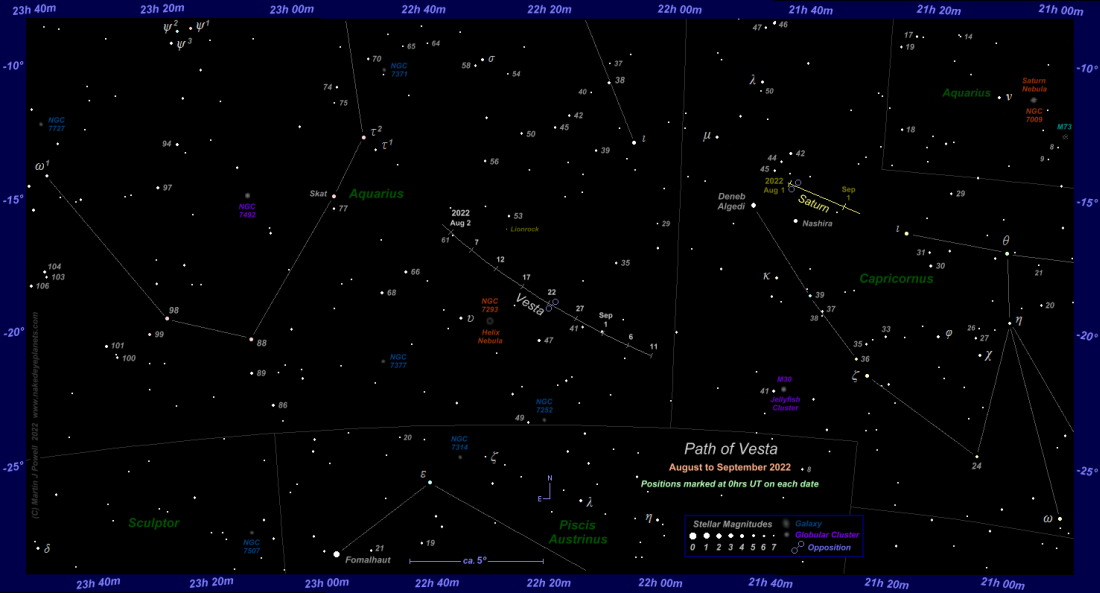
The dwarf planet Vesta (4 Vesta) will enter in opposition with the Sun on August 22. This means that the Earth on this day will be closest to the line connecting the centers of these two bodies. On this day, the conditions for observing this asteroid will be the best.
Vesta in opposition
After the opposition of Saturn to the Sun took place on August 14, the next one had to wait a short time. On the 22nd, Vesta will be in opposition to our luminary. This is the brightest object of the main asteroid Belt. This night it will be visible especially well.
You need to look for Vesta not far from Saturn, which is located in the southeastern part of the sky in the evening. Throughout August, it moves through the southern part of the constellation Aquarius. However, it is worth remembering that this is a fairly small object, which on August 22 will be located from us at a distance of 1.2853 AU, that is, 192.3 million km. Therefore, its apparent magnitude will reach approximately +6.1ᵐ. Theoretically, this is within the sensitivity of the human eye, but in practice, only people with sharp eyesight and in the absence of light pollution will be able to see Vesta as a tiny dot. The rest are better equipped with binoculars.
Why is the planet seen best during the opposition
The opposition of celestial bodies in the sky is called any situation when the moments of their culmination differ by exactly 12 hours (180° of the Earth’s rotation).
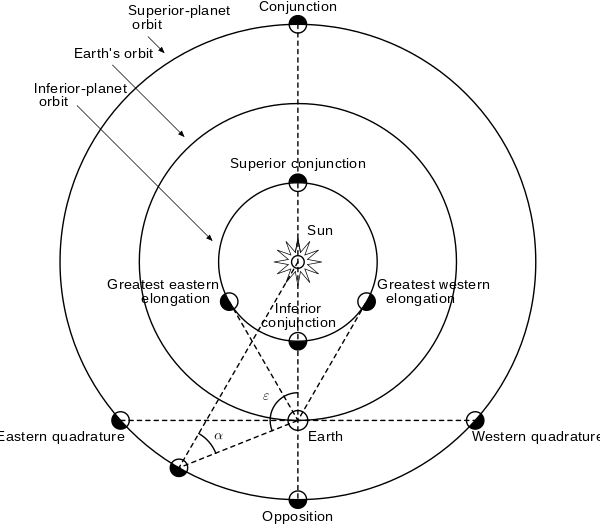
But most often they remember the opposition of the planets with the Sun, because at this moment they are visible in the sky better than ever. There are two reasons for this. Firstly, during the opposition, the Earth is closest to the celestial body. Secondly, at the moment of opposition, the object is maximally turned towards us with its illuminated hemisphere, and its glow becomes the greatest.
Vesta
Vesta is an interesting object to observe. It is the fourth discovered object of the Main Asteroid Belt and the second largest after the dwarf planet Ceres (1 Ceres). Its average diameter is 525 km.

Despite the fact that Vesta is the only asteroid that is sometimes visible to the naked eye, not much is known about it. For example, there is still debate whether to consider it a dwarf planet. The size of this body completely allows this to be done. And the differentiation of depths on it, as it is believed, also occurred. But still, it has a shape too different from the spherical one.
Basic knowledge about the asteroid was obtained using the Dawn automatic probe, which worked in its orbit in 2011-2012. It turned out that Vesta is covered with giant craters. The largest of them, Rheasilvia, is located at its south pole. It has a diameter of about 500 km, which is not much smaller than the size of the asteroid. It is responsible for the irregular shape of this celestial body.
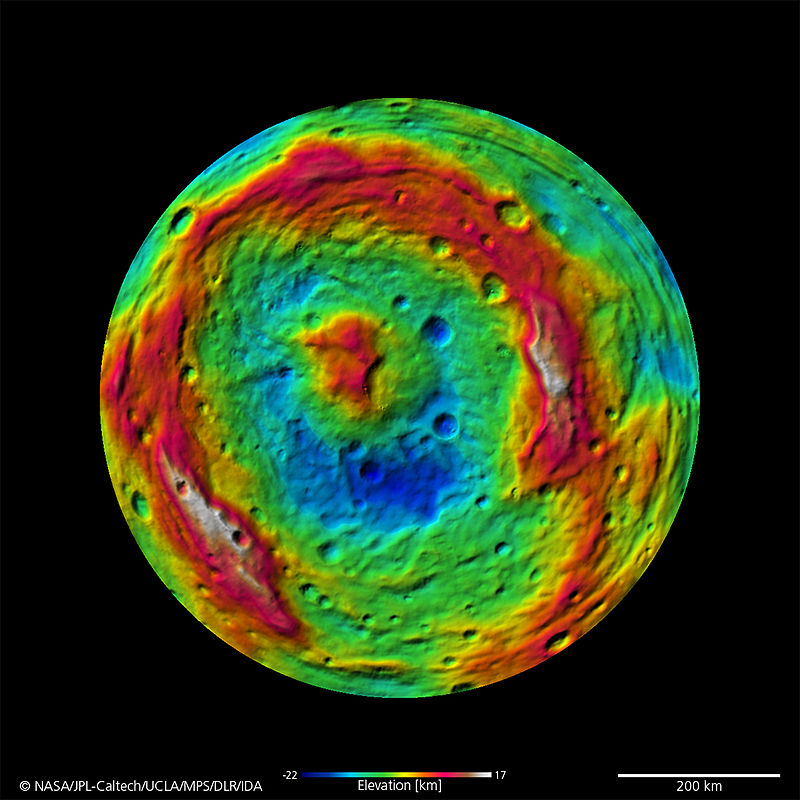
Rheasilvia is not only one of the most famous craters. Its central peak is considered the second highest mountain in the Solar System after the Olympus volcano on Mars. Its height is 22 km, and the diameter of the base is 180 km.
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

