In 2016, the UN General Assembly proclaimed June 30 as international Asteroid Day. The date was chosen not by chance. On June 30, 1908, an explosion of a celestial body occurred over Siberia, which became known as the Tunguska meteorite. This is the largest such an event ever documented by mankind. If the Tunguska meteorite had exploded over a large city, the death toll could have been measured in thousands. One of the key goals of Asteroid Day is to inform the public about the dangers of such events and find ways to prevent them.
On the occasion of Asteroid Day, we have compiled a selection of 12 interesting facts about these celestial bodies.
The first object of the Asteroid Belt was discovered on the first night of the 19th century
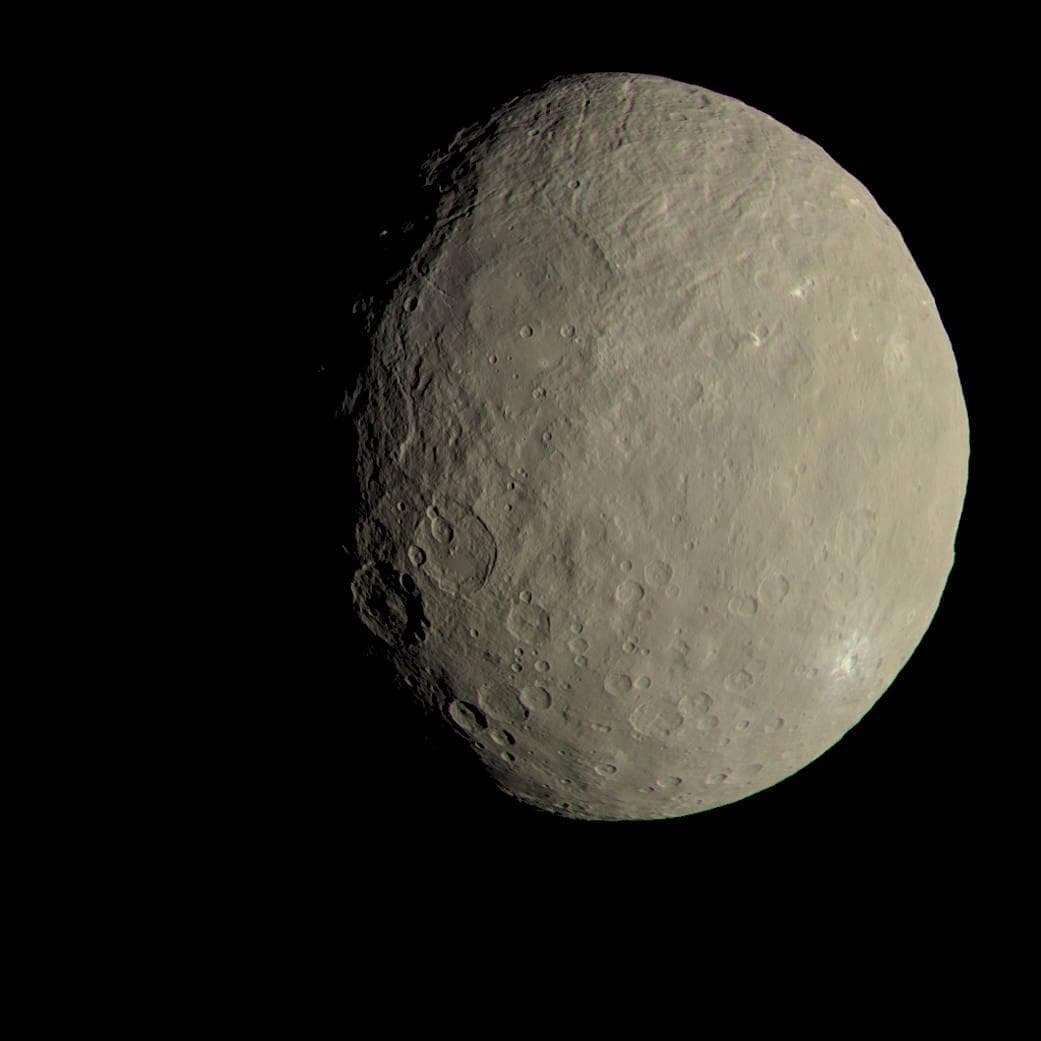
The first of objects, located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, was discovered by the Italian astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi on the evening of January 1, 1801. It was named Ceres — in honor of the Roman goddess of agriculture.

Asteroids were considered planets until the middle of the nineteenth century,
Within a few years after discovery of Ceres, astronomers discerned three more objects between Mars and Jupiter. They were named Pallas, Juno and Vesta. The question of classification, of newly discovered celestial bodies, has long been the subject of debate. Because even in the largest telescopes, these objects still looked like stars, William Herschel proposed the term asteroids (ie, “star-shaped”).
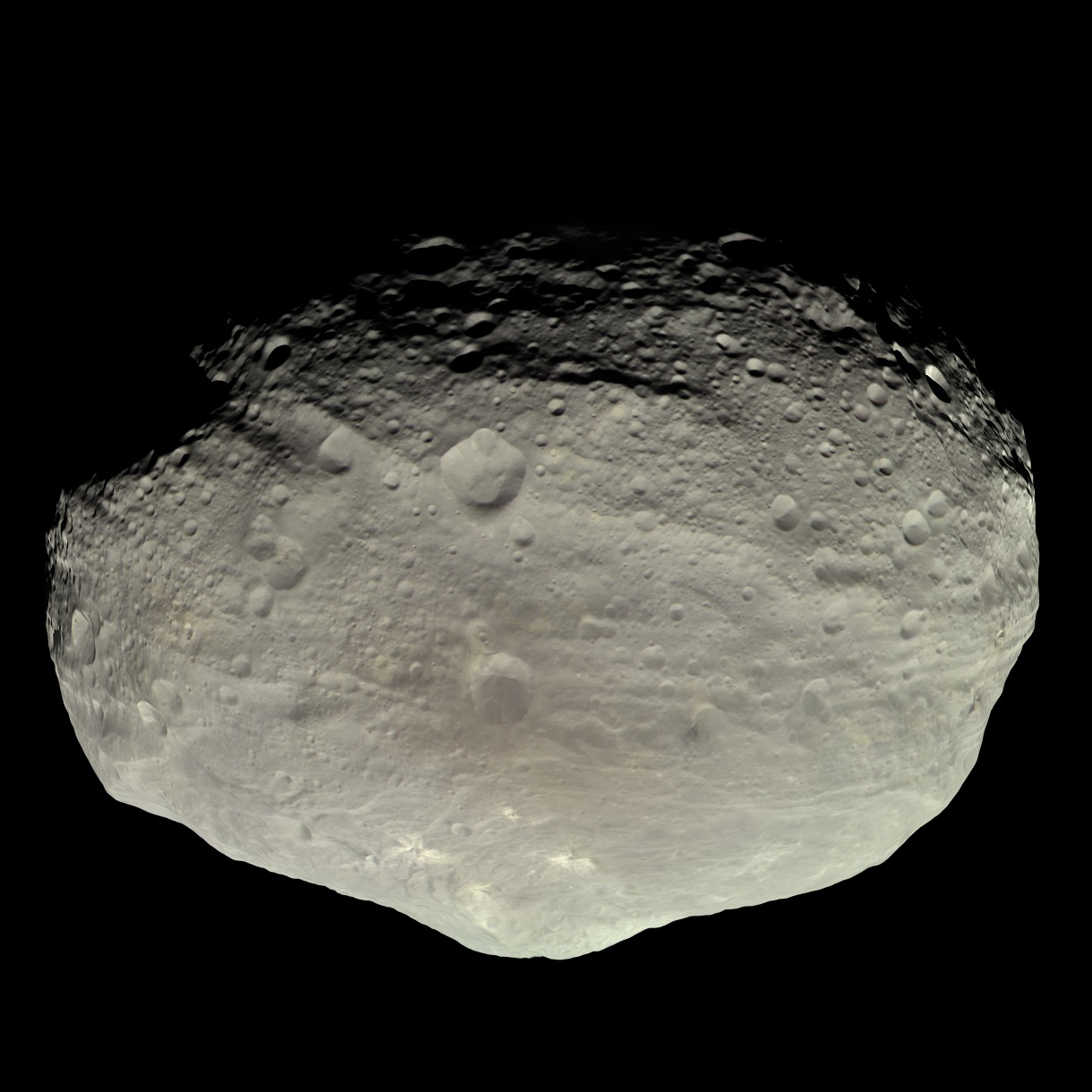

However, most astronomers of that era still regarded Ceres, Pallas, Juno, and West as planets. The situation changed only in the middle of the XIX century after the discovery of more celestial bodies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It became clear that they form a single belt. After that, the term “asteroids” was finally fixed for them. Interestingly, in 2006, the International Astronomical Union again “promoted” Ceres, reclassifying it as a dwarf planet.
Most asteroids are concentrated in the belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter
As for today, astronomers have discovered more than a million asteroids. Most of their orbits lie between Mars and Jupiter. So this region is designated as The Main Asteroid Belt.
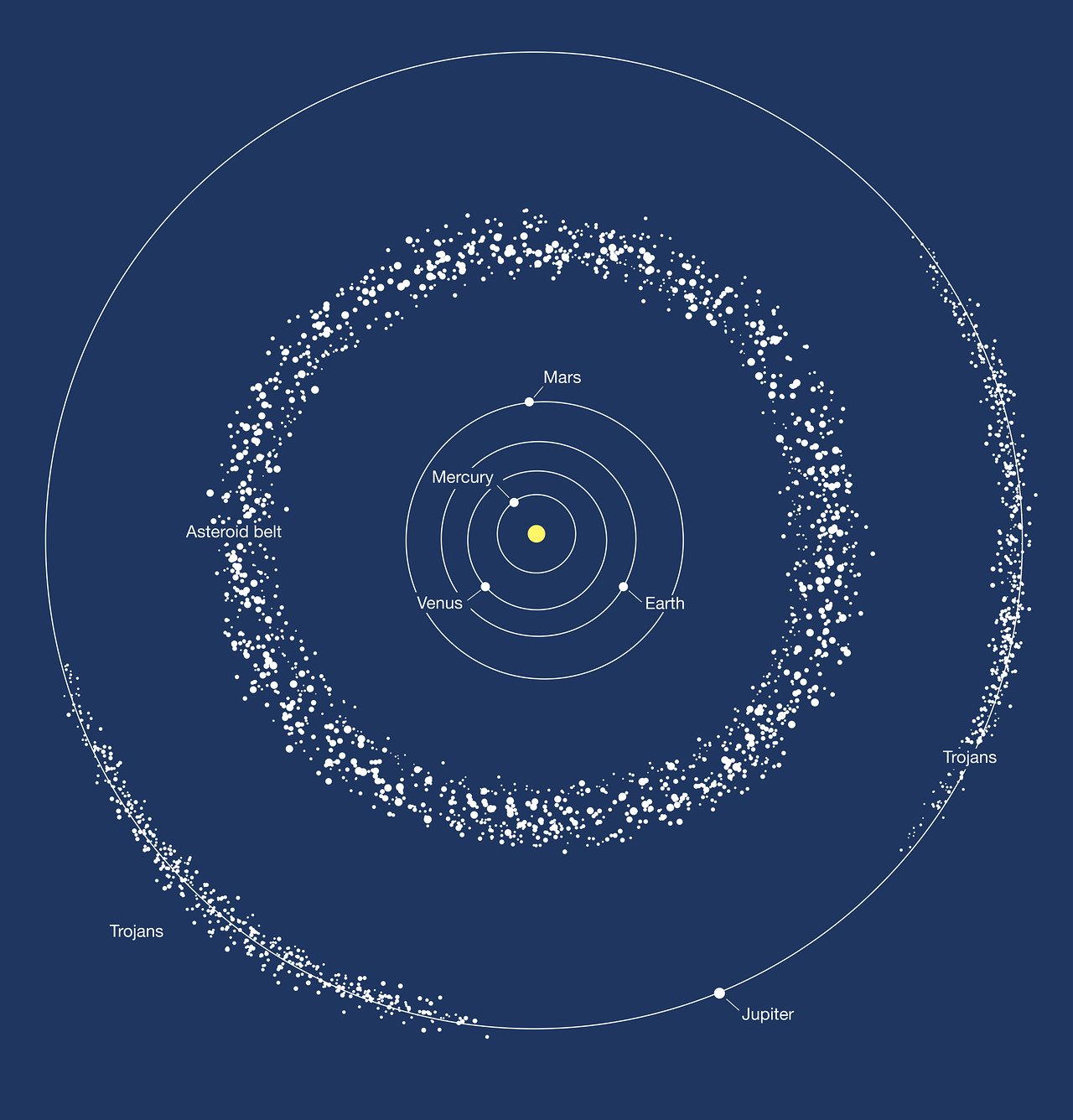
At the same time, the area of distribution of asteroids is not limited to the Main Belt. They can also be found inside the orbit of Venus, in the Lagrange points of Jupiter and in the orbit of Saturn.
There has never been a planet in the asteroid belt
According to a fairly common misconception, asteroids in the Main Belt are fragments of a lost planet. But this is not the case. The fact is that the mass of all asteroids is absolutely small on a cosmic scale and is only 4% of the mass of the Moon. It is now believed that this is a kind of construction debris left over from the formation of the solar system. Due to the gravitational influence of Jupiter, asteroids have not been able to become part of any planet.

There are several types of asteroids
Depending on their chemical composition and albedo, all asteroids are subdivided into many different classes. Simplifying, we can single out three main types of asteroids: carbon ones (they have very dark surface), silicon ones (stone) and metal ones. The first two categories account for approximately 75% and 17% of all known asteroids.
The dinosaurs were killed by an asteroid
There were several mass extinctions in the history of the Earth. The last of them happened 66 million years ago and led to the extinction of dinosaurs. There is a consensus in scientific community that it happened due to the consequences of the fall of a 10-kilometer asteroid on the Yucatan Peninsula. The impact left a 180-kilometer crater. It is believed that the dinosaurs were killed by an asteroid and not by a comet due to the chemical composition of the sediment found.
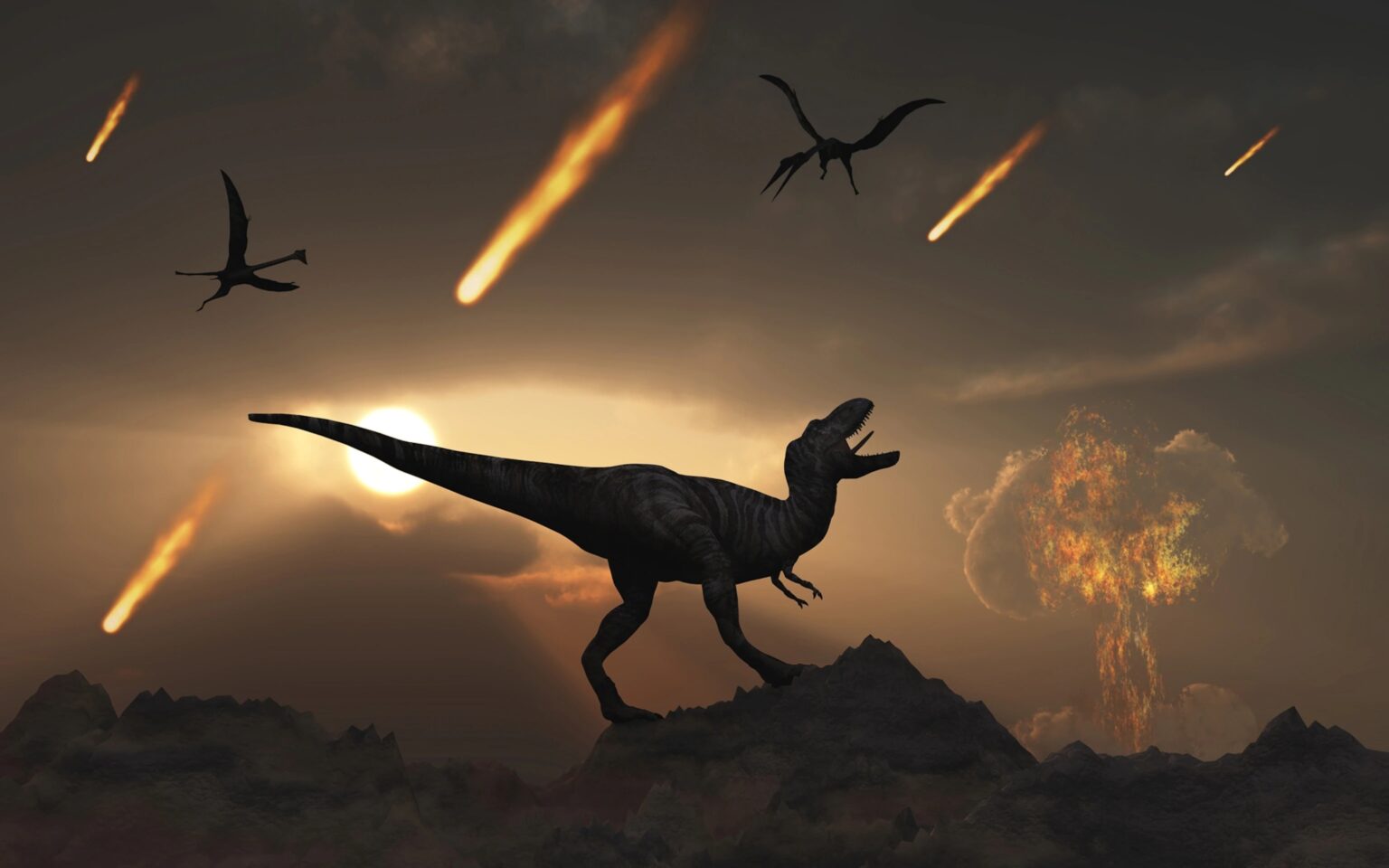

After the collision with that sinister asteroid, the entire planet plunged into darkness for a period of 650-700 days, killing up to 75% of living things.
The asteroid belt was the first time crossed by a human spacecraft in 1972
The first probe to cross the Main Asteroid Belt was the Pioneer 10. It happened in 1972. The device refuted the theory that the belt was filled with dust that could damage technological units onboard. Since then, the region has been safely crossed by eight more Earth’s envoys, and the Dawn spacecraft has made a real voyage about it. First it settled into permanent orbit around the asteroid Vesta, and then flew to Ceres.

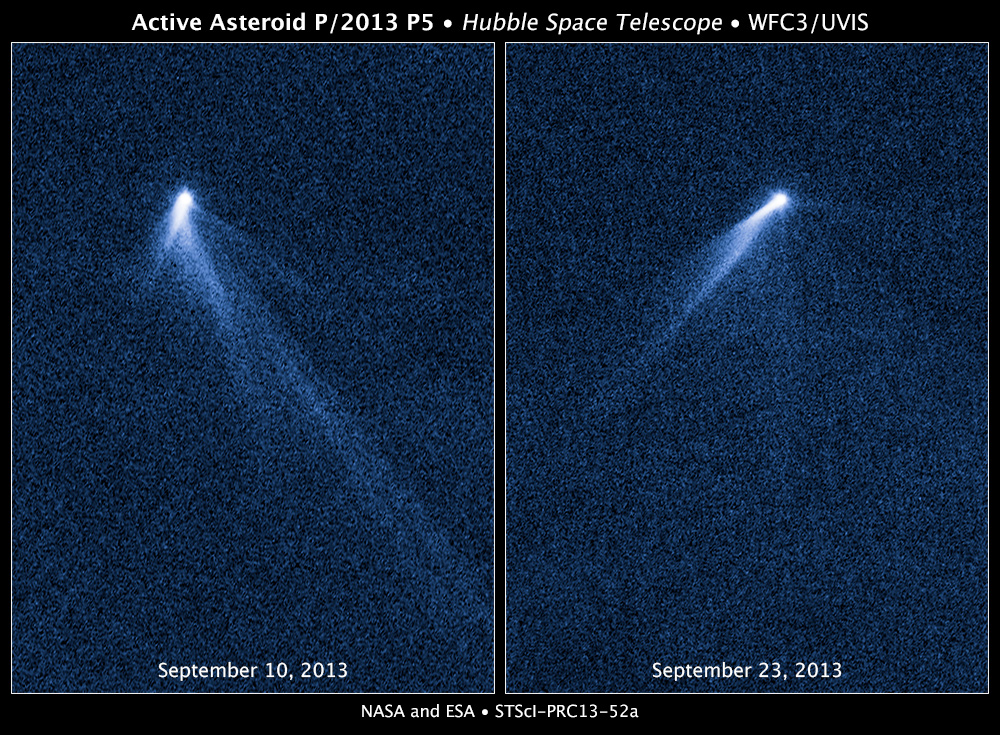
Some asteroids can behave like comets
Some of the objects in the Main Belt sometimes show cometary activity and acquire tails. According to scientists, this may be due to the fact that they contain water ice. It is also possible that some of these bodies are “degenerate” comets — the comets that have almost completely lost their volatile matter and are now little different from conventional asteroids.