The European Space Agency provided new details about an extremely bright and long-lasting gamma-ray burst recorded last year by satellites. The event was so powerful that it caused a disturbance in the Earth’s ionosphere.

A record gamma-ray burst was registered on October 9, 2022. It received the designation GRB 221009A. In the past, gamma-ray bursts were a mystery to astronomers, but now it is believed that they represent energy emissions that occur during supernova flares or collisions of neutron stars.
But despite the fact that we now know much more about such events than before, GRB 221009A still surprised researchers. It turned out to be the brightest gamma-ray burst recorded since the 1960s. According to astronomers, GRB 221009A was ten times stronger than the nearest “competitor”. According to statistics, such a powerful gamma-ray burst reaches the Earth only about once every 10 thousand years.
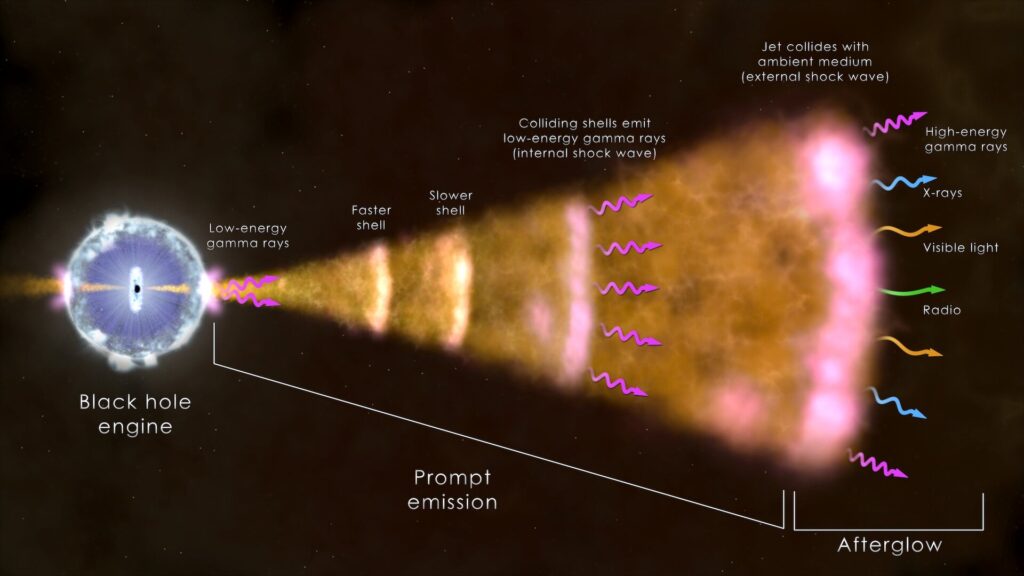
In the 800 seconds during which the burst lasted, enough energy was released to activate lightning detectors in India. And instruments in Germany recorded signs that the ionosphere (the upper layer of the Earth’s atmosphere containing electrically charged gases) was disturbed by the explosion for several hours. Subsequently, the scientists checked the data collected by the CSES satellite. They confirmed that the gamma-ray burst caused a strong variation of the electric field in the upper part of the ionosphere.
It is worth noting that GRB 221009A occurred in a galaxy almost 2 billion light-years away from us. And, nevertheless, its energy was enough to affect the Earth. This supports the idea that such an event that occurred in the Milky Way can have very serious consequences for our planet. If the Earth is in the path of a gamma-ray burst, it can destroy the ozone layer, which is allowing dangerous ultraviolet radiation from the Sun to reach the Earth’s surface. According to some researchers, the Ordovician-Silurian extinction that happened 445 million years ago could have happened for just this reason.
According to https://www.esa.int
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
