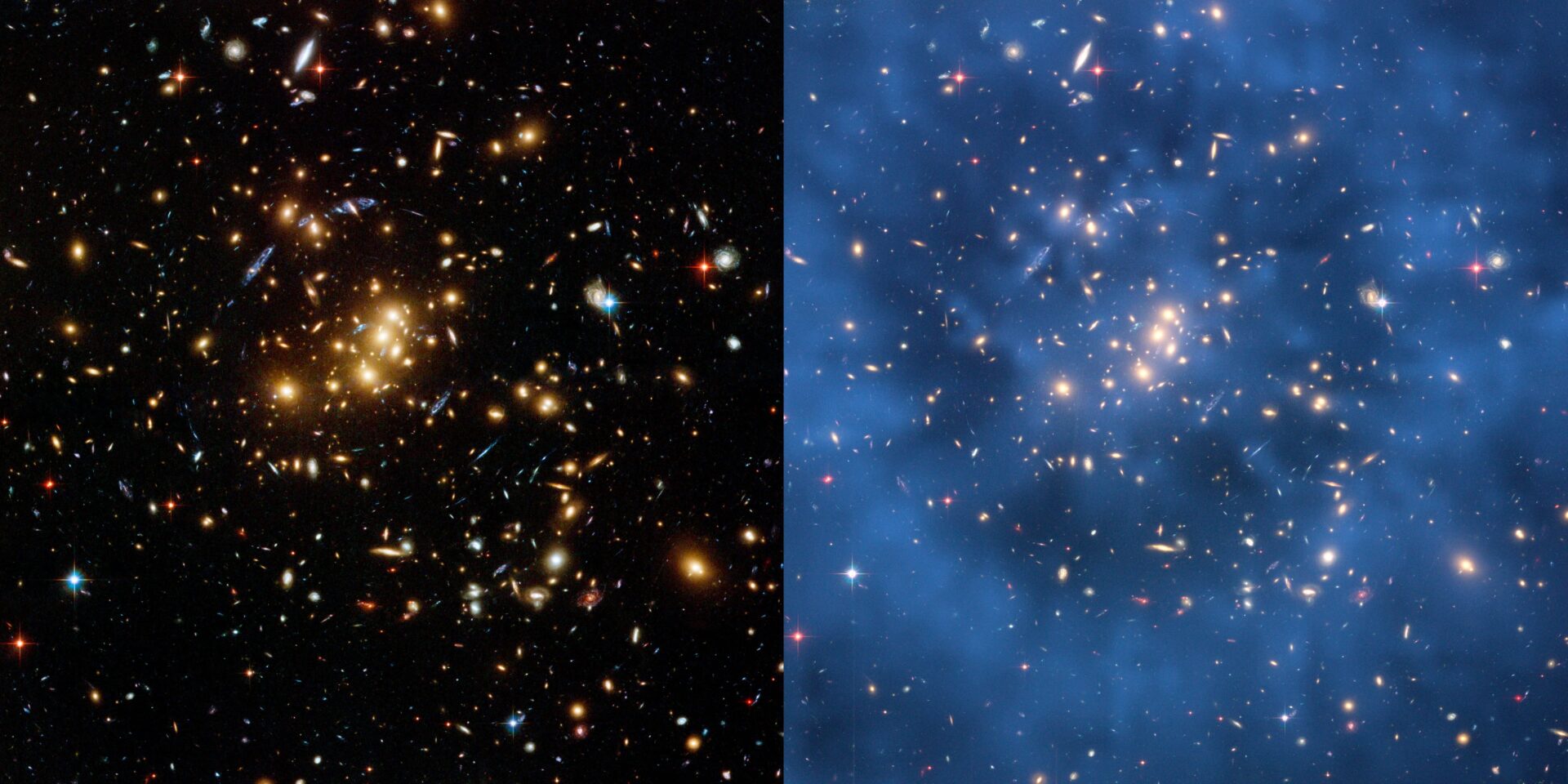
Researchers have just studied the gravitational lensing of the oldest light we can see. The oldest dark matter that surrounds galaxies at the age of 12 billion years was discovered in it. Dark matter was observed when observing how some galaxies distort the light of the cosmic microwave background, which occurred immediately after the Big Bang.
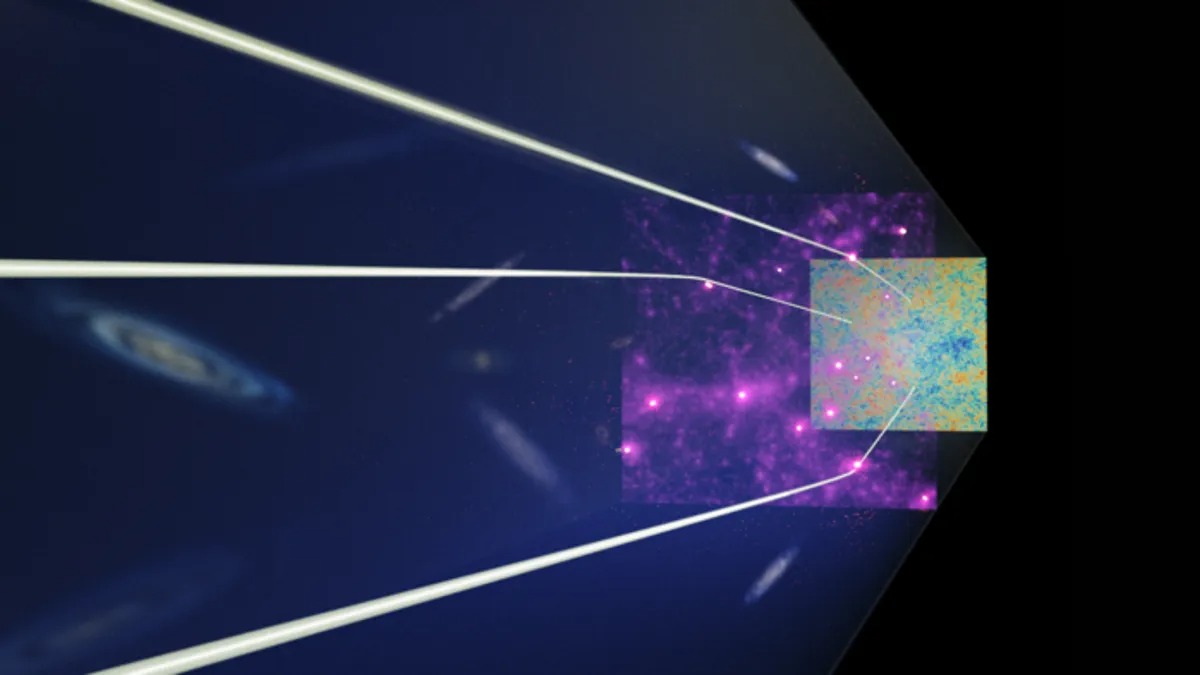

When the James Webb Telescope recently took the famous image of the SMACS 0723 galaxy cluster, it was actually looking at ancient galaxies that had been enlarged by SMACS 0723, including the oldest galaxy we’ve seen formed just 300 million years after the Big Bang. The team found that dark matter in these most remote regions of space turned out to be less complex than it should correspond to the standard theory of cosmology.
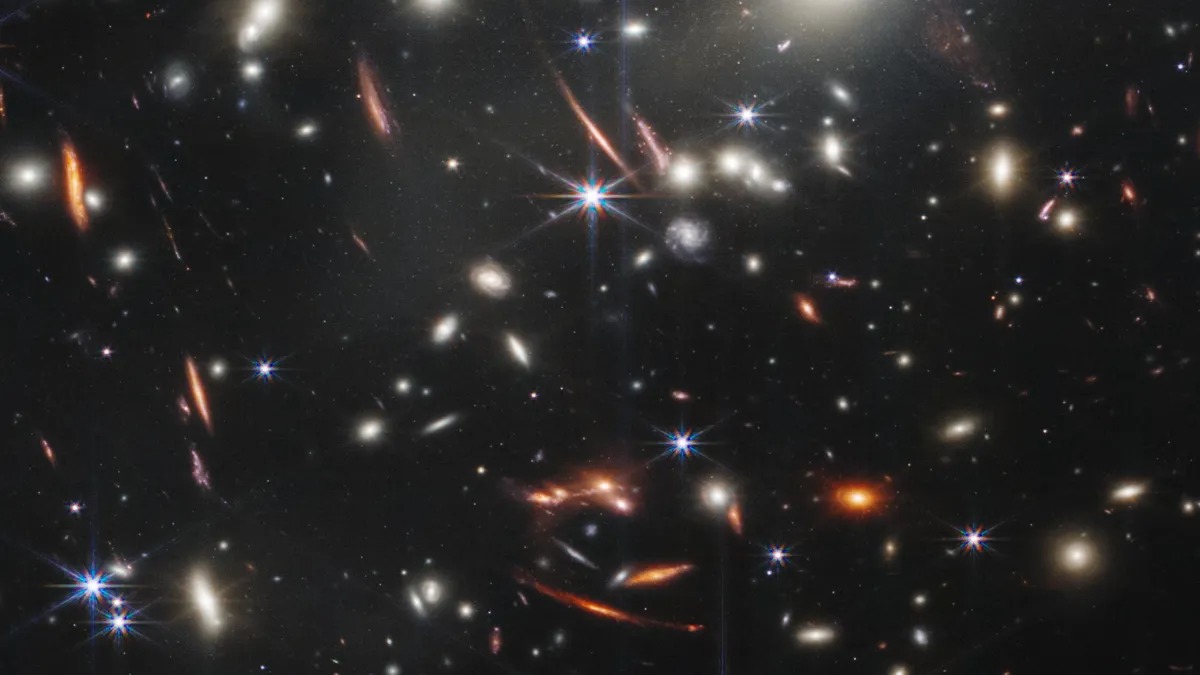

“Our discovery of the past still remains uncertain. If the data is confirmed, it means that the whole model of the cosmological model has flaws. This will force scientists to refine existing models to improve our understanding of the nature of dark matter,” said Hironao Miyatake, an astronomer at Nagoya University.
What is black matter?
Dark matter makes up about 27% of the Universe. It is impossible to detect it directly, because it is not fixed in any of the spectra. It manifests itself only in gravitational interaction with ordinary matter on a galactic scale. Scientists do not know what dark matter is. Therefore, dark matter is actually a universal term for this unaccounted-for mass.
There are some candidates for the role of dark matter: elementary particles called wimps (WIMP, or weakly interacting massive particles) and even smaller particles called axions. It is quite possible that both wimps and axions make up dark matter. The search for dark matter continues, but at this time astronomers can look and see its influence on a huge scale. Dark matter acts as a kind of invisible glue that holds together a cluster of galaxies. It also acts as a lens for more distant light, magnifying ancient objects for our observation. Although dark matter is a mystery, it also helps scientists study the early universe.
Earlier we reported on how the alternative theory of gravity has questioned dark matter.
According to Eurekalert
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
