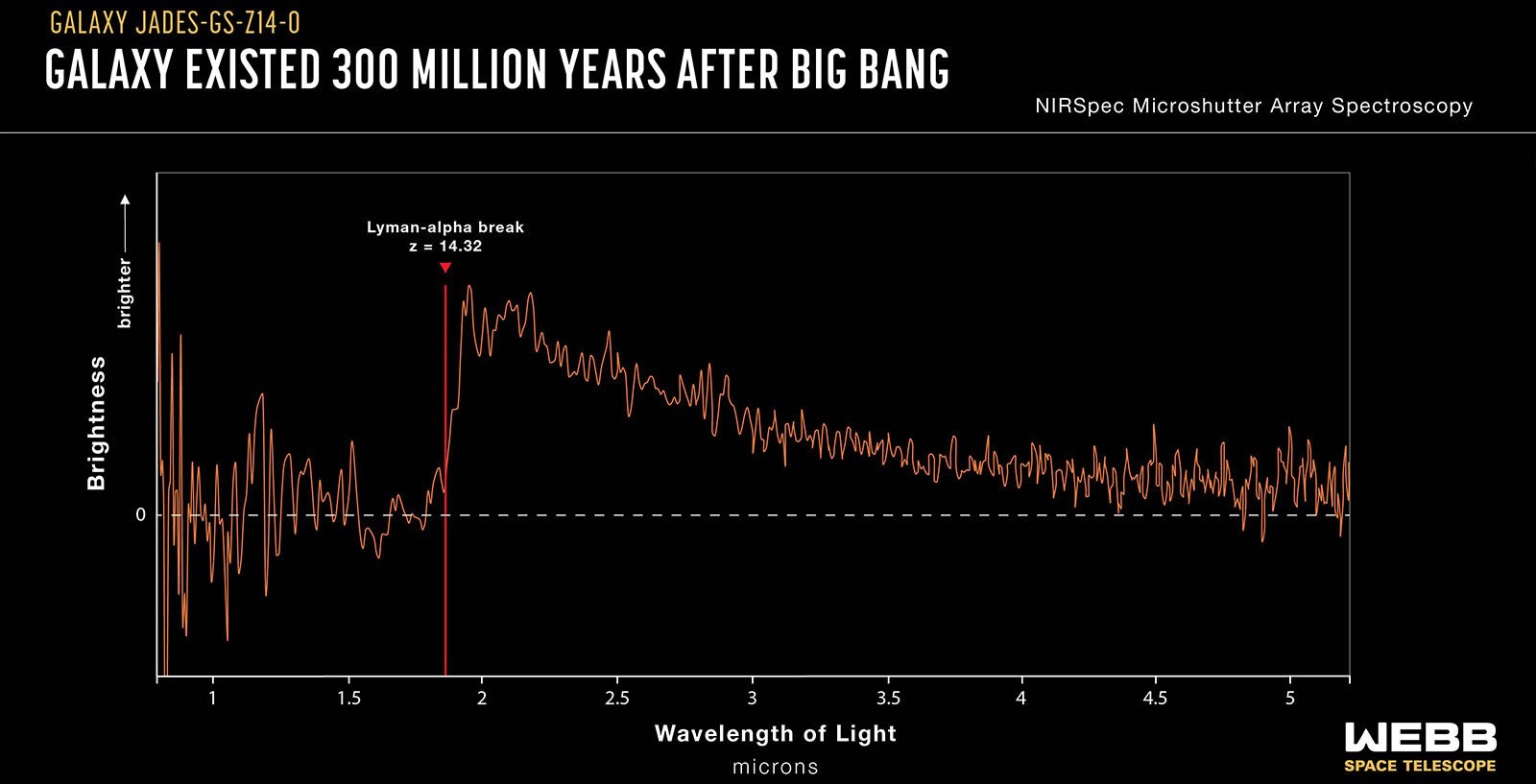
The James Webb Space Telescope has broken its own record by discovering the most distant galaxy ever observed. It has the name JADES-GS-z14-0. The redshift of the galaxy corresponds to a value of z=14.32, which means that its light left the galaxy when the universe was only 290 million years old.
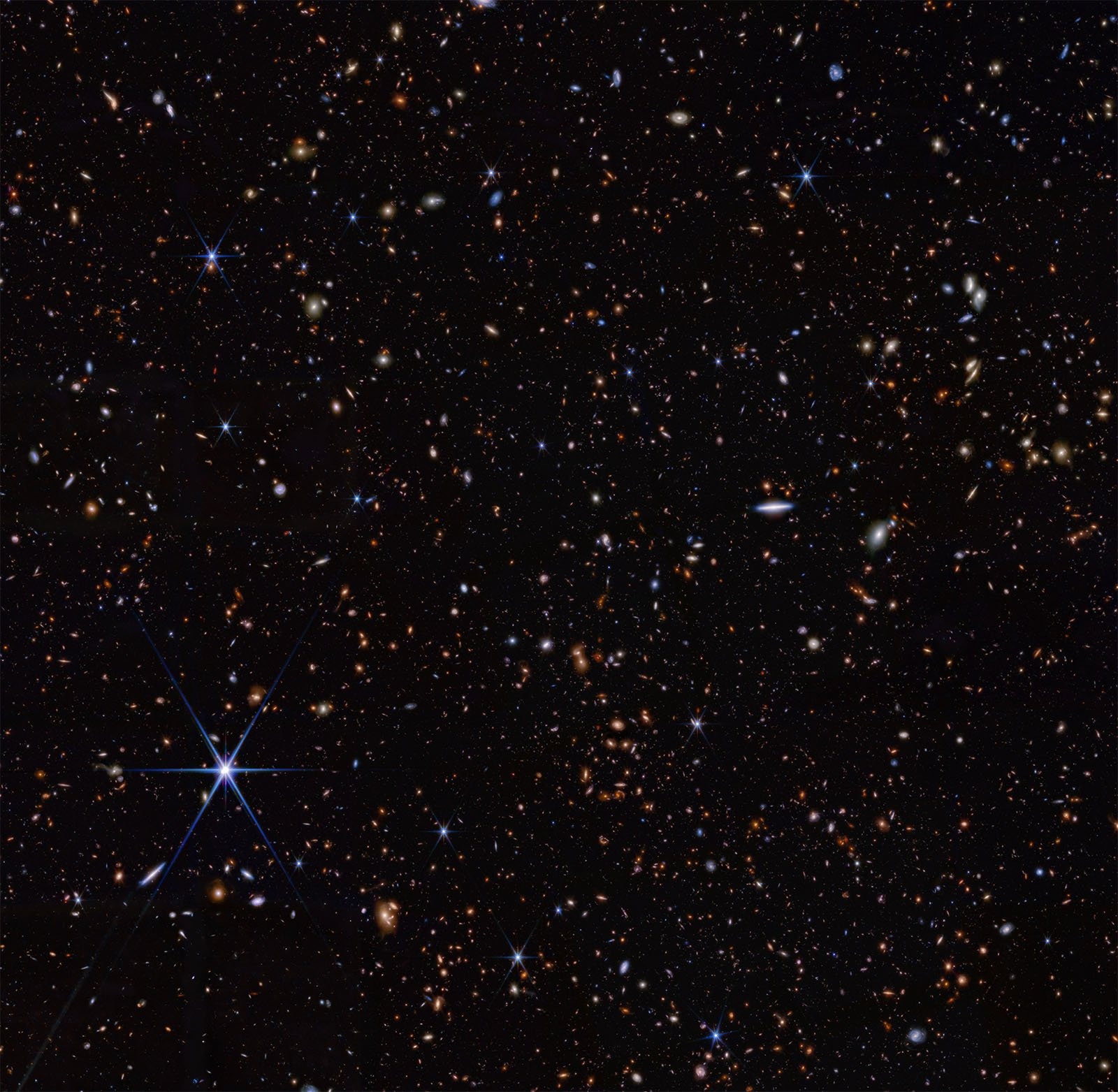

James Webb’s ultra-sensitive instruments allow astronomers to use the telescope to study the Cosmic Dawn, a period that existed only a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. The international team used JWST data collected as part of the Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) project using NIRSpec (near-infrared spectrograph). They obtained the spectrum of the galaxy, which detected a redshift of 14.32. The redshift of JADES-GS-z14-0 makes it the most distant known galaxy.
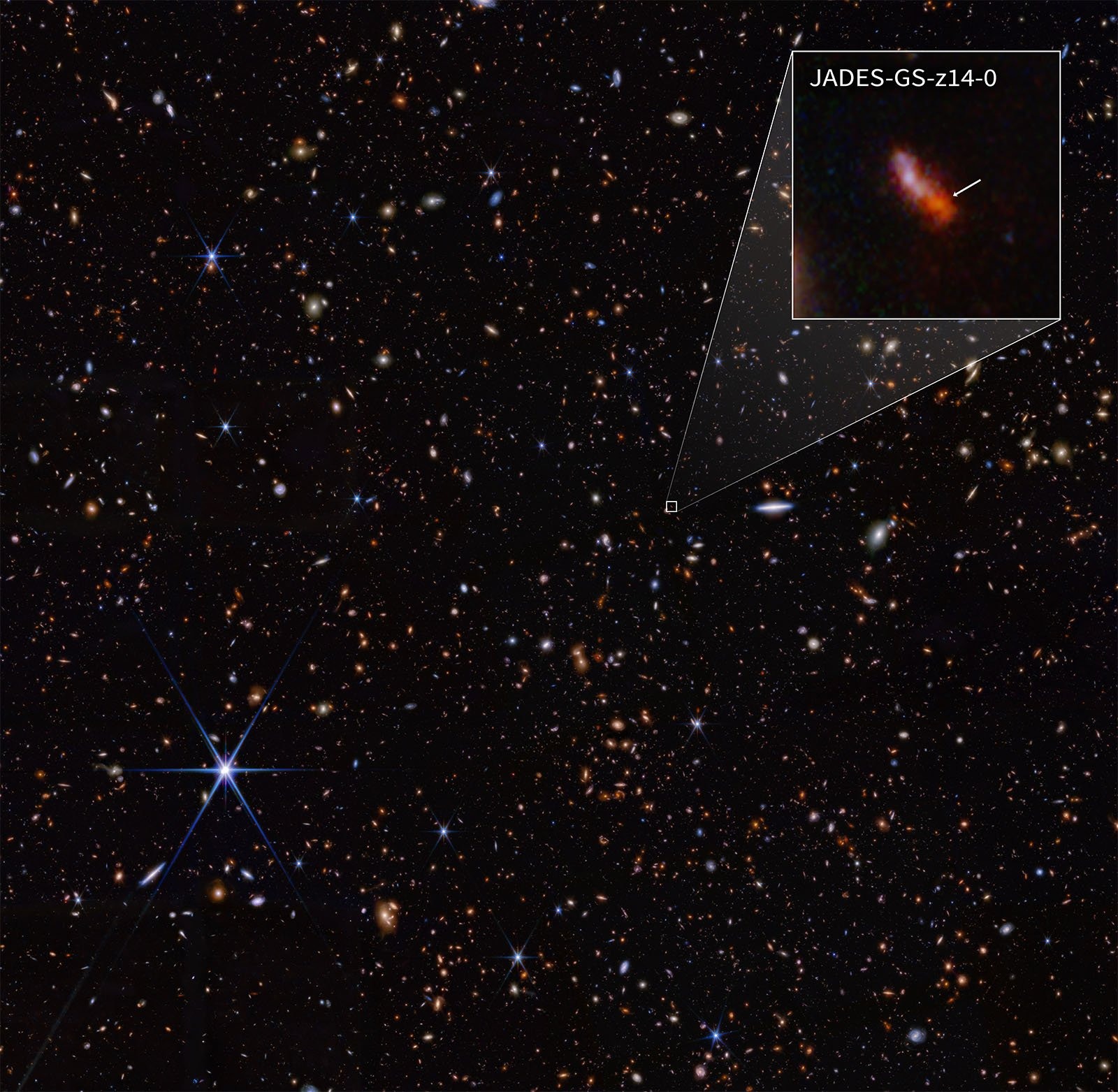

The phenomenon of redshift occurs when light from distant objects in space shifts to the red end of the spectrum due to the expansion of space. The greater the redshift, the further away the object is.
The galaxy looks very different from modern ones with its shapeless structure. Its dimensions are just over 1,600 light-years across. For example, the Milky Way has a diameter of 100 thousand light-years. That is, this distant galaxy is extremely tiny. Such sizes are typical for distant and early galaxies. But unlike the Milky Way, JADES-GS-z14-0 is very bright because of the light emitted by hot young stars. The ancient distant galaxy is also not as blue as scientists expected, indicating that some of its light is reddened by dust, even at this very early stage of the universe.
The James Webb Space Telescope with a 6.5-meter mirror was launched on December 25, 2021, and quickly became the most powerful space telescope ever built. It is designed to explore the universe in visible and infrared radiation, which allows scientists to see through cosmic dust and reveal hidden details. The telescope is located at the second Lagrange point, where the gravity of the Earth is balanced by the gravity of the Sun, at a distance of 1.5 million km from Earth.
Earlier, we reported on how James Webb found the farthest organic molecules in the universe.
According to universetoday.com


