In 1952, three stars suddenly disappeared. They are present in one image of a section of the sky, but they are absent in another, taken an hour later. Scientists have not yet come to a conclusion about this and are putting forward different versions.
Where did the three stars disappear?
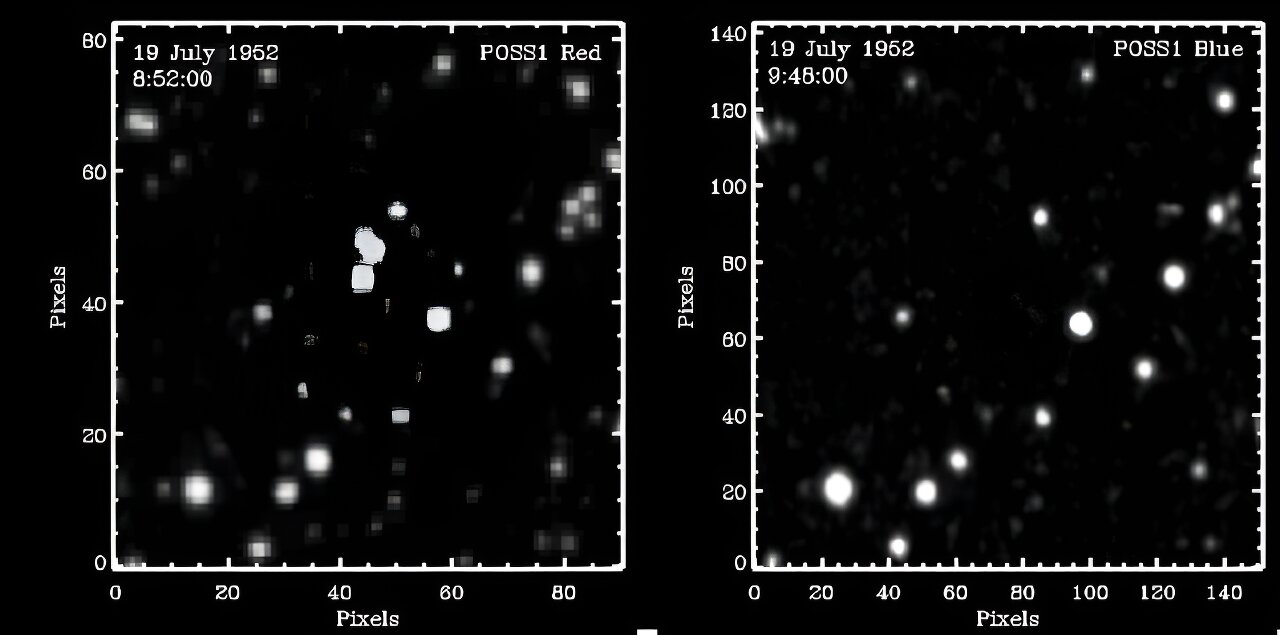
For more than 70 years, scientists have not been able to solve the mystery of the sudden disappearance of three stars from the starry sky. In 1952, the Palomar Observatory in the USA carried out a photographic survey of the sky. One of the goals of the scientific project was to search for asteroids. Therefore, the photos were taken in pairs after a certain period of time.
So it was on July 19, 1952. At around 8:52 p.m., the photographic plate recorded the light of three stars of approximately 15 stellar magnitude. And on the second one, taken at 9.45 p.m., they were not found. They did not appear in any other photos taken in subsequent years.
There are enough short-term events in space, called transients. However, a very small number of them implies such a large decrease in brightness in less than 50 minutes. Intrigue is also added by the fact that the following images of this area were taken with more powerful telescopes. Therefore, the stars should reduce their brightness to at least 24 magnitudes, that is, 10 thousand times.
What could it be?
Modern researchers put forward three main theories as to what it could be. The first of them was that they were not three objects, but one. For example, a star that unexpectedly increased its brightness due to a rapid radio burst of a magnetar. At the same time, a wandering black hole passed between us. Its gravitational field distorted the path of light and led to the appearance of erroneous images.
The effect of gravitational lensing could indeed explain the observed pattern. It has repeatedly multiplied images of distant galaxies. However, even in the case of a tiny black hole and this particular sky survey, such an option looks unlikely.
The second theory was based on the fact that the three stars were separated by 10 angular seconds. If these are three separate objects, then whatever they are illuminated by, the limited speed of light does not allow them to be far from each other and from the source.
The calculation shows that the distance to the stars cannot be more than 2 light years, and they should be separated by only 6 au. This indicates that, in fact, these objects were asteroids from the Oort Cloud that were “highlighted” by some event.
Finally, the third theory was that the “three stars” were not space objects at all. The Palomar Observatory was located close enough to the New Mexico desert, where nuclear weapons tests were conducted. Radioactive dust could easily get on the plate and create a false image. Since other images of the 1950s show similar “disappearances”, this theory looks more than likely.
According to phys.org
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
