During the implementation of the asteroid hunting algorithm for the Vera Rubin Observatory, which is designed for research lasting 10 years, the first potentially dangerous asteroid is discovered. The danger to the Earth was discovered even before the observatory began its full-fledged work.
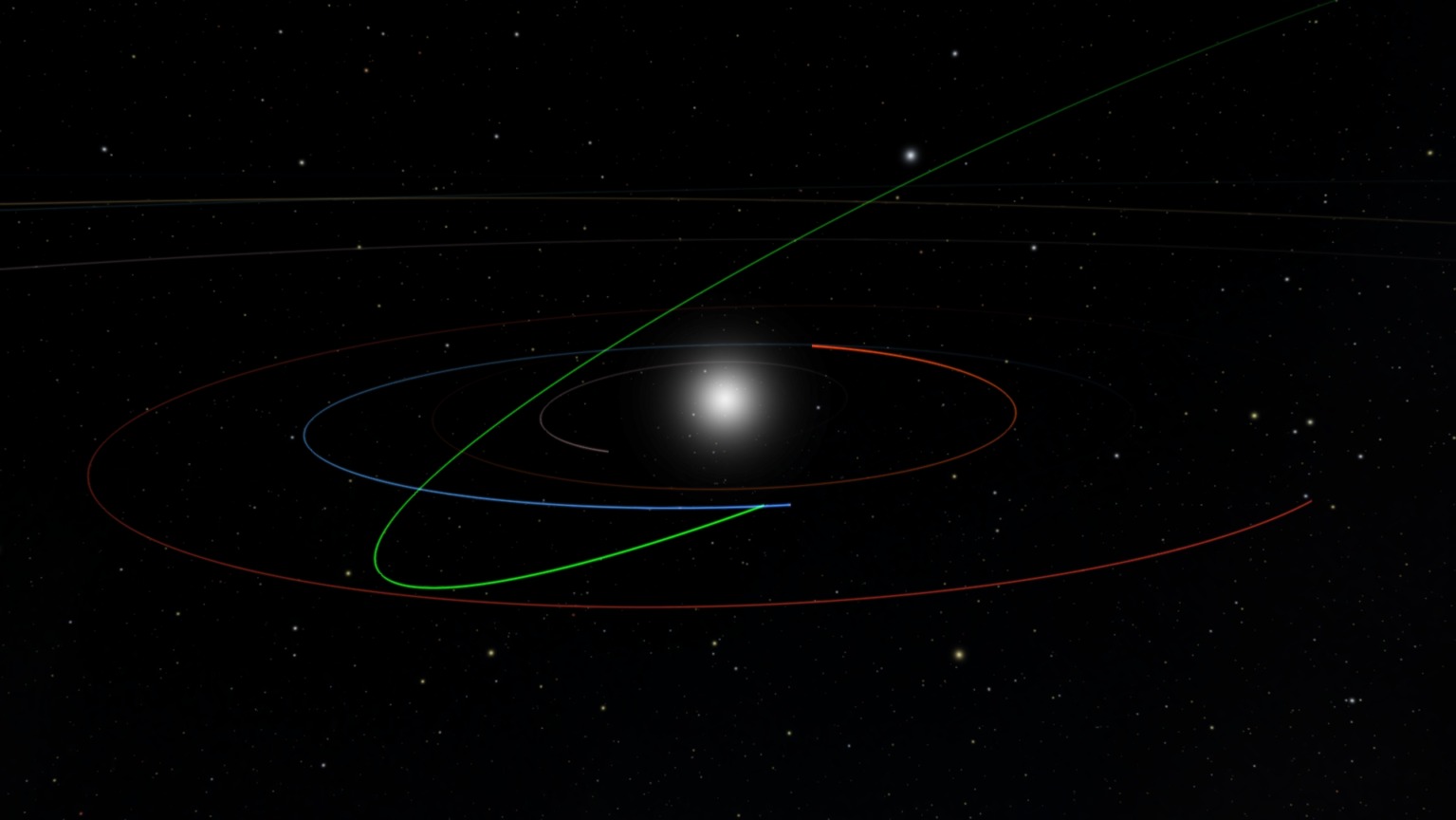
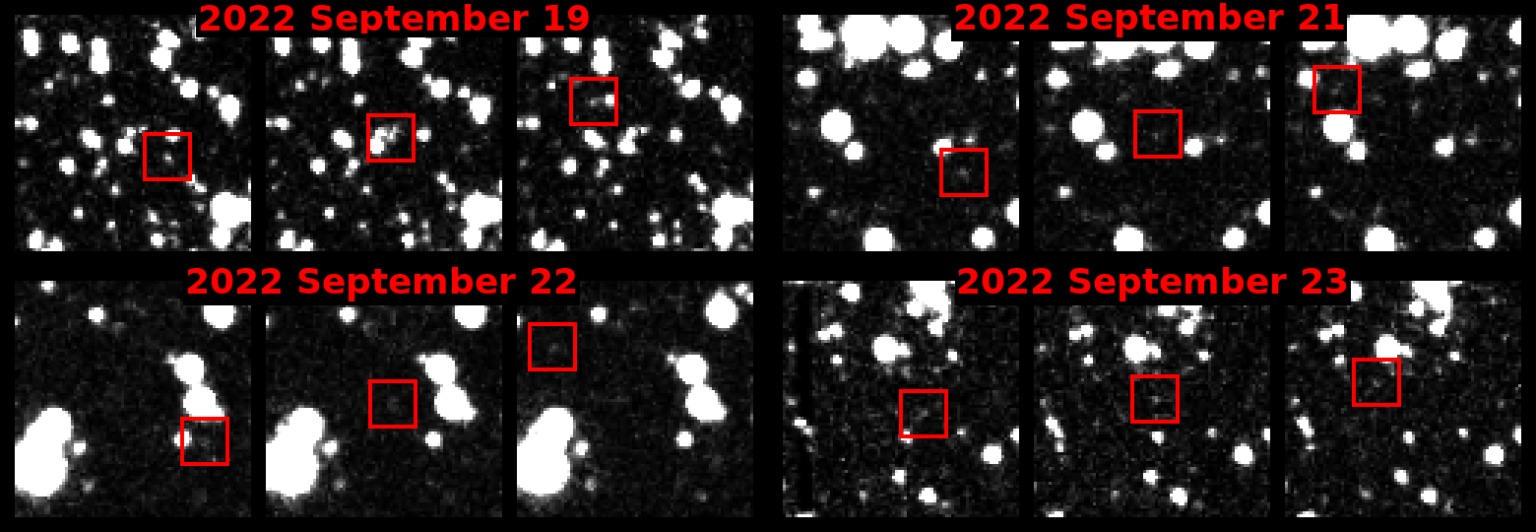
The asteroid found was named 2022 SF289. It has a width of 182 meters and is located at a distance of about 4 astronomical units from the Earth. Artificial intelligence has calculated that the asteroid will fly past the Earth at a very close distance, which defines it as potentially dangerous.
The concept of “potentially dangerous” is a professional term for scientists, so it sounds creepy to the public. An asteroid is classified as “potentially dangerous” only when there is a certain probability of its collision with the Earth, which can cause significant damage on Earth. Therefore, special attention is paid to this object. Last month, an asteroid with a length of 487 meters flew past the Earth without consequences.
First catch of HelioLinc3D
But the main news is not the fact of the danger of asteroid 2022 SF289, but the fact that it is detected using a new algorithm called HelioLinc3D. This artificial intelligence can analyze asteroids, and identify those that are closest to the Earth. At the same time, their detection requires significantly fewer observations than it is with traditional methods of “hunting”. Although the Vera Rubin Observatory has not yet started its work, HelioLinc3D has been successfully tested using the ATLAS Observatory at the University of Hawaii.
“By demonstrating the real-world effectiveness of the software that Rubin will use to look for thousands of yet-unknown potentially hazardous asteroids, the discovery of 2022 SF289 makes us all safer,” said Ari Heinze, chief developer of the new algorithm and a scientist at the Vera Rubin Observatory and the University of Washington.
Legacy Survey of Space and Time
The main asset of the future Vera Rubin Observatory is its 10-year Legacy Survey of Space and Time program, which provides for photographing the night sky about once a week. The observatory is located high in the Chilean Atacama Desert, which provides a clear view of space without significant atmospheric distortion and light pollution.
It was planned that the observatory would open in 2022. But the COVID-19 pandemic has become a hindrance. Now it is planned that it will begin its work in 2025. The observatory’s camera has a resolution of 3.2 billion pixels and measures 1.68 meters by 3 meters, making it the largest digital camera ever created.
Earlier we talked about 12 interesting facts about asteroids.
According to washington.edu
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
