It is impossible to look at the image of the galaxy NGC 6872 without emotions. This impressive image of a spiral galaxy shows long whiskers emerging from opposite ends of the structure, as if invisible giants are playing a tug of war. But there is something that makes NGC 6872 really striking – its extraordinary size. It is the largest spiral galaxy in the Universe. From end to end, the galaxy stretches for 522 thousand light-years. Thus, it is 5 times larger than our Milky Way.
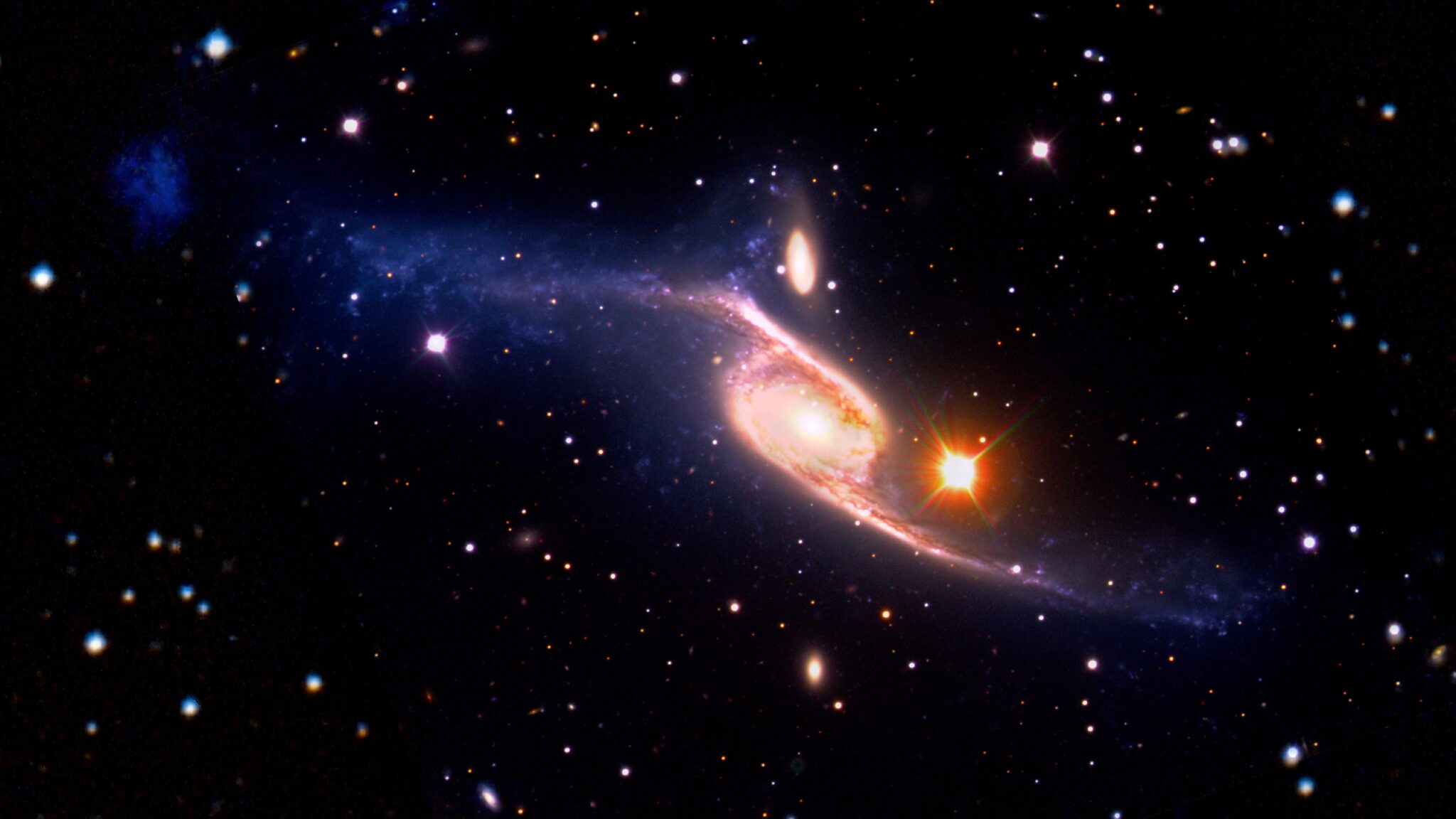

A recently published image shows the galaxy in the most detailed photo. It was obtained by combining the visible spectrum, ultraviolet and infrared radiation. All these data were obtained from the Very Large Telescope (VLT) of the European Southern Observatory and two space observatories GALEX and Spitzer, which had long ceased their work.
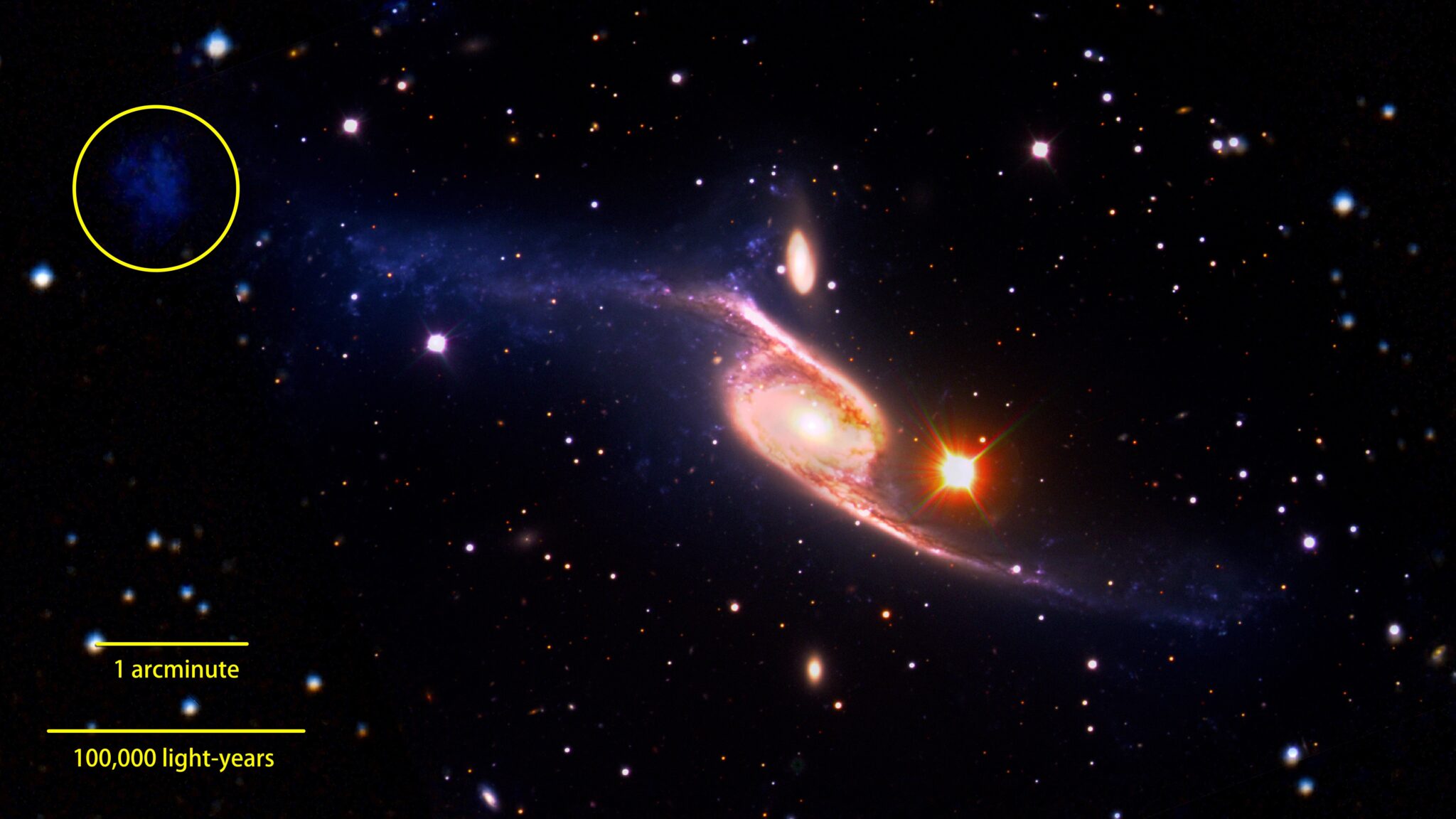

It is believed that NGC 6872, located at a distance of about 212 million light-years from Earth, has such an elongated shape due to its gravitational interaction with the neighboring disk galaxy IC4970, which has only 1/5 of the mass of its larger neighbor. Usually such gravitational interactions lead to galactic merger. But in this particular case, according to the analysis of the new combined image, astronomers claim that a new galaxy appears as a result of the interaction of NGC 6872 and IC 4970.
“Understanding the structure and dynamics of nearby interacting systems like this one brings us a step closer to placing these events into their proper cosmological context, paving the way to decoding what we find in younger, more distant systems,” explained Eli Dwek, an astrophysicist at NASA’s Space Flight Center.
Now it remains for James Webb to examine and study this space giant in more detail.
According to Space
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
