Scientists have observed the formation of stars in the gas clouds of the Orion nebula. They saw one of them throwing out a powerful jet of matter. It can influence the formation conditions of its neighbors.

Observation of the Orion Nebula
A group of Kyushu University graduates could see how the newborn dawn “shot” a jet of matter falling into a cloud of gas in which new luminaries were formed. It happened when they were working with the Atacama Large Millimeter/Submillimeter Array (ALMA) radio telescope array.
Scientists have observed the birth of a massive cluster in one of the nebulae of the constellation Orion. Local star formation zones are divided into several close “patches”. Scientists saw how one of the luminaries from the FIR 3 site “threw out” a high-speed jet of matter. It got into the neighboring FIR 4 region, where several young stars were forming.
Scientists cannot say how this affected their development yet. They plan to continue studying this area of space with ALMA and establish whether the effect of the gas flow was positive or negative.
How will the gas flow affect star formation?
The processes of star formation in gas clouds are still not fully understood. Even at the level of a single star, the phenomena are clearly not limited to a simple scheme in which matter collapses under the influence of gravity and contracts to a state in which thermonuclear reactions begin.
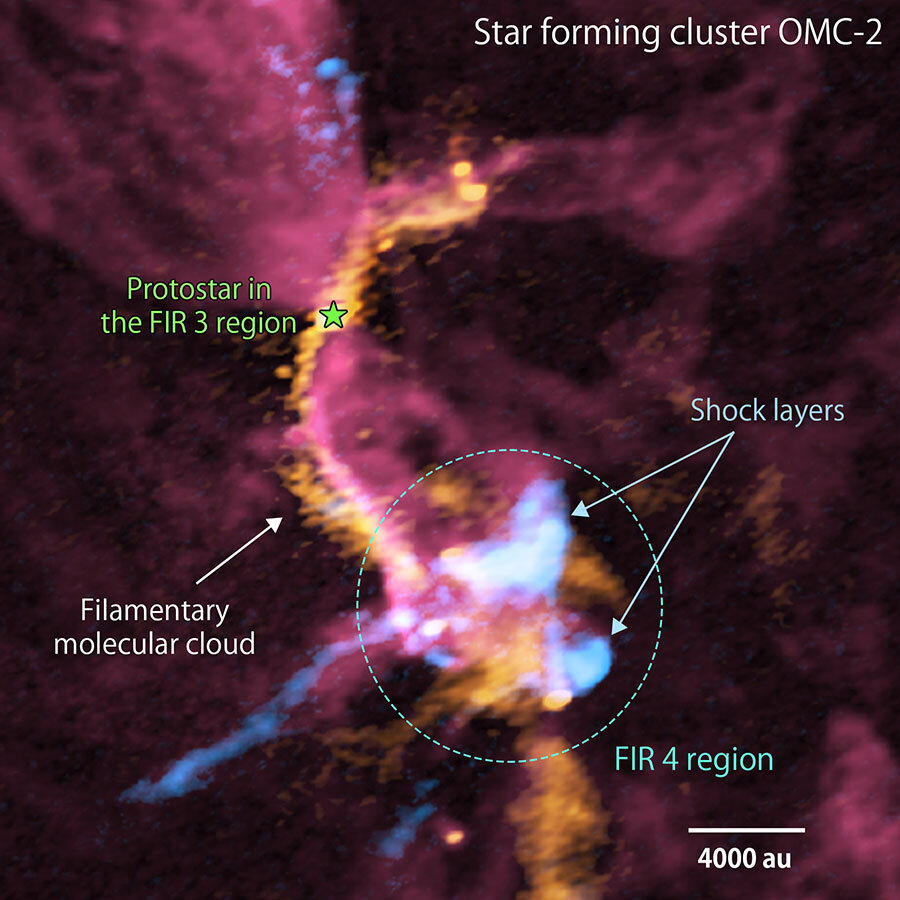
Not all the matter of the gas-dust cloud is used in this process. Part of it is accelerated by the gravity of the newborn star in a random direction. Such flows have been observed repeatedly before.
If we remember that stars are almost never born alone, then everything becomes much more complicated. Astronomers have already established that together with “normal” luminaries, a huge number of orphan planets and brown dwarfs are born.
In addition, the gas environment can contribute to the formation of binary systems from single stars, which does not happen in ordinary space. Now they will also have to understand how gas jets from newborn luminaries affect their surroundings.
According to phys.org
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

