We have already told you about five automotive innovations that have become an essential part of our daily life thanks to NASA. Our new article will focus on ecology. This time, you will learn about five important technologies for environmental protection that have emerged thanks to the achievements of the space era.
Solar Energy
Just like thousands of years ago humanity today mainly relies on burning fossil fuels to obtain energy. But the balance is gradually shifting towards using renewable sources, with solar energy playing the most crucial role.
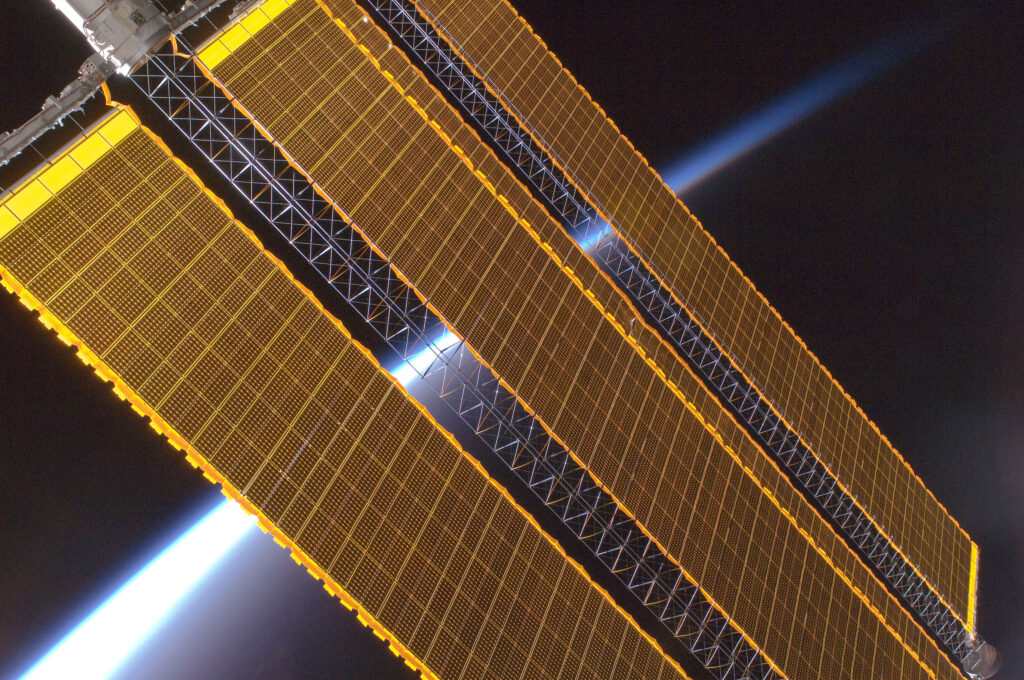
Spacecraft can be considered pioneers in using the energy of our luminary. The first satellites equipped with solar panels (Vanguard 1 and Sputnik-3) were launched into orbit back in 1958. Over the next 60 years, technology made significant progress. Modern photovoltaic elements are much more efficient than the solar panels installed on the first spacecraft.
However, it’s not that simple. Among the solar panels available today, the most efficient ones are made of gallium arsenide. Their efficiency reaches a record 44%. But they are quite expensive to produce and have a negative impact on the environment. That’s why their use is mainly limited to space.
The US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is actively working on solving this problem, involving private developers such as MicroLink Devices. Under a contract with NASA, they have developed a technology that significantly reduces the cost of creating gallium arsenide solar panels and reduces their weight. This will allow their use not only in space but also on Earth.
Wind Energy
In the early 1990s, NASA began developing a project for a self-sustaining base on Mars. For the sustainable functioning of such a settlement, energy is crucial. The main question is about its source.
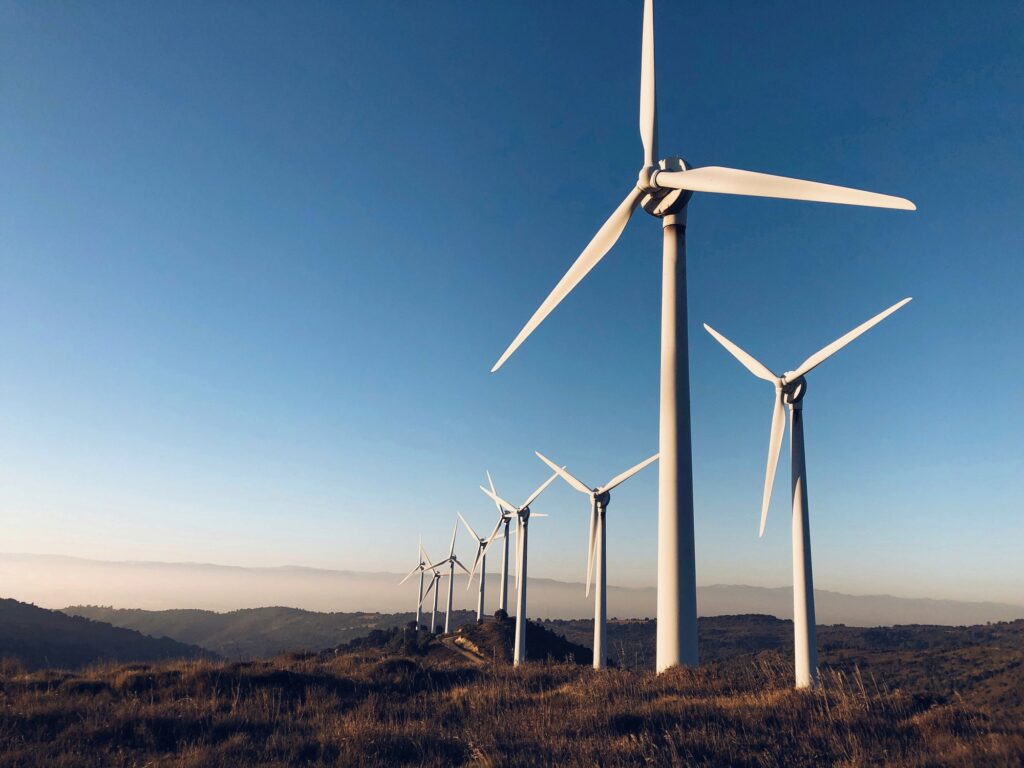

At first glance, the obvious solution is to use solar panels. However, the Red Planet is known for its dust storms, which can cover the sky for long periods. Therefore, researchers concluded that the most optimal option would be a combined system that generates energy from both sunlight and Martian winds.
To test the feasibility of this concept, in 1997, NASA experts and Northern Power Systems conducted an experiment using a prototype Martian wind turbine. The role of the neighboring planet was played by the South Pole of the Earth.
The results of the experiment encouraged Northern Power Systems to develop a new wind power station designed to operate in adverse weather conditions. The project was named Northern Power 100. After successful tests, the turbine was put into serial production. Nowadays, wind power stations are quite common on our planet. Last year, they generated almost 27% of electricity in Germany.
Air Purification Systems
In recent years, air purification systems have become widespread. They are actively installed in shopping centers, grocery stores, hospitals, offices, and residential buildings.
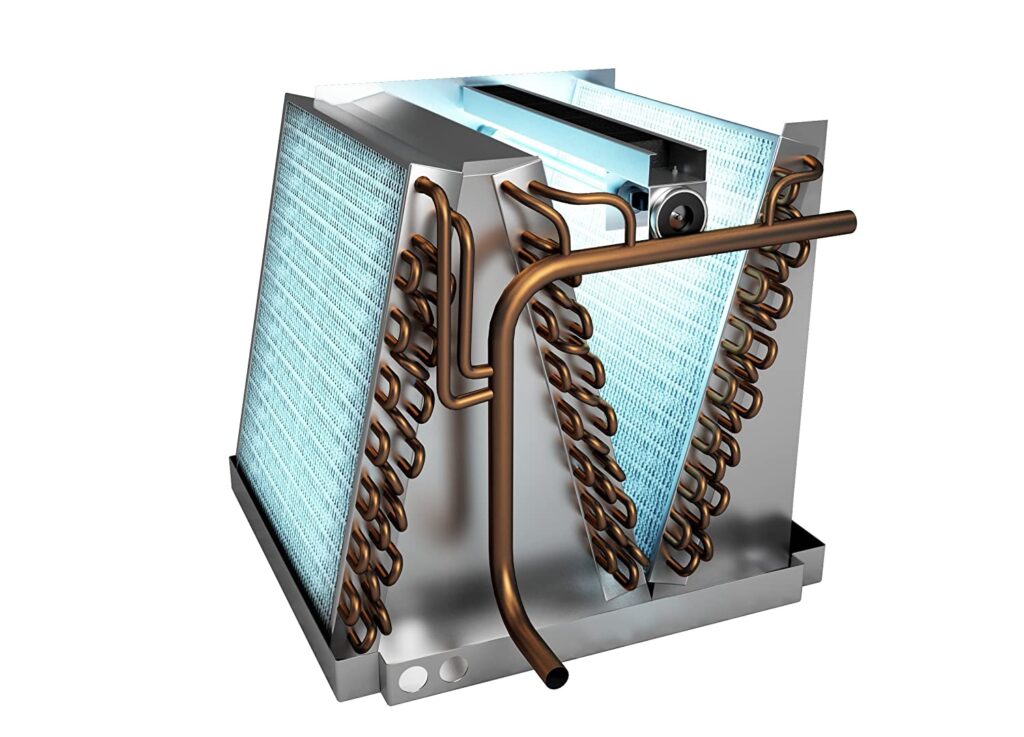
NASA played a significant role in the development of such systems. In the early 1990s, NASA researchers started studying ways to purify the air on space stations from ethylene. This gas tends to accumulate around plant products and accelerate their decay. Scientists discovered that ultraviolet irradiation of titanium dioxide produces free electrons, which convert oxygen and humidity into highly reactive hydroxyl radicals. These radicals then react with volatile organic compounds, converting them into carbon dioxide and water.
This discovery not only helped solve the ethylene problem but also provided a safe method to remove harmful organic compounds, pathogenic microorganisms, and mold from the air. The technology quickly gained popularity and is now actively used in air purification devices found all over the world.
Wastewater Treatment
In the 1970s, NASA sponsored a project aimed at creating closed water and air purification systems using plants. It was expected that they would be installed on orbital stations and settlements located on other celestial bodies in the not-too-distant future.

Certainly, this forecast was too optimistic. Human activity in space is still limited to low Earth orbit, and the life support system of the ISS is far from being fully autonomous. However, the data collected during the research, which did not find application in space, turned out to be useful on our planet.
Scientists found that some aquatic plants can effectively remove organic compounds and heavy metals. This discovery became the basis for inexpensive and ecologically safe wastewater treatment techniques. This approach turned out to be cheaper than building traditional sewage treatment facilities and is also suitable for restoring valuable wetlands. Different variations of this method are now actively used in the USA and many other countries.
Fighting Oil Pollution
In the early 1990s, researchers from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Marshall Space Flight Center developed a technology for creating homogeneous spherical microcapsules with a size of about 10 micrometers. This project had a medical focus, as it was envisioned that such capsules could be used for controlled delivery of antibiotics or microdoses of other medications into the body.
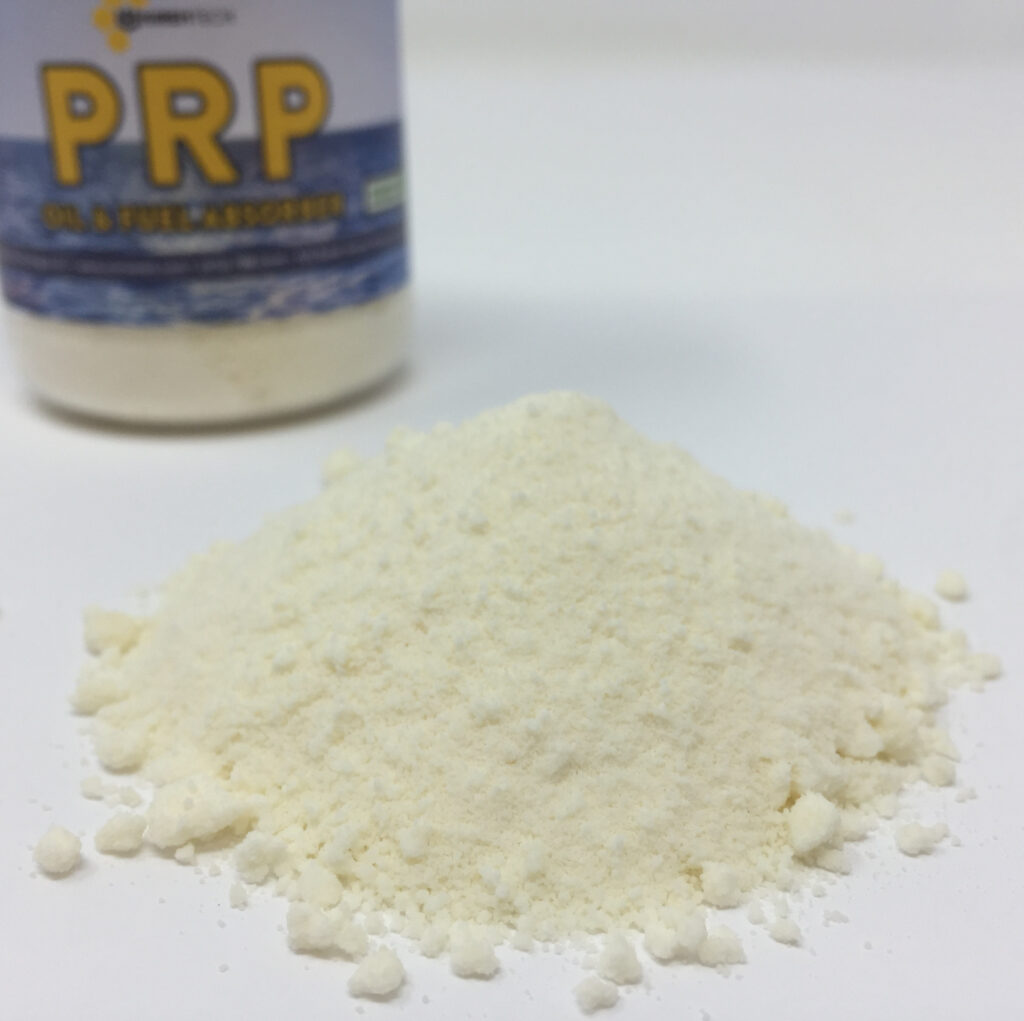

Soon, the industry became interested in this technology, and it was quickly applied to solve numerous other tasks. Nowadays, it is actively used in restoratives, flavor enhancers, bee feed, and many other products.
But the most interesting application of microcapsules was in the fight against oil pollution. A method developed by UniRemInc involves creating hollow spheres from beeswax. Water cannot penetrate inside the microcapsules, so they do not sink and remain on the surface. At the same time, the spheres can absorb oils (such as fuel, motor oils, or crude oil) before they cause harm to the environment.
This method quickly gained popularity. Currently, similar microcapsules are used in filters for fishing boats, to purify polluted water bodies, and in combating the consequences of large-scale industrial oil spills.
