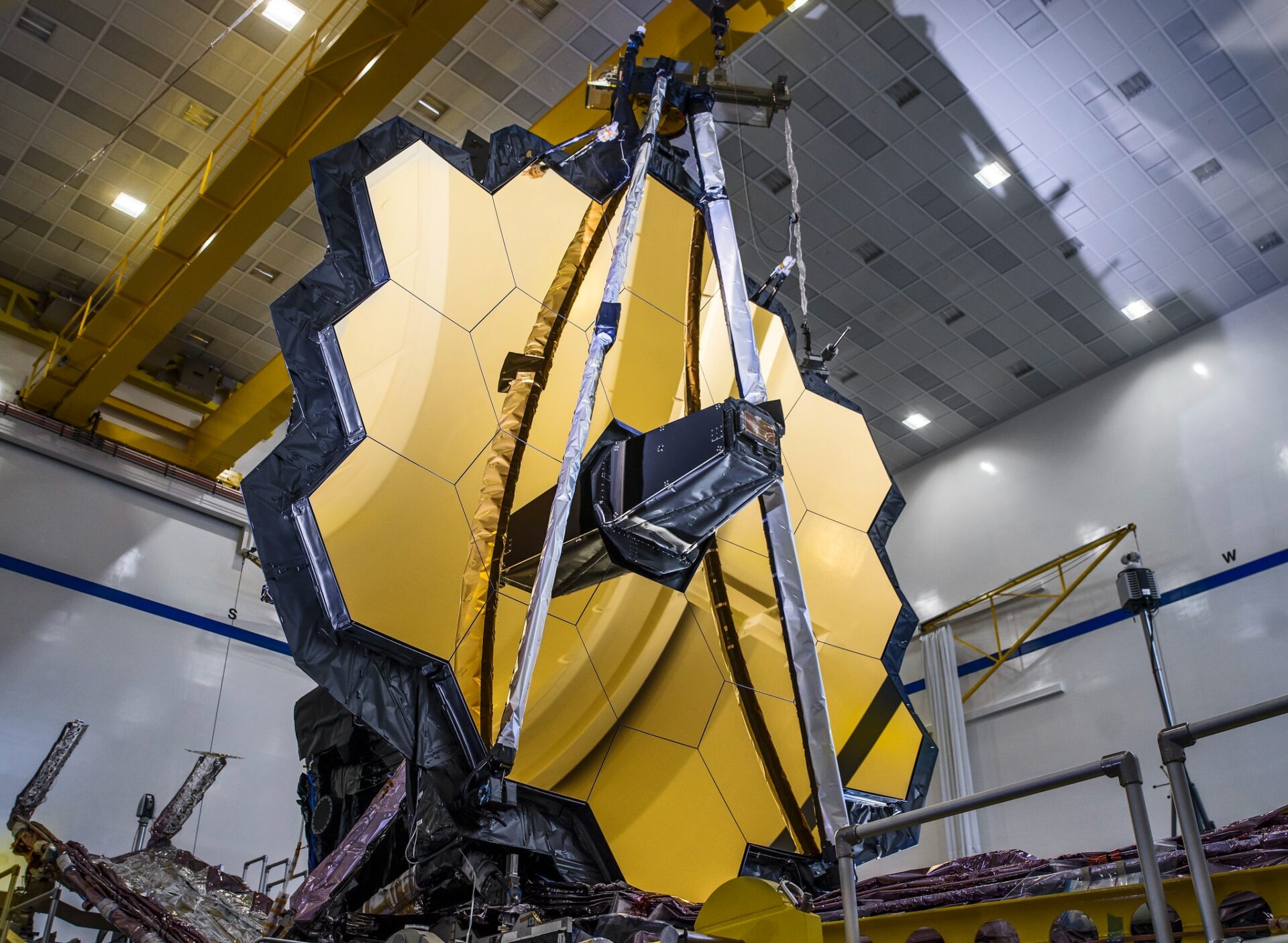

To get the first images, James Webb observed the target objects and areas of space for 120 hours. Until now, we do not know what the first images of JWST will be. There were only some hints without details. Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA assistant administrator for science, said that the society will see light reflected from the atmosphere of a planet outside our Solar System. And NASA administrator Bill Nelson assured that the second photo will be “the deepest image of our Universe that has ever been taken.”
Now we can study these directions of the deepest cosmos before seeing them in vivid detail. The list of targets was selected by an international team of people from NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency and the JWST-controlled Space Telescope Science Institute.
We saw some of the targets earlier thanks to images taken by James Webb’s predecessor, the Hubble Space Telescope. But the JWST mirror is three times wider than the “veteran” Hubble. Compared to Hubble images, JWST images should be impressively detailed.
List of James Webb targets
Carina Nebula. It is one of the largest and brightest nebulae in the sky, located about 7,600 light-years away in the southern constellation Carina. Nebulae are stellar nurseries where stars are formed. The Carina nebula is home to many massive stars, several times the size of the Sun.
WASP-96b (spectrum). This is a giant planet outside our solar system, which consists mainly of gas. The planet, located at a distance of almost 1,150 light-years from Earth, orbits its star every 3.4 days. It has about half the mass of Jupiter, and its discovery was announced in 2014.
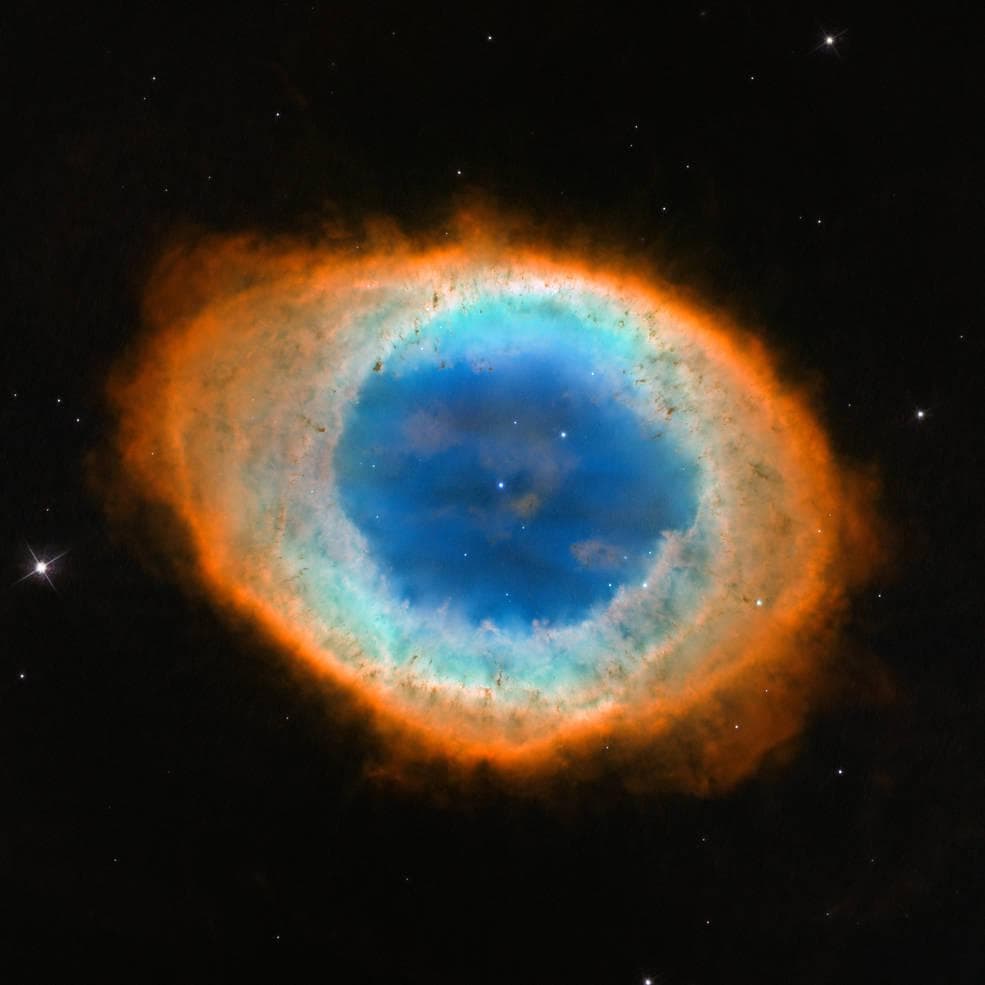
Ring Nebula. This emission nebula, known as NGC 6720 and Messier 57, is a cloud of gas surrounding a dying star. Its diameter is almost 0.5 light-years and it is located at a distance of about 2 thousand light-years from Earth.
Stephan’s Quintet. It is a group of five galaxies located about 290 million light-years away in the constellation Pegasus. The quintet is known for being the first compact group of galaxies ever discovered in 1877. Four of the five galaxies in the quintet are locked in a cosmic dance of repeated close encounters.
SMACS 0723 – Massive clusters of galaxies in the foreground magnify and disfigure the light of objects behind them, allowing to deeply see both very distant and weak populations of galaxies.
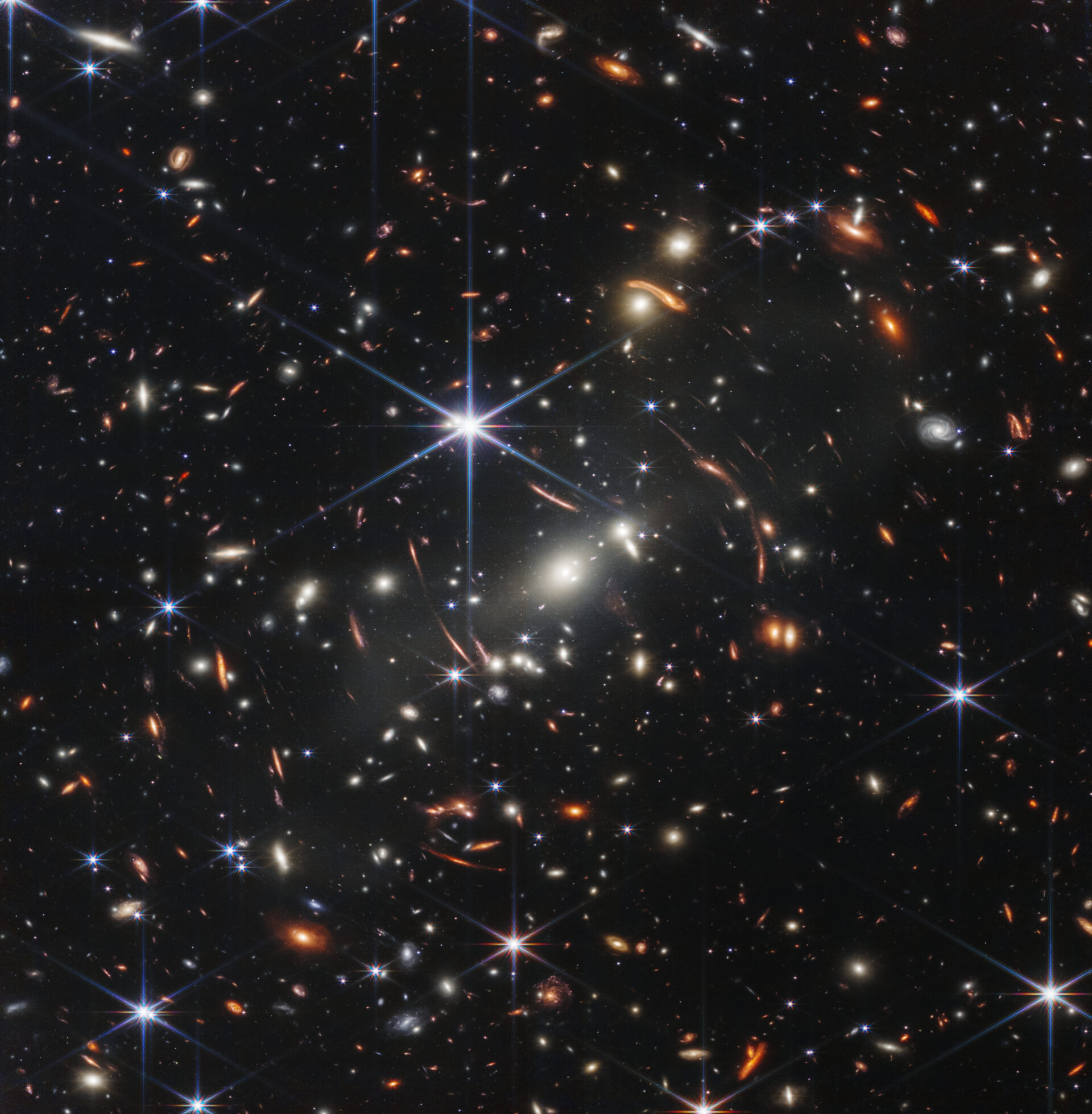

NASA intends to publish the image on July 12 at 05:30 p.m. GMT+3. And they will definitely take your breath away.
Recall that James Webb in the first year of its work will explore a black hole in the center of the Milky Way.
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
