Scientists investigated the previously discovered exoplanet Gliese 367 b, which was already known to be smaller than Earth and very hot. Now they have learned that it is also dark and devoid of atmosphere.
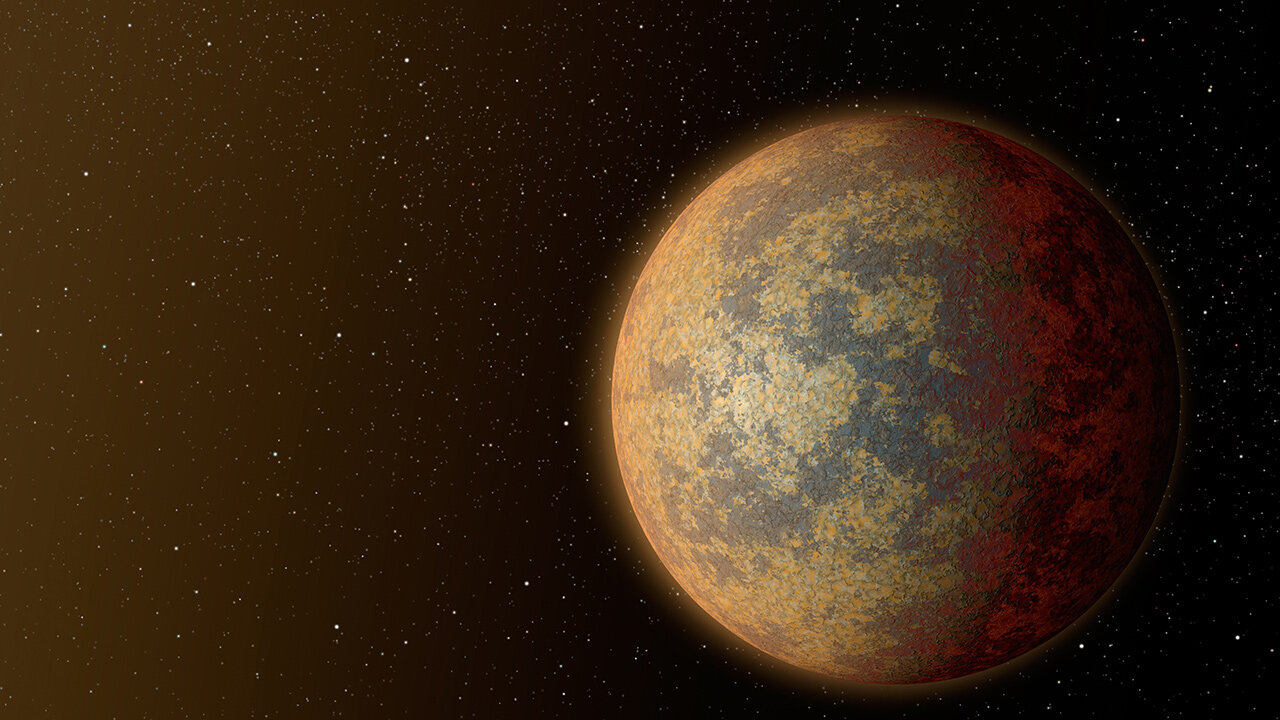
Hot planet Gliese 367 b
Scientists working with the James Webb Space Telescope have published a new study of the exoplanet Gliese 367 b, which has the unofficial name Tahay. It orbits a red dwarf, 31 light-years away from us, which is quite a bit by cosmic standards.
Gliese 367 b was discovered in 2021 during observations made by another space telescope, TESS. Its parent star is a red dwarf of the M1.0V class, has a size half the size of the Sun, and is tens and hundreds of times lower in luminosity.
However, Gliese 367 b orbits its star in just 7.7 hours, that is, extremely close to it and therefore very hot. The temperature on its surface, according to preliminary studies, was about 1100 °C. Besides it, there are at least two other planets in the system, but they are much further away from the star.
In size, Gliese 367 b is 30 percent smaller than Earth, and its mass is only 67 percent of our planet. Scientists decided to find out more about whether there was an atmosphere on it and used the MIRI infrared camera installed on James Webb.
What scientists found out
New research of Gliese 367 b has helped to learn several interesting things about it at once. For example, it has become clear that the temperature of the hemispheres of the planet is very different. The “dayside” is heated to 1500 °C, while the nightside is only up to 600 °C.
In addition, the surface of the planet should have a dark color. But the most interesting conclusion concerns the atmosphere of Gliese 367 b. According to research, it is almost completely absent and this is an interesting result.
The fact is that, judging by the temperature, the dayside of the planet should be molten. In the liquid state, there should even be silicates. And volatile substances such as water should definitely form the atmosphere.
Its absence shows that there are practically no volatiles on Gliese 367 b. Scientists do not really understand the reasons for this, but they suspect that over hundreds of millions of years, powerful red dwarf flares simply “blew away” the entire atmosphere from the planet.
According to phys.org
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine


