The US House of Representatives and the US Senate have prepared bills on NASA funding for 2024. Both documents suggest a reduction in the organization’s budget, instead of the increase requested by it.
How is the NASA budget formed?
At the beginning of each year, the current US administration publishes a so-called budget request with proposals on the structure of government spending for the next fiscal year. It also includes the costs of maintaining NASA’s activities.

The budget request, in fact, is only a general recommendation, because it is not the White House that is responsible for allocating money in the United States, but Congress. It passes appropriations laws. After receiving the budget request, the committees in the House of Representatives and the Senate consider the document and decide whether to support the White House proposal or change the amounts on the points of expenditure. They can be either increased or decreased. Also, legislators can make their own proposals and allocate money for articles that are not contained in the request.
NASA’s draft budget for 2024
In March, the White House released a draft NASA budget for next year. It provides for the allocation of a total of USD 27.2 billion for the needs of the department — 7% more than this year (25.4 billion). The document, in particular, assumes an increase in funding for the Artemis program and the creation of a special tag designed to lift the ISS from orbit. In addition, the authors of the document requested the allocation of USD 949 million to finance the joint US-European Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission. Within its framework, samples of Martian soil collected by the Perseverance rover will be delivered to Earth.
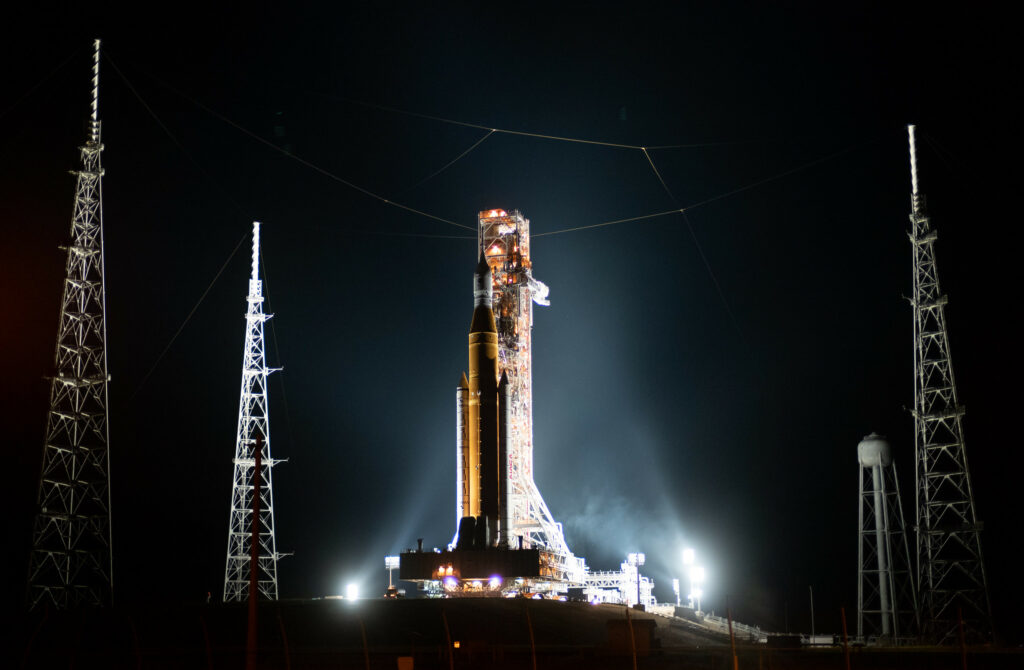

Unfortunately, NASA is unlikely to receive such money. The bills on the financing of the aerospace administration, recently prepared by the House of Representatives and the Senate, do not provide for an increase, but a decrease in its budget in 2024.
Thus, the Senate Appropriations Committee approved a bill providing for the allocation of USD 25.0 billion for the needs of NASA. The brief does not provide an article-by-article breakdown, but it is noted that USD 7.74 billion will be allocated for manned programs, which is less than USD 7.97 billion requested for 2024, but more than USD 7.47 billion received in 2023. According to the authors of the bill, this amount will fully provide funding for the SLS and Orion spacecraft.
Science and planetary research programs have suffered the most. A draft document circulating on the Internet says that the Senate is ready to allocate only USD 300 million for MSR. The senators also want to oblige NASA to set a limit on the cost of the mission at USD 5.3 billion. If it is exceeded, the delivery of samples of Martian soil will be canceled, and its funds will be given to Artemis.
As for the House of Representatives, its bill provides for the allocation of USD 25.367 billion for the needs of NASA. Manned cosmonautics will be fully funded (USD 7.97 billion), while USD 7.38 billion will be spent on science. This is USD 880 million lower than the requested level and USD 415 million less than in 2023.
Reasons for reducing NASA’s budget
The decision to reduce NASA’s budget is mainly due to an agreement reached in May 2023 between Congress and the White House to raise the debt ceiling in exchange for limiting spending in the non-defense sphere (which includes NASA) to the level of 2023. In this situation, legislators have predictably chosen to keep funding for the SLS and Orion projects, which have a very powerful lobby, sacrificing science and planetary research.
It is worth emphasizing that at the moment we are talking only about draft laws. After approval, they will be consolidated into a single document, on which a vote will be held. But in any case, it is already obvious that NASA is unlikely to expect any financial increase next year.
According to https://spacenews.com
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

