During a solar eclipse, a unique opportunity is created to study the effect of these short periods of darkness on the upper layers of the Earth’s atmosphere. A total solar eclipse will occur over the United States next month, so scientists are preparing to use this phenomenon for scientific research.
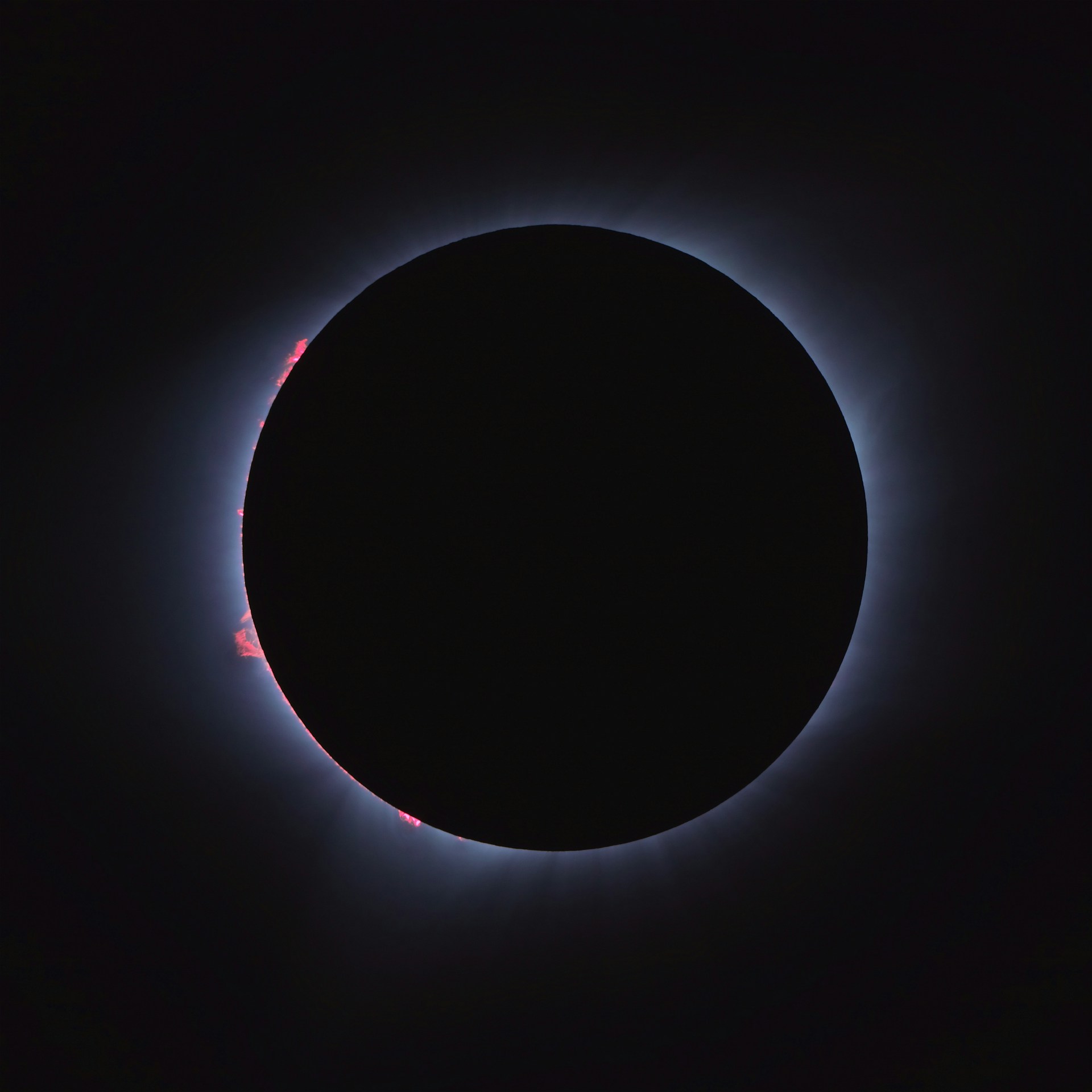

This rare cosmic phenomenon affects the Earth’s atmosphere, causing disturbances that can interfere with communication on Earth. The ionosphere, which is part of the upper atmosphere, contains many electrically charged particles and reflects radio waves. Its condition is important to ensure the smooth operation of communication and navigation systems.
On April 8, NASA plans to launch three sounding rockets from the Wallops spaceport in Virginia. These rockets are designed to study disturbances in the ionosphere at the time of a solar eclipse. According to NASA’s plan, the rockets will launch at different time intervals: 45 minutes before the start, during and 45 minutes after the peak of the eclipse.
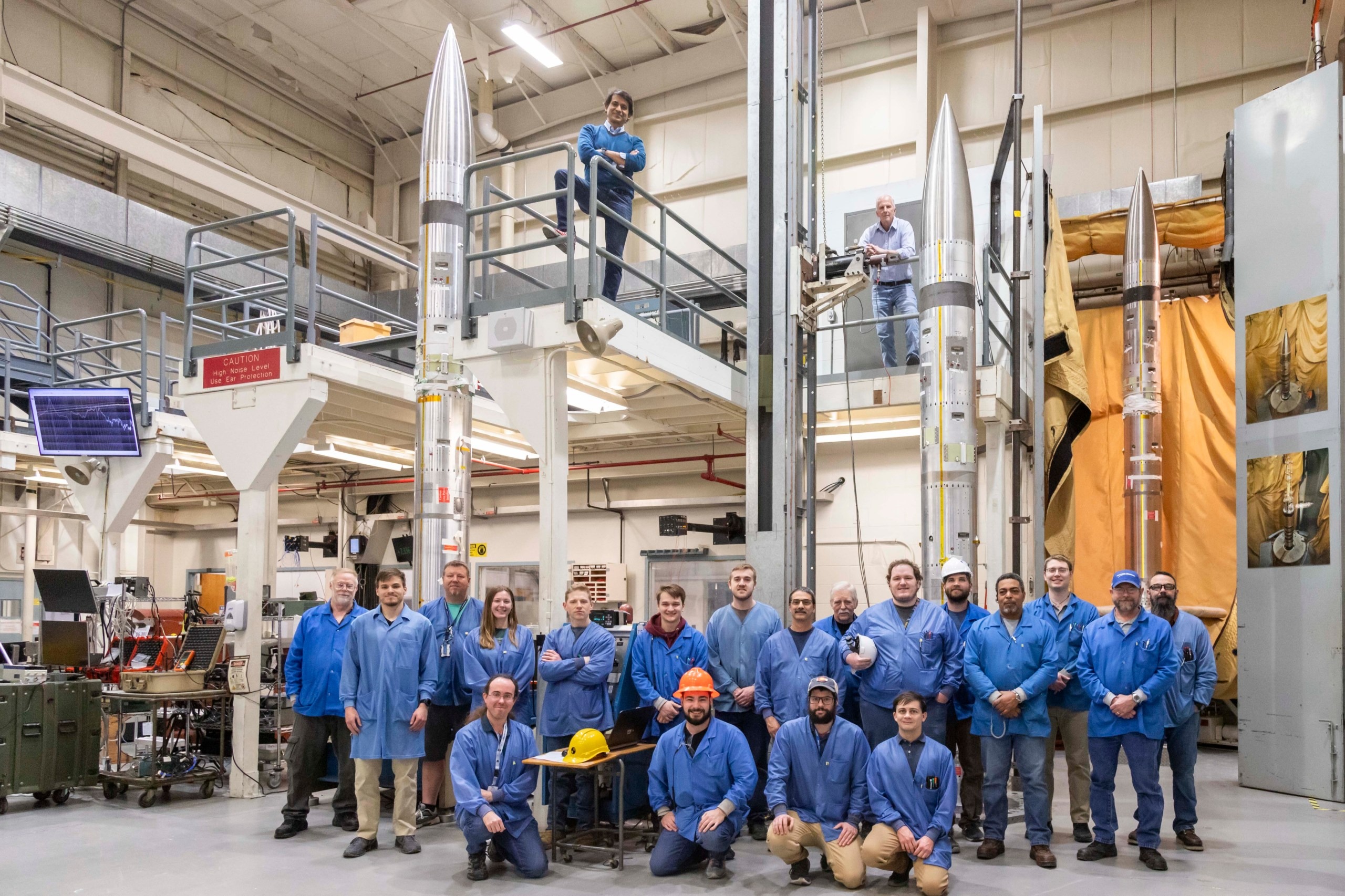

The NASA mission is important for understanding disturbances in the ionosphere in order to better predict their impact on communication systems. For this purpose, the rockets will release special instruments that will measure changes in the ionosphere during the eclipse. This data will help scientists improve existing models.
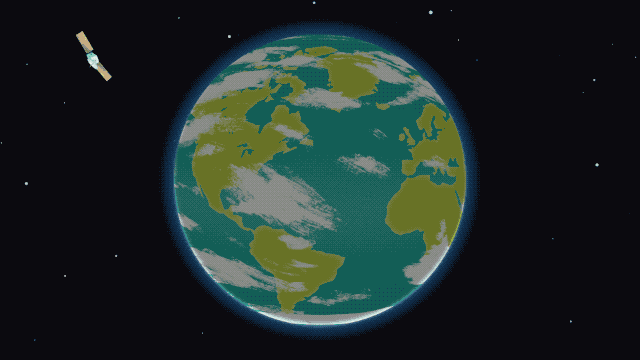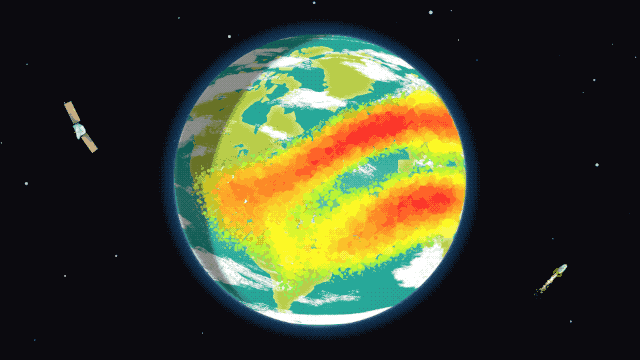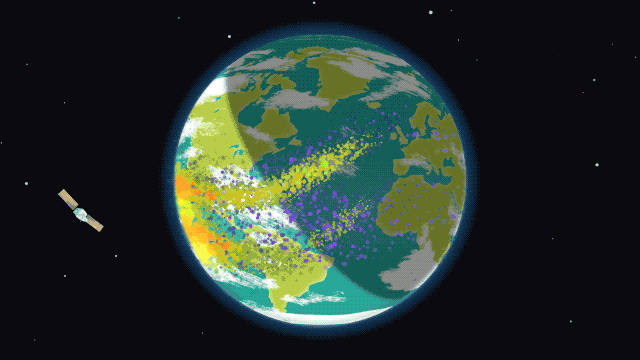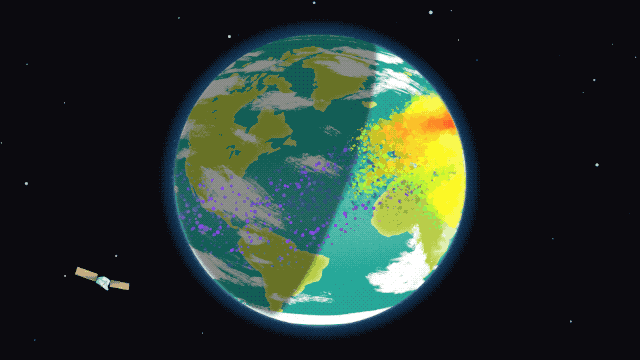
The upcoming eclipse on April 8 will provide an opportunity to study the effect of the temporary disappearance of the Sun on the ionosphere. Each rocket will release instruments to measure disturbances. In addition, measurements will also be carried out on Earth.
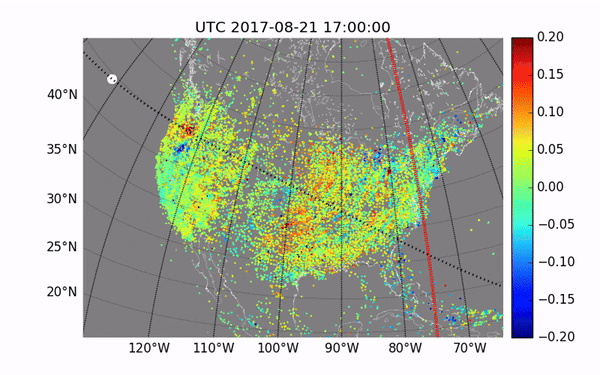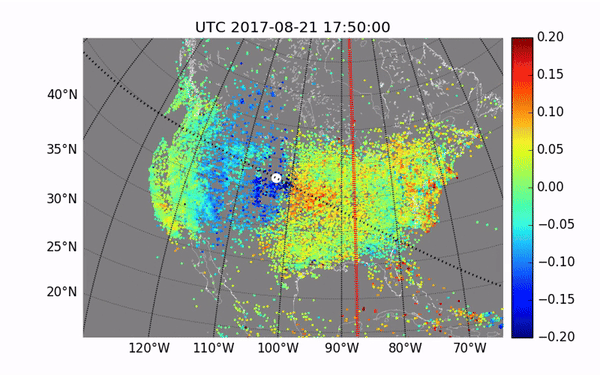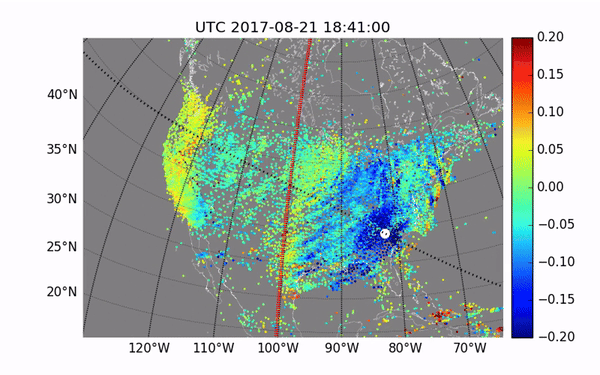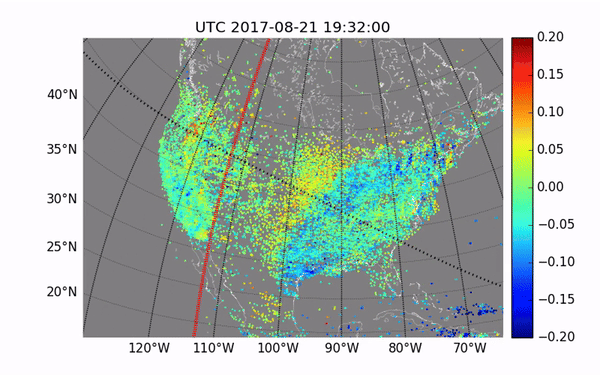
Previous studies have already been conducted during solar eclipses. They showed disturbances in the atmosphere. However, the next eclipse will be important to get more data for accurate measurements. These studies are of great importance for the development of communication technologies, as they will help to avoid communication interference due to disturbances in the ionosphere.
Earlier, we reported on how the first lunar eclipse of 2024 took place.
According to NASA
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine


