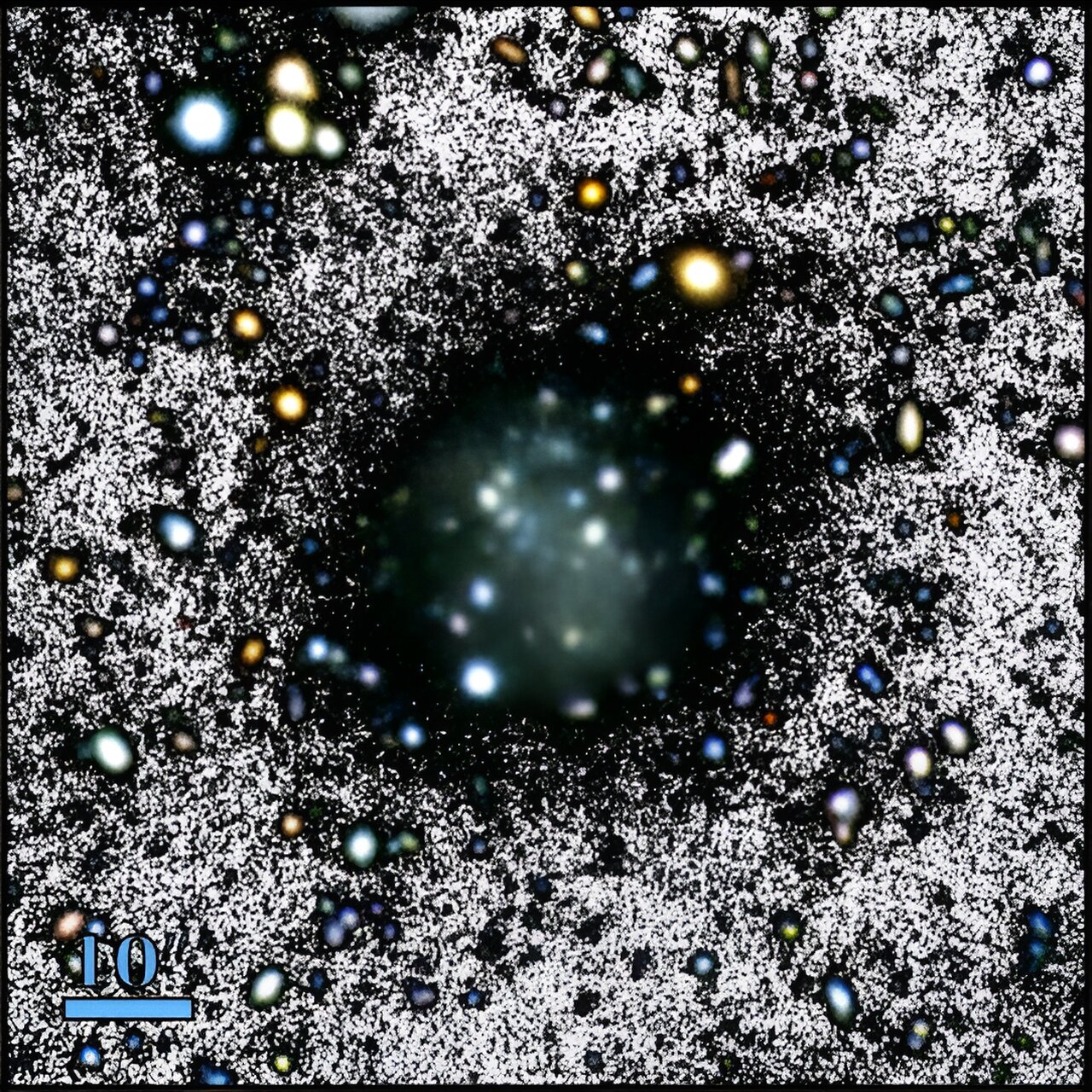
The Nube Galaxy, which was recently discovered by astronomers during the IAC Stripe 82 Legacy sky survey, turned out to be almost completely dark. It has a size comparable to the Small Magellanic Cloud, but at the same time, it practically does not emit light in the visible range.
Nearly dark galaxy
A group of astronomers led by Mireia Montes from the University of La Laguna (Spain) recently discovered an amazing star system named Nube. They implemented the IAC Stripe 82 Legacy project. Its goal is to search for extremely weak objects in a 2.5 degree wideband located in the southern part of the celestial sphere parallel to the equator.
This star system belongs to a type that is called “almost dark galaxies”. These systems have sufficiently large masses but, at the same time, extremely low brightness. Often, in the visible part of the spectrum, they are not visible at all.
At the same time, almost dark galaxies should not be confused with star systems in which there is a lot of dark matter or gas and dust. They mostly have low brightness precisely because their stars are quite rare and dim.
What is interesting about the new discovery
The Nube Galaxy is located 350 million light-years away from us. Its mass is estimated at 390 million solar, and its diameter is 22,500 light-years. In addition, it is surrounded by a halo of 26 billion solar masses. At first glance, it may seem that this is a lot, but in fact, a much smaller Small Magellanic Cloud, which is a satellite of the Milky Way, weighs so much.
However, it was the size that surprised scientists the most. Nube is much larger than any previously known almost dark galaxy. In terms of its size, it approaches ultra-diffuse systems. They have a diameter comparable to the Milky Way but contain only 1 percent of its stars.
The new system is at least 10 times dimmer than any of them. But what such features of Nube are connected with, researchers cannot say. Perhaps the initial conditions of its formation played a role, as did the factors that acted during its evolution, which lasted 10 billion years.
According to phys.org.
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
