The firing test of the updated solid-fuel engine of the Vega-C rocket ended in failure. Because of this, the carrier is unlikely to return to flights before 2024.
Shortage of European rockets
Russia’s large-scale invasion of Ukraine and the subsequent rupture of relations with Roscosmos put ESA in a difficult position. Europeans have lost the opportunity to continue launching Soyuz rockets from the Kourou cosmodrome in French Guiana. On the other hand, the debut of the new Ariane 6 rocket, which is supposed to replace the decommissioned Ariane 5, is constantly shifting and will take place only in 2024.
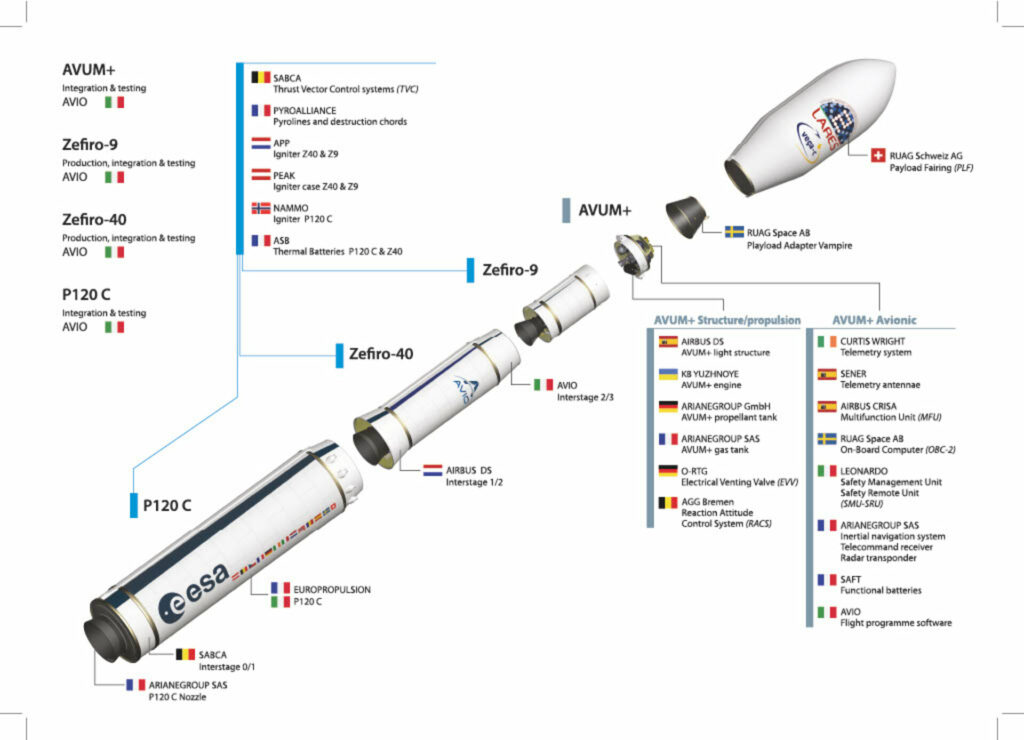
The only bright spot on this background was Vega-C. This is a modification of the Vega light rocket, designed to launch cargo into polar and low Earth orbits. It can put up to 2.3 tons of payload into a 700-kilometer sun-synchronous orbit. The rocket has a four-stage design. The first three stages of the carrier are equipped with solid-fuel engines, the fourth (AVUM+) is liquid. It is equipped with the RD-843 power unit developed by the Yuzhnoye Design Office, which has the possibility of multiple activation in space.
Vega-C Successes and Failures
The debut launch of Vega-C took place in July 2022 and ended with success. Alas, but during the second flight of the rocket in December 2022, an accident occurred. It was a big blow for ESA, further complicating the situation with Europe’s ability to independently launch cargo into space.
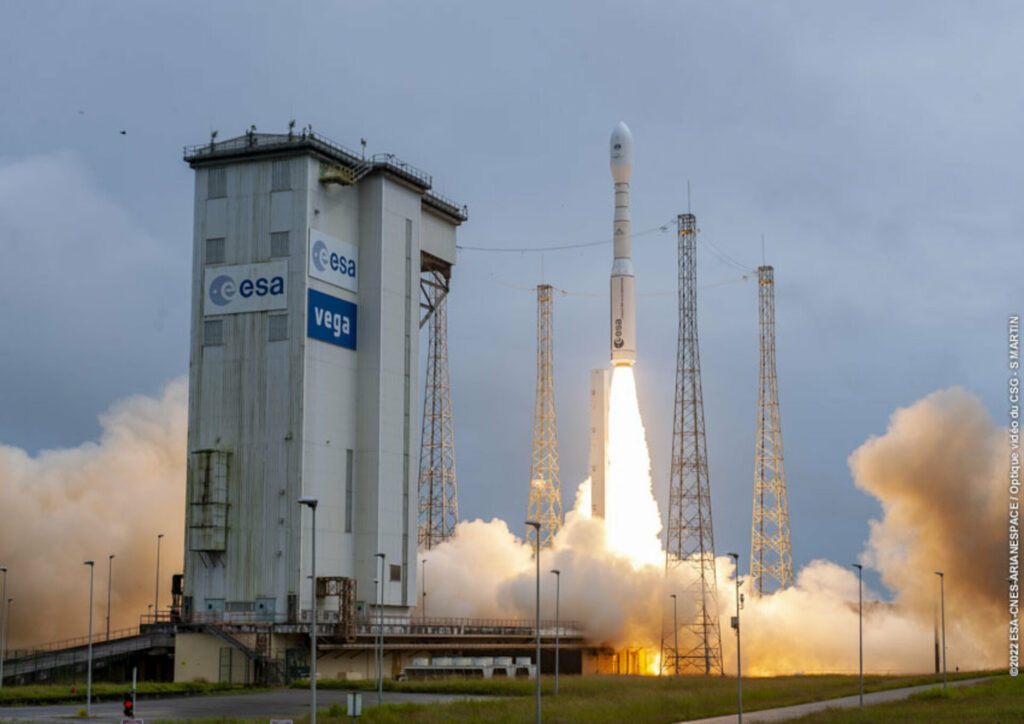

In the spring of 2023, the ESA published the results of the accident investigation. The Commission concluded that its cause was the destruction of the nozzle component of the Zefiro 40 engine on the second stage of the rocket. The report caused a small scandal. The fact is that the engine nozzle was made of a material supplied by a Ukrainian company. Ukraine did not agree with the commission’s conclusions, but despite this, ESA decided to replace the supplier of the material.
On June 28, Avio (the main contractor of the project) conducted a fire test of the updated Zefiro 40 engine. The 97-second test failed. According to Avio’s statement, an “anomaly” was detected at the 40th second of the firing, which led to a loss of pressure in the engine.
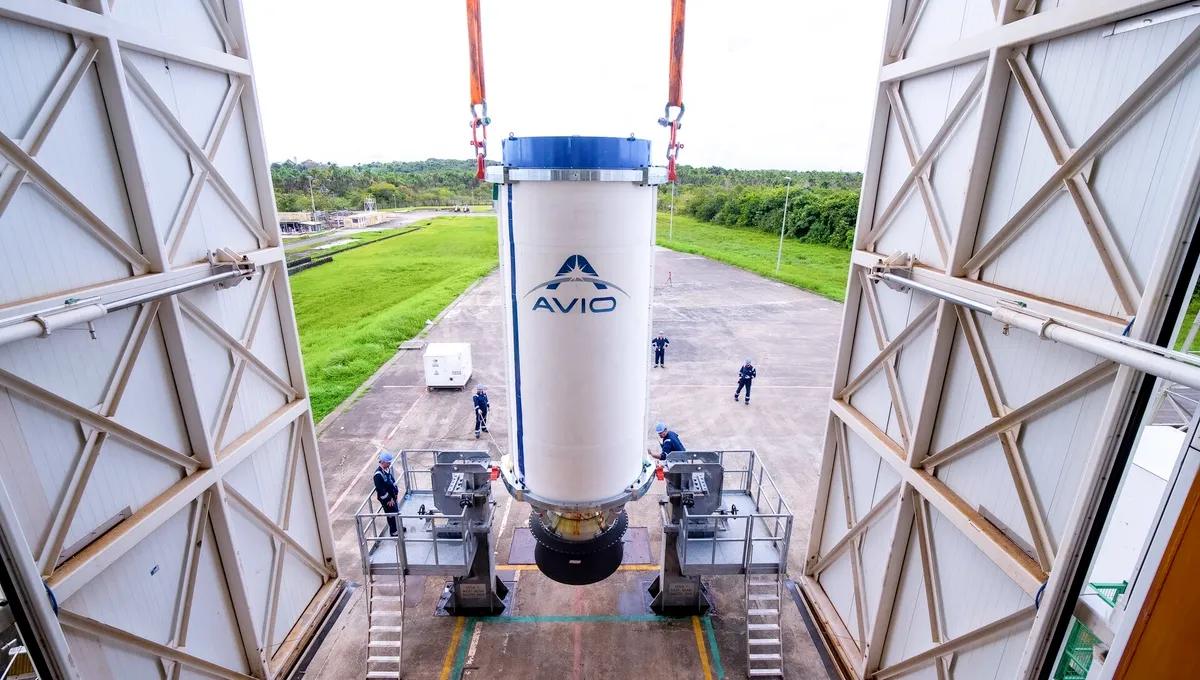

The failed test was very unpleasant news for ESA. The Space Agency planned to resume operation of Vega-C in September. As part of its next mission, the rocket was supposed to launch the Sentinel-1C radar satellite into orbit. Despite the fact that Avio has not yet made any statements about changing the Vega-C flight schedule, it is obvious that the next mission is unlikely to take place before 2024. In this situation, the ESA management recently recommended transferring the launch of the EarthCARE satellite to SpaceX. Given the current situation with European carriers, it is possible that this is not the last such recommendation.
According to https://spacenews.com
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine
