Selection of the most interesting space news for breakfast: South Korea canceled the mission to study the asteroid Apophis, France joined the Artemis agreements, Elon Musk talked about the prospects for the IPO of Starlink, and an American startup is going to demonstrate an alternative to the GPS system.
South Korea cancels Apophis mission
South Korea has decided to cancel the planned mission to the asteroid Apophis. This was reported by the Ministry of Science of the country. The reason given is the lack of technical capabilities to manufacture a spacecraft and a launch vehicle by 2027, when the launch was supposed to take place.
Probe for Europa exploration delivered to NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Europa Clipper spacecraft platform has been delivered to NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). This will allow the assembly of the probe to begin and conduct tests designed to certify its ability to withstand interplanetary travel.
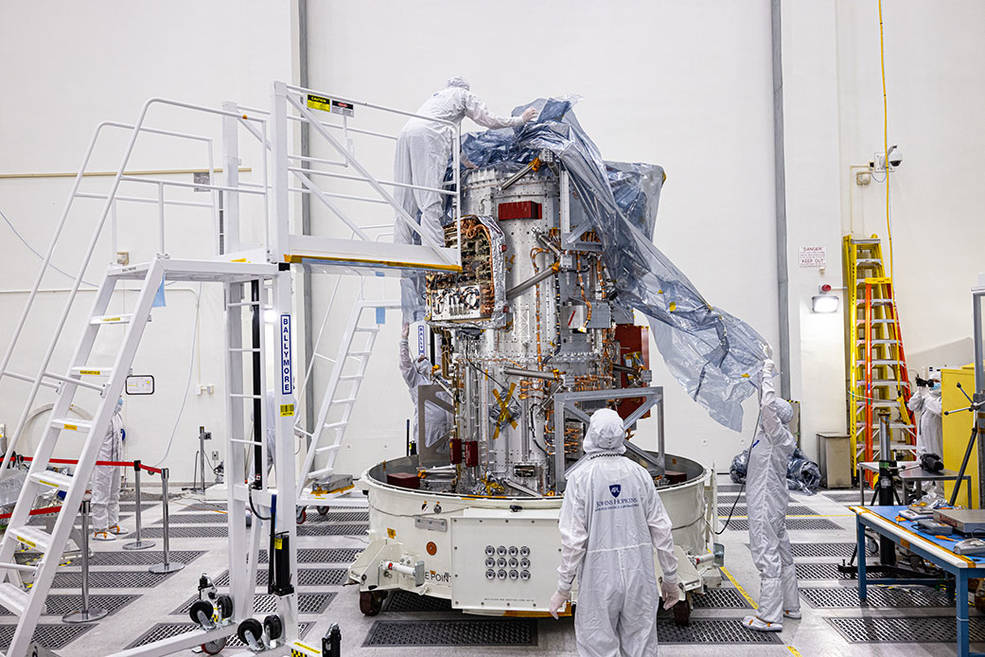

Europa Clipper will be launched in 2024 by a Falcon Heavy rocket. The main task of the device is to study Europa, an icy moon, under the surface of which a giant ocean hides. During its mission, the probe will have to perform about 50 satellite flights, determine the characteristics of its ocean and the degree of potential viability.
Market News
Elon Musk talks about the prospects of the IPO of Starlink
The Starlink service is unlikely to become public until 2025 or even later. The corresponding statement was made by Elon Musk at a meeting of SpaceX employees held on June 2. The head of the company argued his position by saying that before the public offering of shares on the market, Starlink should acquire greater financial stability. According to Musk, this will take at least three or four years.

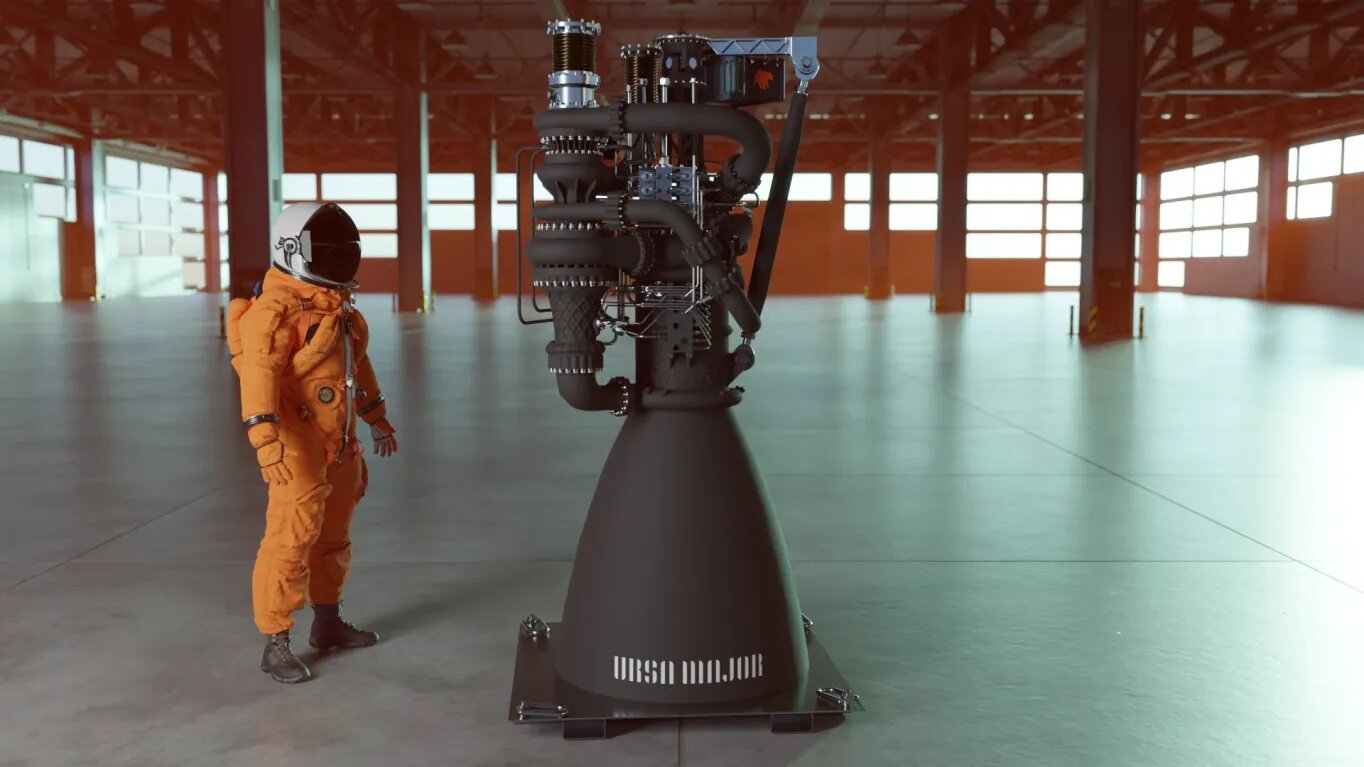
Ursa Major shows new rocket propulsion
The American company Ursa Major held a presentation of its new reusable rocket engine Arroway. It runs on an oxygen-methane fuel pair and develops a thrust of 90 tf. The company hopes that both military and commercial customers will show interest in the power unit. Ursa Major plans to begin firing tests of Arroway in 2023 and begin its serial deliveries to customers in 2025.

France joins Artemis Accords
France becomes the 20th nation to sign the Accords, an intergovernmental agreement that defines the principles of cooperation and civil activities for the exploration and use of the Moon, Mars, comets and asteroids for peaceful purposes. The signing ceremony took place on June 7. It was attended by NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and President of the National Space Research Center, Philip Baptist.
S7 Space stopped developing rockets
The Russian space company S7 Space has announced the termination of the development of a light launch vehicle with a returnable stage. This decision is motivated by the “lack of the possibility of attracting financing”. In addition, S7 Space has started to reduce staff. 52 employees have already been dismissed from the company (with a staff of about 100 people).
Xona to demonstrate an alternative to GPS
Aerospace startup Xona Space Systems is preparing to start testing the Hugin satellite, which was launched into orbit by a Falcon 9 rocket at the end of May. The device is a demonstrator of the Xona Pulsar navigation system being developed by the company, which can become an alternative to such services as GPS, Galileo and Beidou.
The essence of the concept is to deploy a constellation of 300 small satellites in low Earth orbit. Due to a much lower altitude compared to competitors, they will provide a more powerful signal for ground users, which will not only increase positioning accuracy, but also significantly complicate the task of jamming, while the overall simplicity of satellites and their output will significantly reduce the cost of the system.
Interesting
Computer algorithm simulated the Universe
Using machine learning methods, a team of researchers from the Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands has developed a Hydro-BAM algorithm that allows to simulate a “virtual universe”. Scientists used it to see the first few seconds after the Big Bang. Hydro-BAM has made it possible to identify phenomena such as dark matter, neutral hydrogen and other cosmic ingredients necessary to understand the structure and subsequent evolution of our universe.

Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

