NASA’s Perseverance rover has used its capabilities to successfully navigate the most difficult route since arriving at the planet 2.5 years ago. Moreover, thanks to advanced technologies, the rover spent only a third of the time on this, during which other NASA rovers would have overcome a similar path.
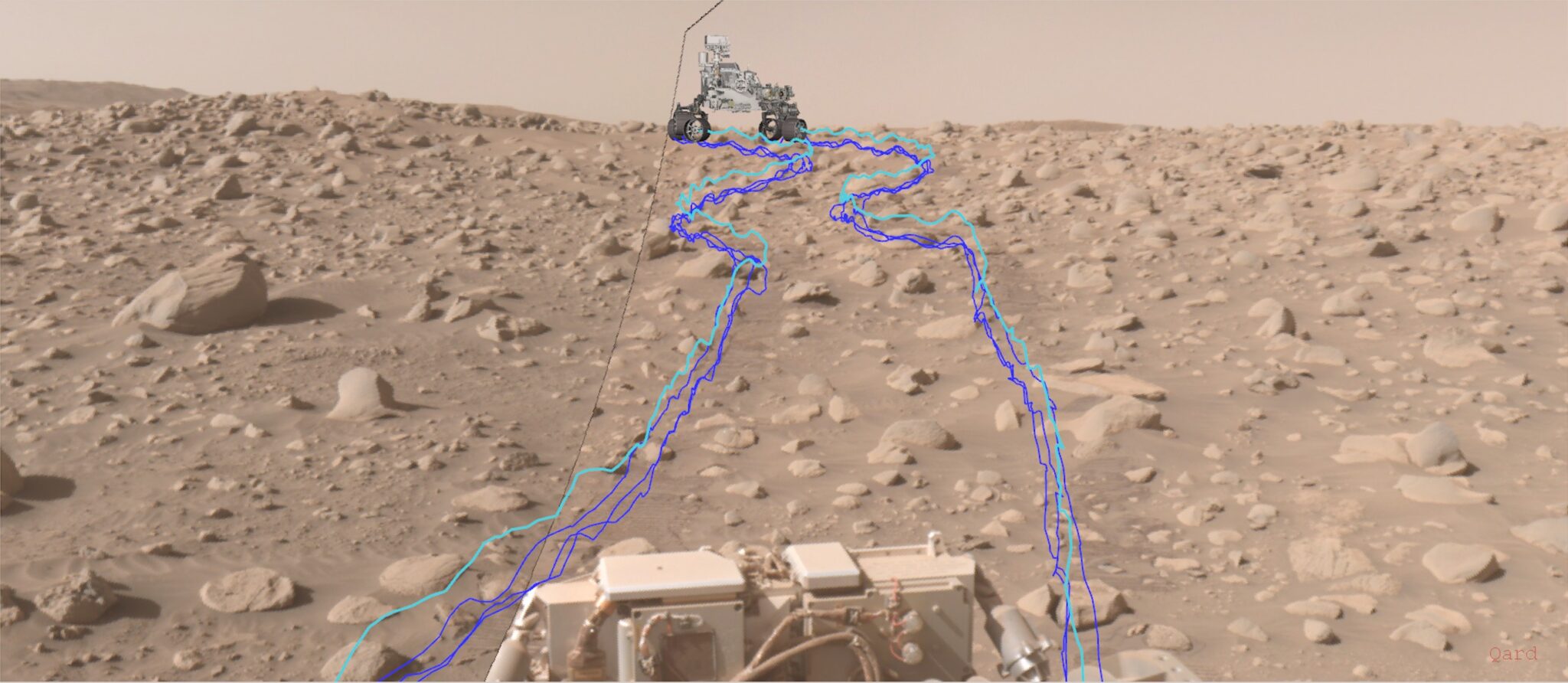
While the mission team from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory sends Perseverance general route maps, the rover uses its autonomous navigation systems to carry out the movement, avoiding rocks and other hazards on its way. The most difficult trip was associated with overcoming the Snowdrift Peak — a place inside the Jezero crater filled with large boulders.
The direct route through the peak extends for 520 m. But by the time the rover reached the opposite side of the slope, it had traveled 759 m, and the route had become longer due to maneuvering around boulders. The Perseverance rover planning team at JPL added that they didn’t want to send Perseverance around Snowdrift Peak as it would take weeks. “More time driving means less time for science,” explains Tyler Del Sesto, deputy head of the Perseverance mission at JPL.
Little steps of trailblazers
The successful trip of the rover is a testament to the work of the team that developed Perseverance and its autopilot system. But Del Sesto takes his hat off to other NASA rovers that have paved this path, including Curiosity, which continues to work on the Martian surface. “Of course, everybody on the team knows we only got to this level of performance by standing on the shoulders of giants. Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity, and Curiosity were the trailblazers,” said the Perseverance route planner.
To move safely, Sojourner had to stop every 13 centimeters so that its onboard computer could analyze and process the terrain in front of it before planning its next move. The next rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, could travel a distance of up to half a meter before stopping to plan their next actions. Curiosity, which arrived on Mars in 2012, recently received a software update. It helps it make decisions faster.
Autonomous Perseverance Capabilities
But thanks to better cameras and advanced software, Perseverance can take pictures fast enough to process its route in real time, and the additional computing power eliminates the need to stop to decide on the next step.
“This autonomous capability has allowed Perseverance to set new records for Mars off-roading, including a single-day drive distance of 1140.7 feet (347.7 meters) and longest drive without human review: 2296.2 feet (699.9 meters). But those achievements took place back when the rover was driving across the relatively flat terrain of Jezero Crater’s floor, without large rocks and other craters standing in its way. That’s why this recent navigation of boulder-festooned Snowdrift Peak impressed even the engineers who plan rover outings,” JPL notes.
Earlier we reported on how Perseverance on Mars generated oxygen for 10 hours of respiration.
According to NASA
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
