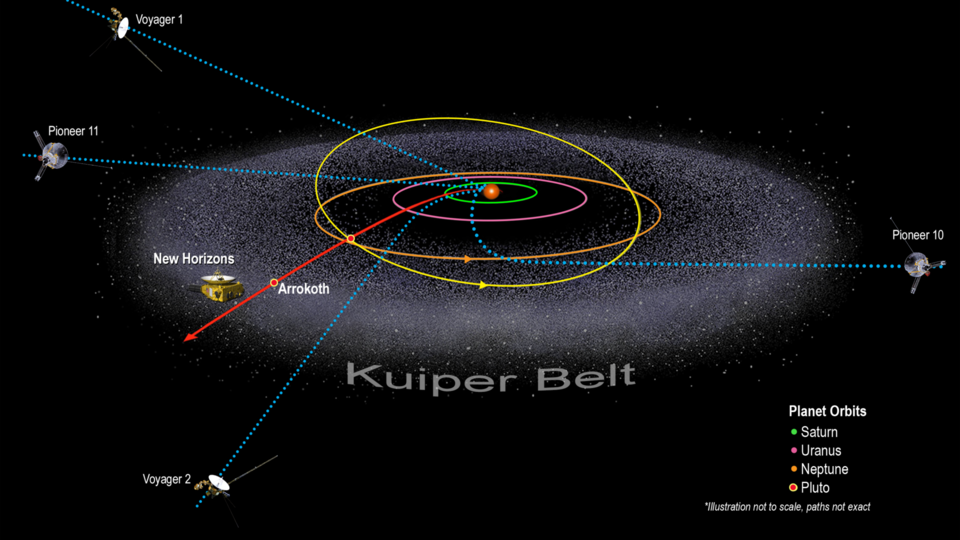
Humanity has been sending spacecraft into deep space for 50 years. In 1972, the Pioneer 10 mission began a journey beyond the Solar System. Now we have five probes that have either reached the edge of our Solar System or are rapidly approaching it: Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 and New Horizons.
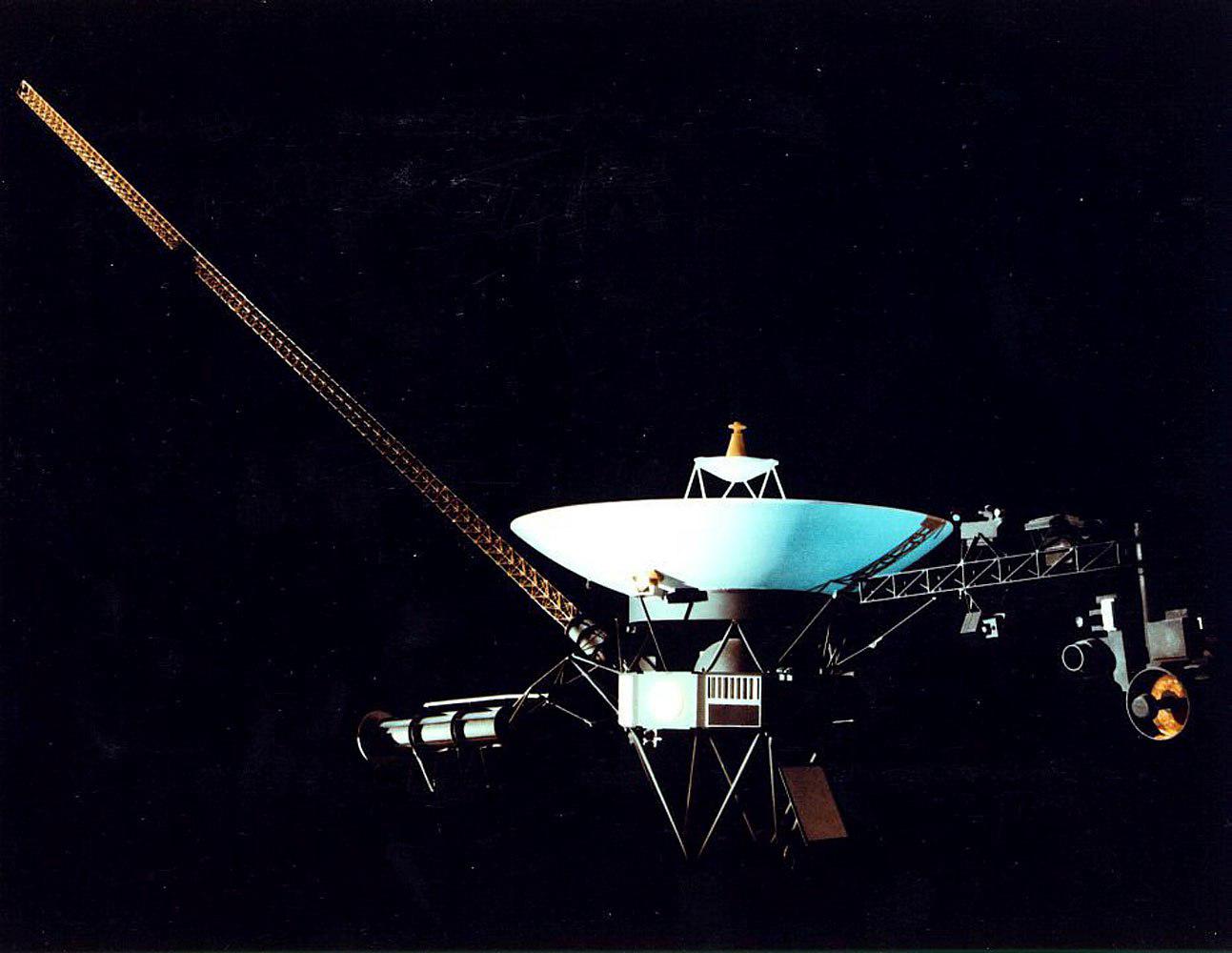
At first, it was planned that these spaceships would explore our neighboring planets, but now they are paving the way beyond the Solar System, providing astronomers with unique vantage points in space — and they have achieved a lot in 2022.
Voyager 1 and 2
Voyager missions celebrated their 45th anniversary in 2022. From close flights of the outer planets to exploring the most remote corners of space, these two spacecraft have made a huge contribution to astronomers’ understanding of the Solar System. Currently, their main project is to explore interstellar space. Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause, the limit at which the Solar particle flow ceased to be a major influence, in 2012, and Voyager 2 followed it in 2018.
The mission team encountered one major problem last year when Voyager 1 began sending distorted information about its location. Engineers found the reason – the culprit was outdated computer equipment. After correction, the probe started working normally. However, similar incidents should be expected with an aging spacecraft.
The team also actively manages the power source on board each Voyager, which is decreasing every year as the probes’ radioactive generators become increasingly inefficient. This year, mission personnel turned off the heaters that kept a number of scientific instruments on board in the harsh, cold environment of space — and, to everyone’s surprise, these instruments are still working.
Pioneer 10 and 11
Pioneer space probes occupy a special place in the history of space. Unfortunately, these outstanding 50-year-old devices have not been functioning for a long time – Pioneer 10 lost contact back in 2003, and Pioneer 11 has been silent since its last contact in 1995. But both of these spacecraft are signs of humanity’s presence in the Solar System, and they are still continuing their travels.

Once a spacecraft is set on a trajectory outside the Solar System, according to the laws of physics, it will not stop until something changes its course. According to calculations, the flight path of Pioneer 10 lies in the direction of the star Aldebaran, which it will reach in 2 million years. Pioneer 11 is flying to the constellation Aquila, one of the stars of which it will reach in 4 million years.
New Horizons
New Horizons is the youngest brother of these pioneering missions, launched in 2006. After completing its famous flyby of the dwarf planet Pluto in 2015, this probe continues its journey beyond the Solar System. According to calculations, it will reach the heliopause around 2040.
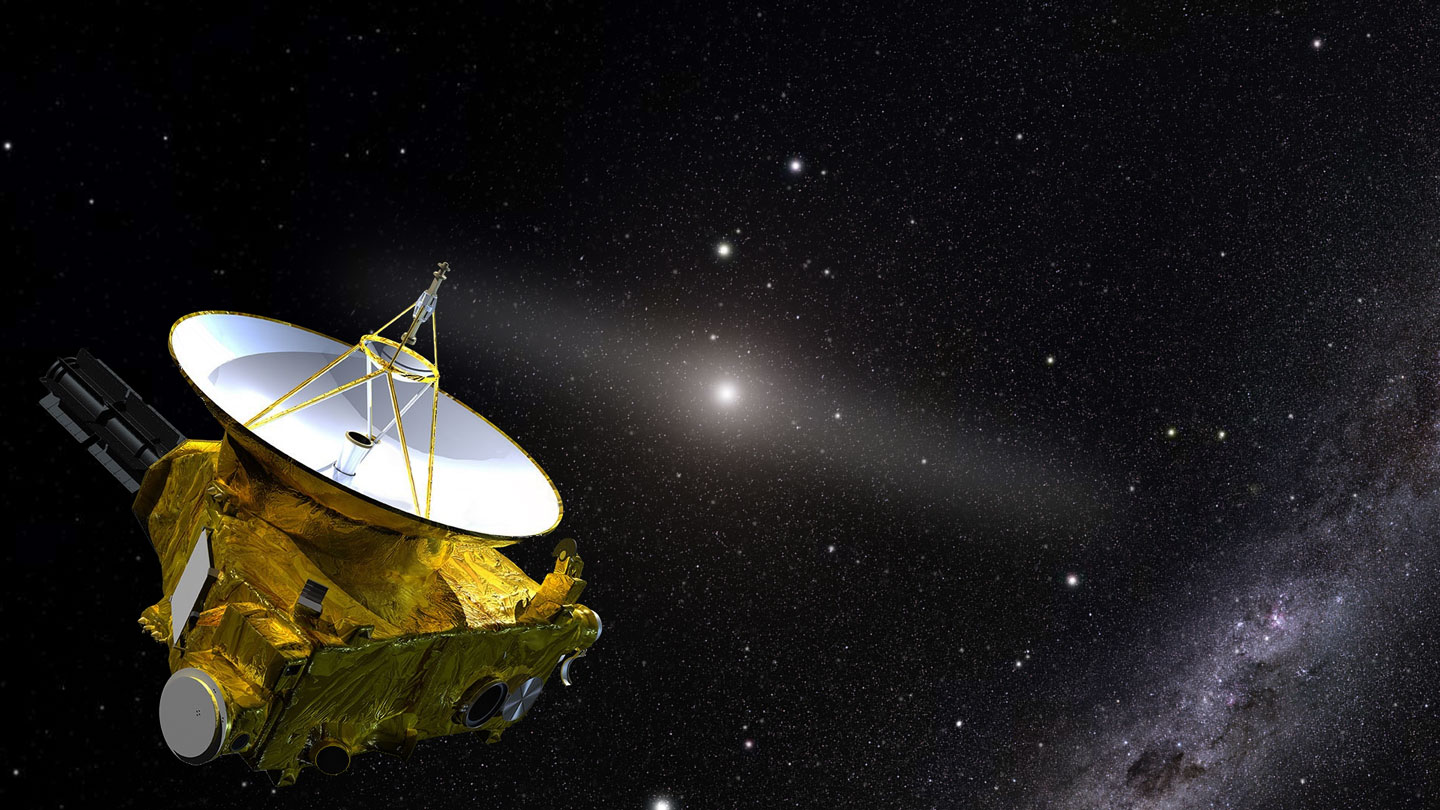

The spacecraft not only completed its main mission, but also successfully completed a flyby of a smaller Kuiper Belt object, Arrokoth in 2019. At the beginning of 2022, New Horizons was put into sleep mode, as it was awaiting approval of new goals as part of the expansion of the mission. Currently, the probe team is moving into the Second Extended New Horizons mission in the Kuiper Belt, or KEM2 for short. The spacecraft will be woken up on March 1, 2023. When the spacecraft wakes up from hibernation, it will pass by the so-called “Kuiper Rock”, where scientists will look for new targets for observations.
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

