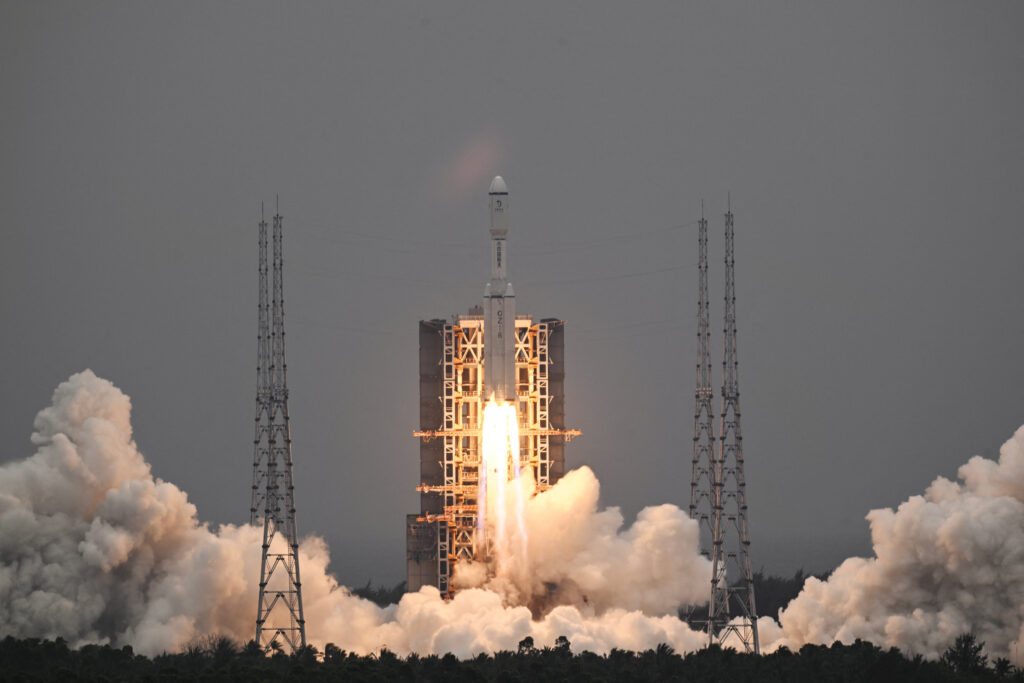
On March 19, the Long March 8 rocket was launched from the territory of the Chinese Wenchang Satellite Launch Center. It sent a Queqiao-2 repeater to the moon.

Queqiao-2 is designed to support missions aimed at the South Pole of the Moon and its reverse side. The satellite will be launched into a highly elliptical selenocentric orbit with an inclination of 55 degrees.
This orbit is specially designed in such a way that both the Earth and the Apollo crater are located in the field of view of Quqiao-2 during most of the round. It has been chosen as the landing site of the Chang’e-6 spacecraft, which is supposed to deliver the first soil sample from the South Pole of the Moon to Earth. Its launch is scheduled for May 2024.
In 2018, China already sent a relay satellite to the Moon, which was used to support the Chang’e-4 mission. It is still operating in a halo orbit around the L2 point. However, the Quqiao-2 is much more powerful than its predecessor. Its weight, including fuel, is 1200 kg. It is equipped with a larger antenna capable of providing a higher data transfer rate.
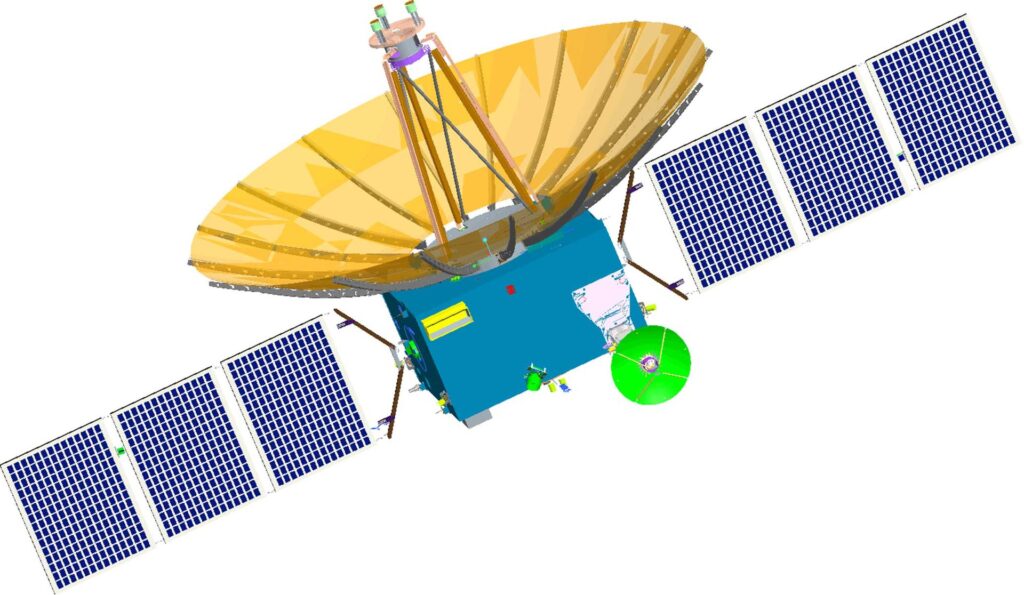
There are also scientific instruments on board the Quqiao-2 — an ultraviolet camera and a neutral atom detector, which will be used during the Chang’e-7 mission. Its launch is scheduled for 2027. Quqiao-2 will also take part in an interferometry experiment with a very long baseline.
A couple of small experimental vehicles also went to the Moon together with the Quqiao-2. They will be used to develop technologies that will find application in the future in the Chinese-designed constellation of satellites intended to provide lunar communications and navigation.
Recall that recently another attempt by China to send a pair of experimental vehicles to the Moon ended in failure.
According to https://spacenews.com
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.comne/ust_magazine


