At the 55th Conference on Lunar and Planetary Sciences, held in Woodlands, Texas, scientists announced the discovery of a giant volcano and a possible layer of buried relict glacier in the eastern part of the Martian volcanic province of Tharsis near the equator of the planet.

The giant volcano that had been hiding in plain sight for decades in one of the most iconic regions of Mars, on the border between the heavily broken labyrinth of Noctis Labyrinthus (Labyrinth of the Night) and the monumental canyons of Valles Marineris (Valleys of Mariner). Noctis volcano is a temporary name until it gets an official name. Its height reaches 9022 meters, its width is 450 kilometers, and the gentle outer slopes extend for 225 kilometers in different directions. The giant size of the volcano and the complex history of its modifications indicate that it has been active for a very long time.
Complex history of formation
Noctis volcano has a long and complex history of formation as a result of a combination of fracturing, thermal erosion and glacial erosion. Researchers interpret the volcano as a huge shield consisting of layered accumulations of pyroclastic materials, lavas and ice. Moreover, the latter was formed as a result of the repeated accumulation of snow and glaciers on its flanks for a long time.
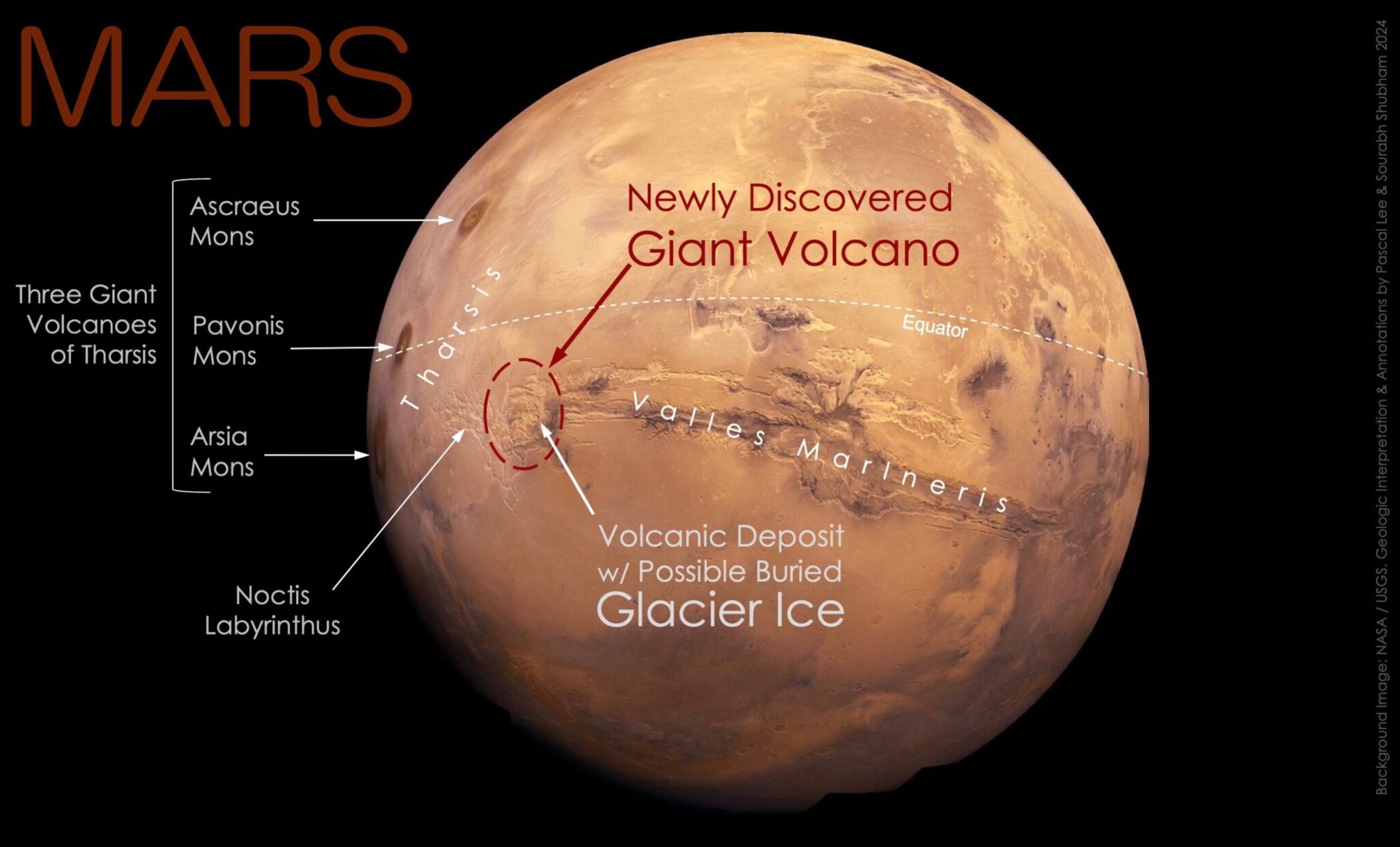
In addition to the volcano, it is reported about the discovery of an extensive area of 5,000 km2 of volcanic deposits around the perimeter of the volcano, which consists of a large number of low, rounded and elongated, blister-like mounds. This area was formed as a result of an explosive release of steam venting or steam swelling, when a thin blanket of hot volcanic materials lies on a surface rich in water or ice.
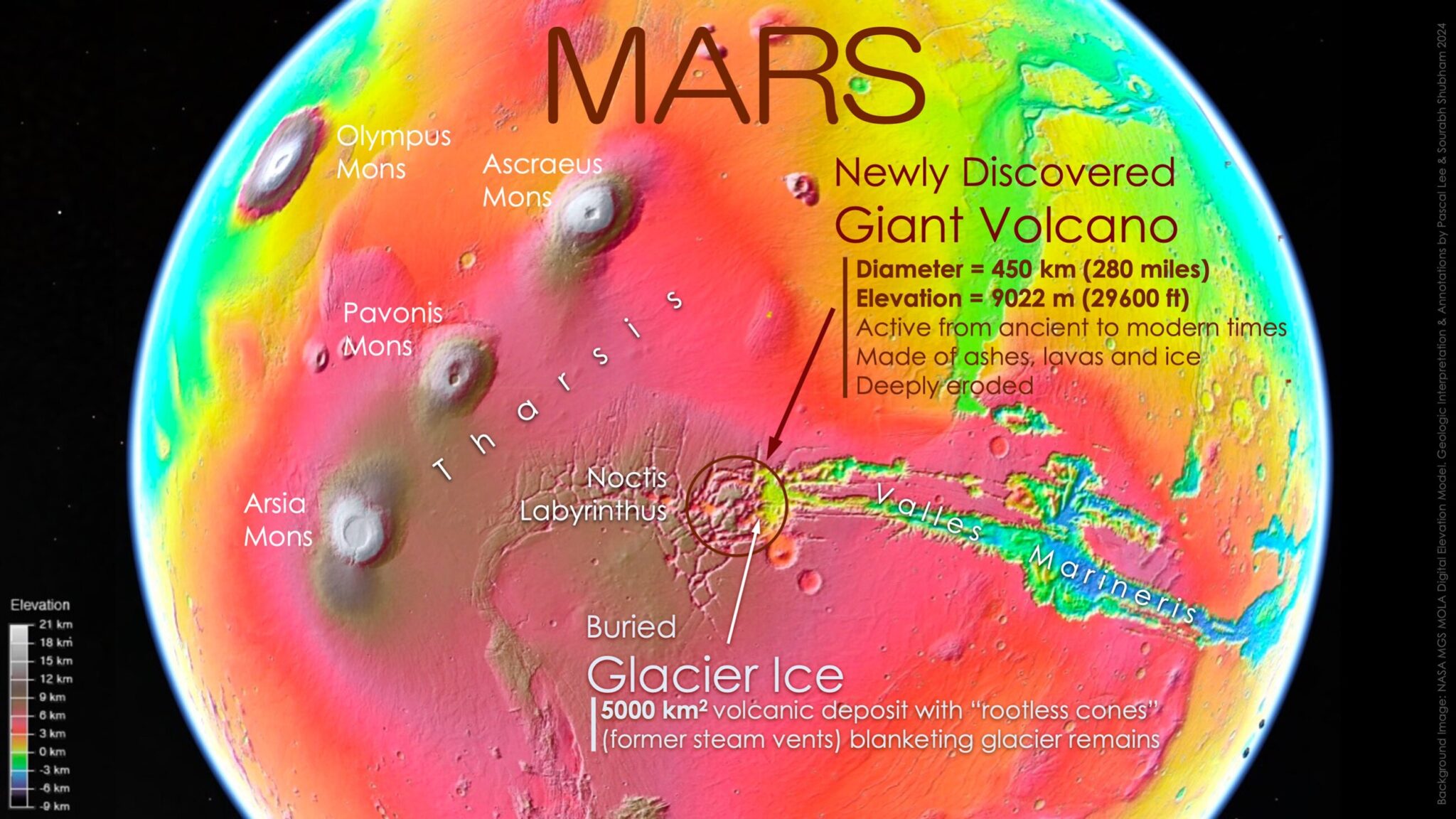
Scientists have also discovered the remains of a relict glacier through a large erosion hole in a volcanic area. They noticed light deposits of sulfate salt with morphological signs of a glacier, which indicates the possibility of the existence of a large layer of ice under the frozen volcanic cover.
Mysterious volcano
But much about the newly discovered giant volcano remains a mystery. Although it is clear that it has been active since the formation of the geological history of Mars, it is not known how ancient it is. It is also unknown whether it is still volcanically active and whether it may erupt again in the future. And if it has been active for a very long time, could the combination of prolonged heat and ice water allow this place to harbor life?
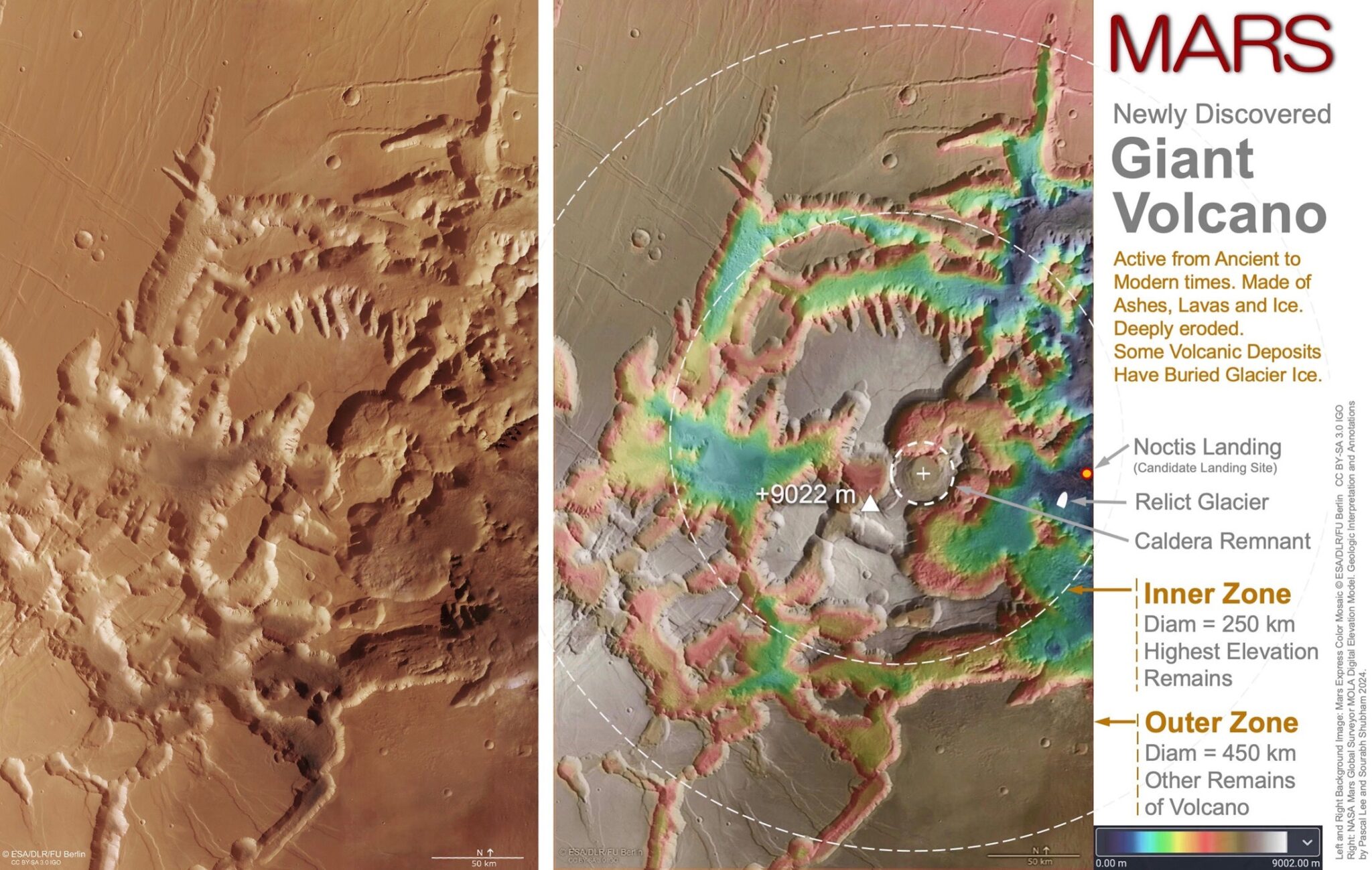
The mysteries surrounding the Noctis volcano continue to puzzle scientists. But this object is already becoming a new interesting place to study the geological evolution of Mars, search for life and plan future missions to colonize the Red Planet.
Earlier, we reported on how Mount Olympus could be an island in the vast ocean of Mars.
According to phys.org
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.comne/ust_magazine


