The Perseverance mission support group has published a panorama. It captures a section of the surface used as a place to store samples of Martian soil.
Creating a depot for Martian samples
The Perseverance rover is equipped with 43 titanium tubes designed to store samples of Martian soil and atmosphere. They are planned to be delivered to Earth as part of the joint US-European MSR (Mars Sample Return) mission, the implementation of which should begin at the end of this decade.
The main plan is that after the MSR landing, Perseverance will drive up to the return module and overload the sample capsules on it. But what if by the time the mission arrives, the rover loses the ability to move? For this, NASA has developed a backup plan that provides for the creation of a depot of samples of Martian soil.
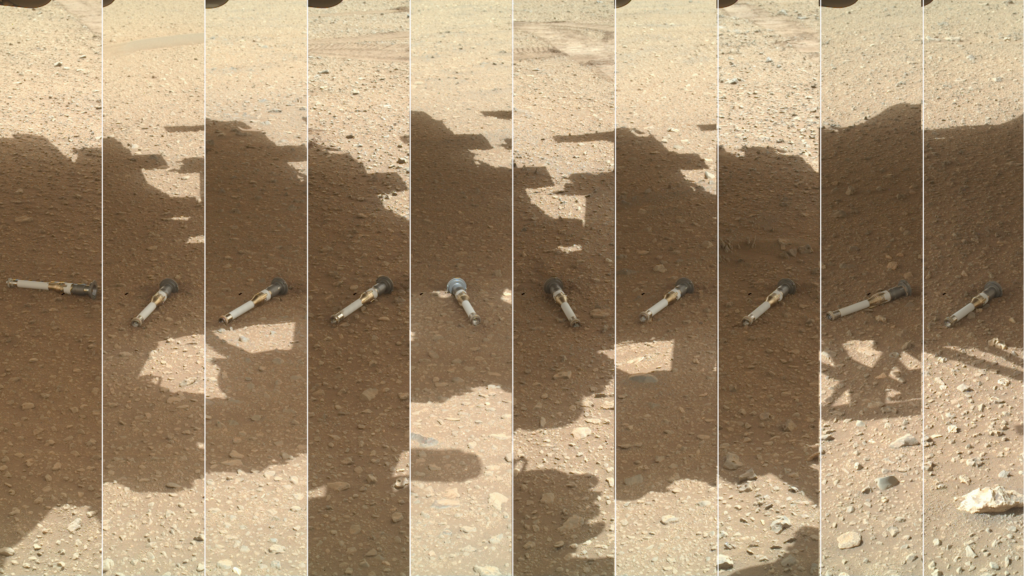
Between December 2022 and January 2023, Perseverance unloaded ten capsules with soil samples. They were placed in a zigzag pattern with a distance of 5 — 15 meters from each other on a surface area called Three Forks. After the drop, each capsule was photographed, and its position was recorded on the map. In the future, they will be picked up and delivered to the MSR return module by two small drones.
Depot of Martian samples
The panorama published by NASA demonstrates the Three Forks site. It consists of 368 images taken on January 31, 2023 using the Mastcam-Z camera — that is, after Perseverance completed unloading the capsules.
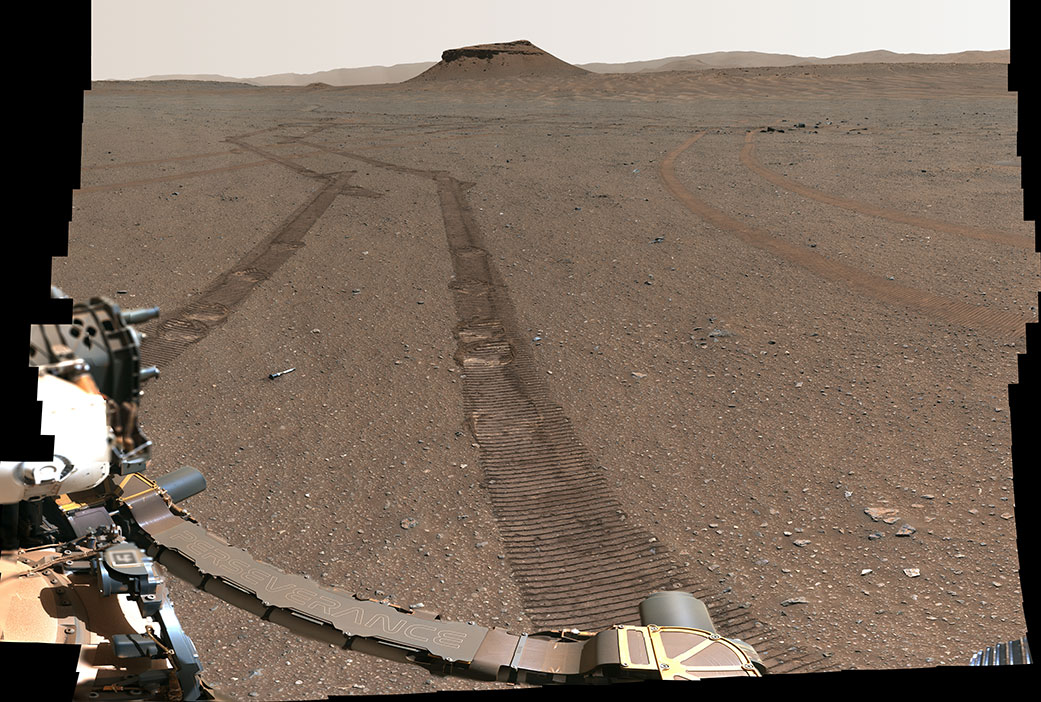


The colors of the image are calibrated to match what the human eye would see. Also, an annotated version of the panorama was published, which marked the placement of capsules.
According to https://www.nasa.gov
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

