In two studies, the results of which were published in the journal Nature Astronomy, astronomers confirmed the discovery of four distant galaxies by the James Webb Telescope (JWST). They existed when the age of the Universe was from 300 to 500 million years.
Why James Webb explores galaxies
One of the key tasks of JWST is to search for and determine the properties of distant galaxies located at the edge of the observable Universe. This is important for testing theoretical models describing the conditions and processes that led to the formation of the first stars, galaxies and black holes.

During its work, JWST has already identified a number of galaxies with a significant redshift, indicating that they are at a very great distance from us. However, all these discoveries were made by the photometric method. To be sure of estimating the distance, astronomers need to study the spectra of galaxies, which takes some time.
Record-breaking distant galaxy
In 2022, JWST discovered four galaxies which had a redshift z of more than 10. They were designated JADES-GS-z10-0, JADES-GS-z11-0, JADES-GS-z12-0 и JADES-GS-z13-0. These galaxies are so far away that the light they emit has already completely shifted to the infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum. JWST is the only telescope in the world capable of detecting it.
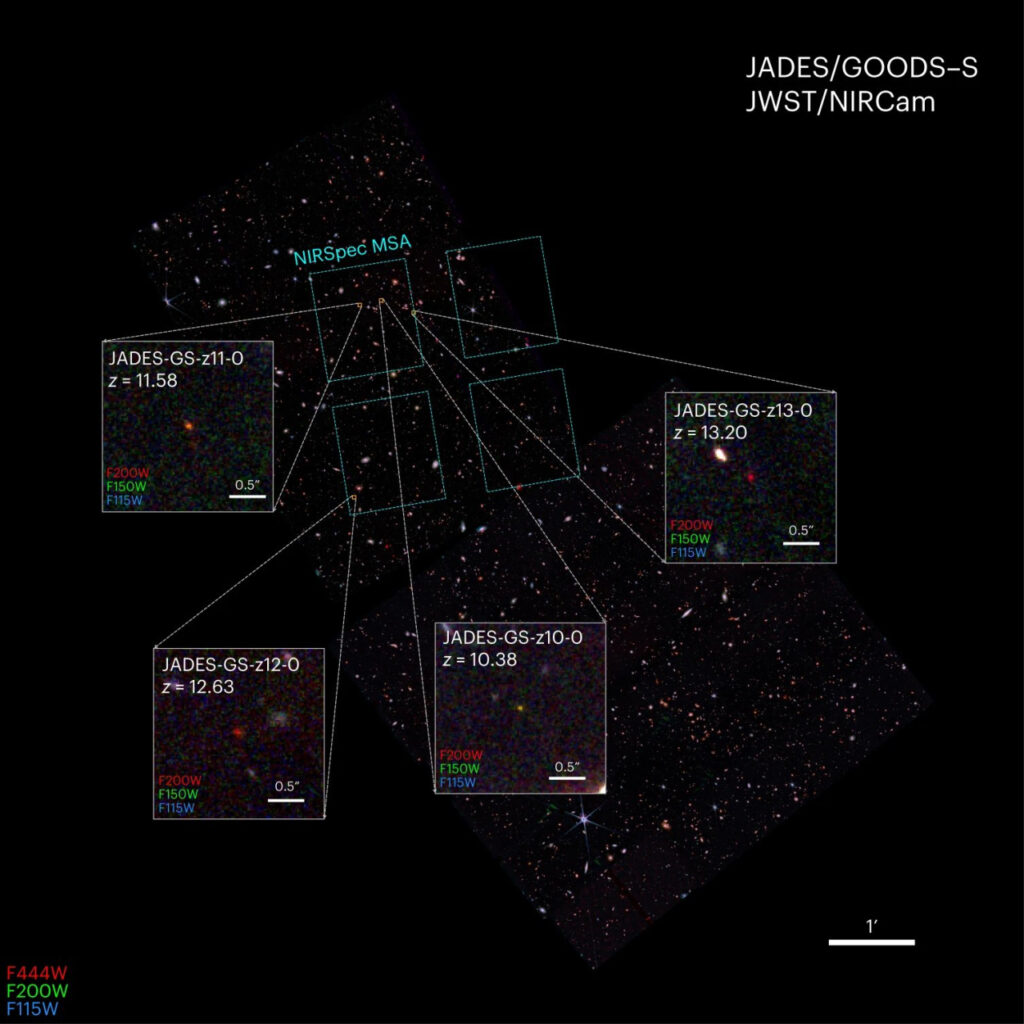
Subsequent spectroscopic studies confirmed the initial estimates. The entire found four existed when the age of the Universe was less than 500 million years. The most ancient of these galaxies is JADES-GS-z13-0. We see it as it was just 320 million years after the Big Bang.
All four galaxies existed in the era of Reionization, when the first stars lit up in the Universe. They were poor in metals and had a very small mass by modern standards, amounting to about 100 million solar masses. For comparison, the mass of the Milky Way is 1.5 trillion solar. At the same time, they were quite actively forming new luminaries. As in our galaxy, several new stars are formed in them every year. Previous models suggested that the rate of star formation was lower in the era of reionization.
Earlier we talked about how JWST discovered a dust storm on an exoplanet.
According to https://phys.org
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

