Using data collected by the Mars Express mission, astronomers have found massive ice deposits near the Martian equator. If they were melted, they would cover the surface of the Red Planet with a layer of water from 1.5 to 2.7 meters thick.
Medusae Fossae Formation
The deposits are located in a region known as the Medusae Fossae. It is a vast area located on the border between the Great Northern Plain of Mars and the southern highlands. The total length of all its sections exceeds 5,000 km, and the area is comparable to the territory of India.
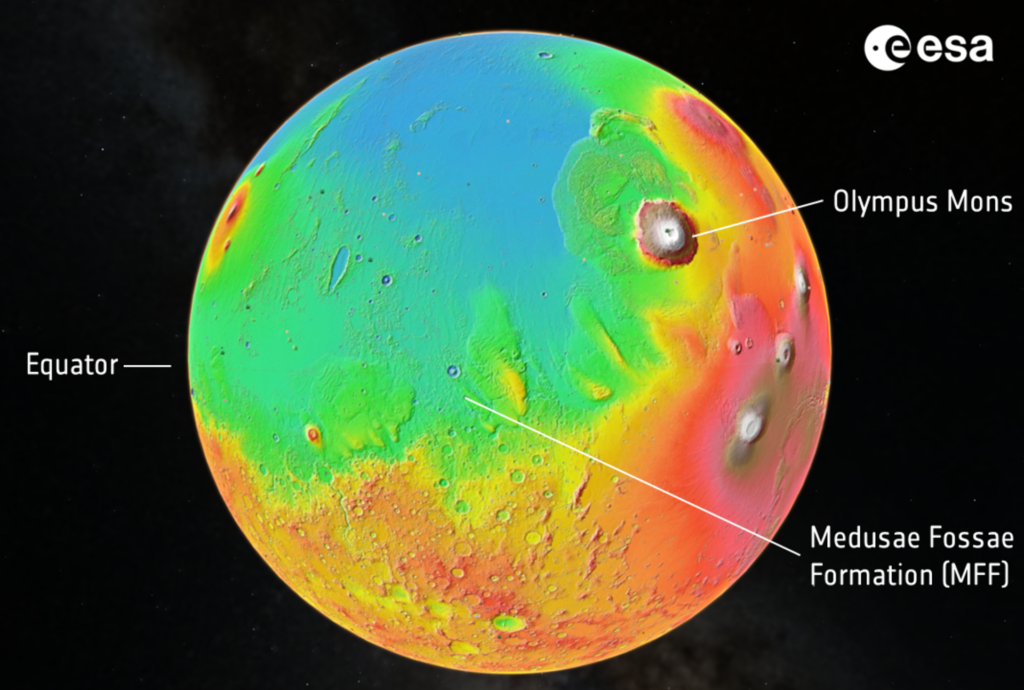
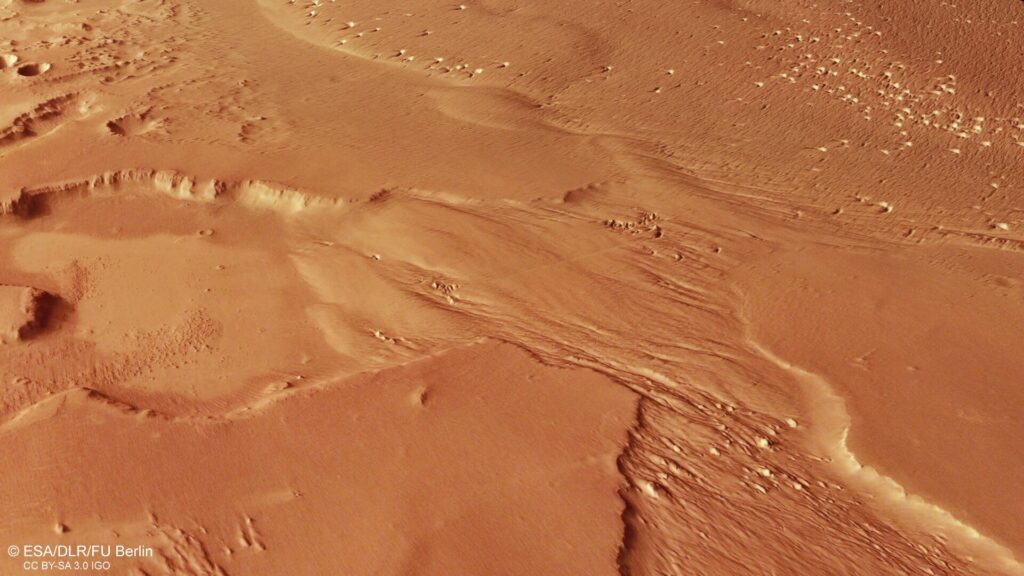
This gigantic structure was formed as a result of volcanic activity. Data from orbiters indicate that it is covered with a porous material. Apparently, these are deposits of volcanic ash. Due to its softness, the material of the Medusae Fossae is actively destroyed by the action of Martian winds. The dust formed during this process is then carried around the planet.
Huge ice deposits on Mars
15 years ago, Mars Express received data indicating that massive deposits of some substance up to 2.5 km thick are located under the surface of the Medusae Fossae. But back then, scientists weren’t sure what it was about.

In the course of the new study, astronomers examined data collected by the MARSIS radar installed on Mars Express. The analysis showed that the characteristics of the radar signal corresponded to the Martian poles. As you know, there is a kind of “sandwich” under their surface, consisting of alternating layers of water ice and compressed dust.
If the Mars Express data is correct, then similar deposits are found in the area of the Medusae Fossae. According to the updated data, their thickness reaches 3.7 km. If you melt all this ice, it will cover the surface of Mars with a layer of water from 1.5 to 2.7 meters thick.
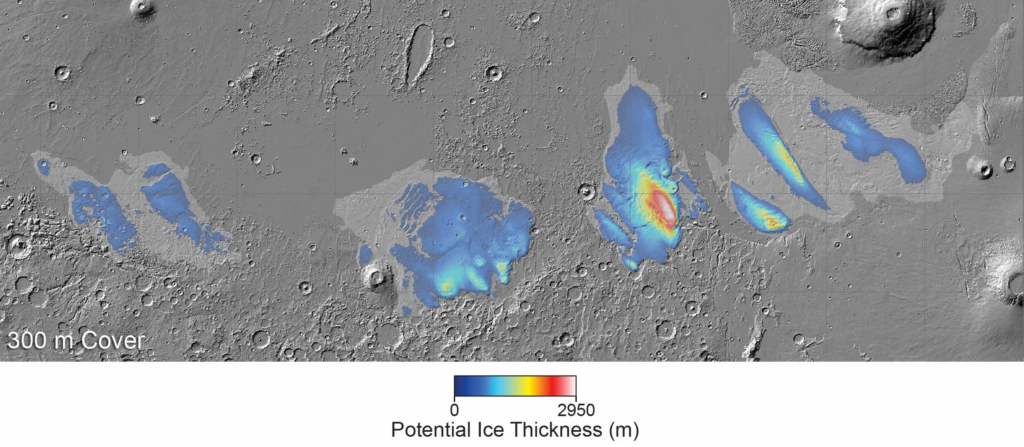

According to the researchers, these ice deposits are left over from past eras, when the Red Planet had a much more favorable climate and dense atmosphere. In the future, they may become an important help for Martian colonists.
You can also read about which animals will live next to colonists on the Moon and Mars.
According to https://www.esa.int
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazin


