Scientists used the gravitational lens of a distant galaxy to look at the gas clouds behind it. They existed at the beginning of the Universe and contain some of the first galaxies.

Integral spectroscopy and gravitational lens
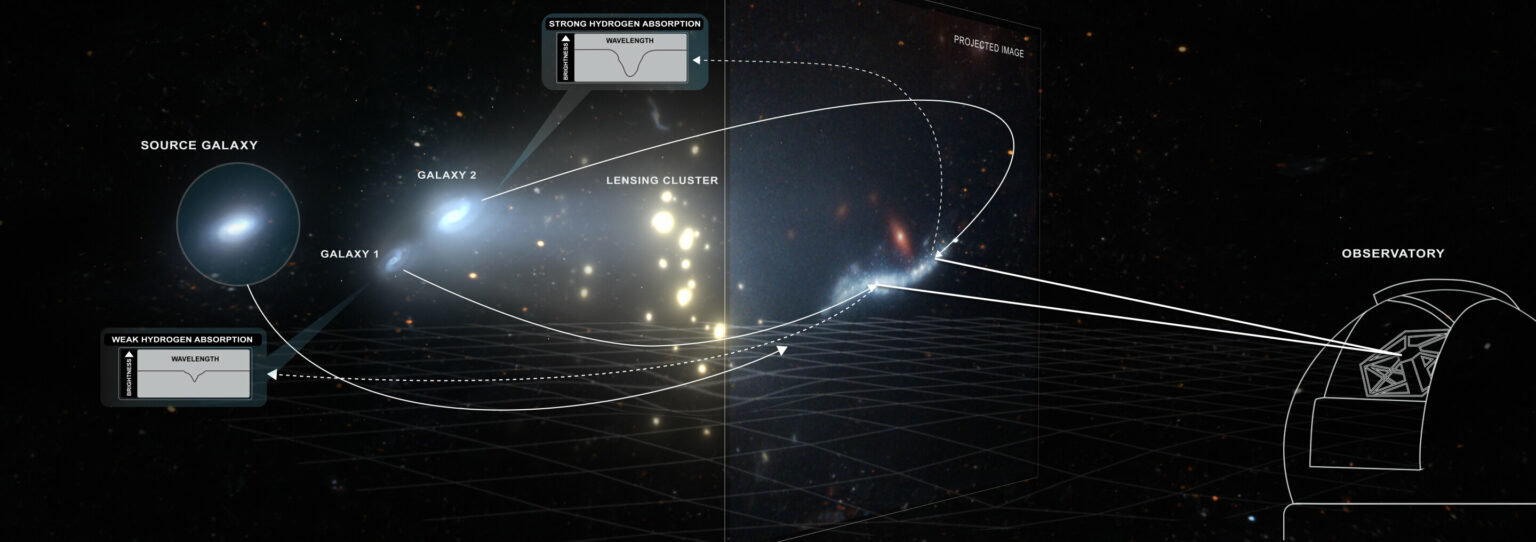
Researchers from the University of North Carolina used a gravitational lens formed by a distant galaxy and its surroundings to collect radiation from objects behind it. They pointed the Keck Cosmic Web Imager telescope, which has the function of integral spectroscopy, at it.
The gravitational field of the galaxy can bend light no worse than ordinary lenses. In this case, with the help of “space optics”, it was possible to see a cloud of diffuse gas that existed shortly after the Big Bang. Such objects are called Damped Lyman-α, or DLA for short.
The most interesting thing about DLA is that it was they who gave birth to the first galaxies. And the The most interesting thing about DLA is that it was they who gave birth to the first galaxies. And the current study allowed us to see this process. The cloud, which was examined with a gravitational lens, contained two newborn galaxies. The size of the cloud is 17.4 kiloparsecs, and the size of the galaxies is about 5 kiloparsecs.
How the early Universe is studied with cosmic objects
The early Universe is quite difficult to study due to there being quite a few objects in it that could emit. But the radiation coming to us since then overcomes a huge distance and on the way passes through a bunch of other objects, interacting with them.
Scientists have already learned how to use these effects. Previously, they had already studied the epoch of reionization with the help of clouds of interstellar gas through which relic radiation passes. Gravitational lenses have already been used to study distant galaxies.
But DLA has so far remained poorly understood. Until now, they have been studied mainly with quasars. These huge active black holes release powerful jets traveling a huge distance. But they only highlight a certain point of the gas cloud. The combination of gravitational lenses with integral spectroscopy will allow us to find out how they formed the first galaxies.
According to phys.org
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
