The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has published images of the solar atmosphere. They were taken with the help of the new CCOR-1 coronagraph.
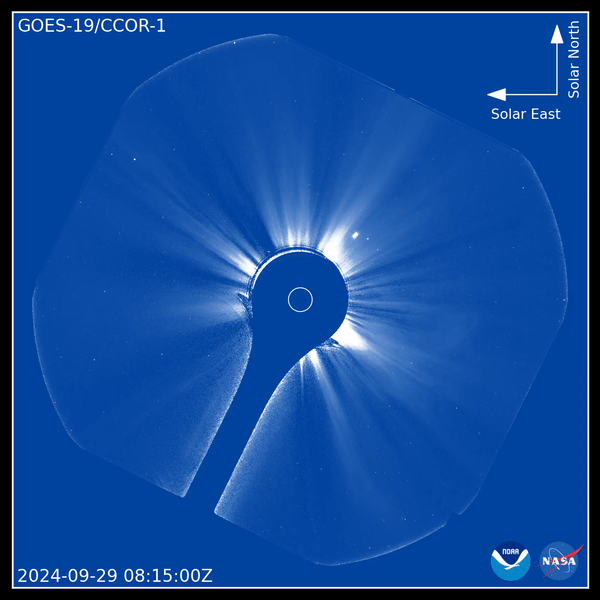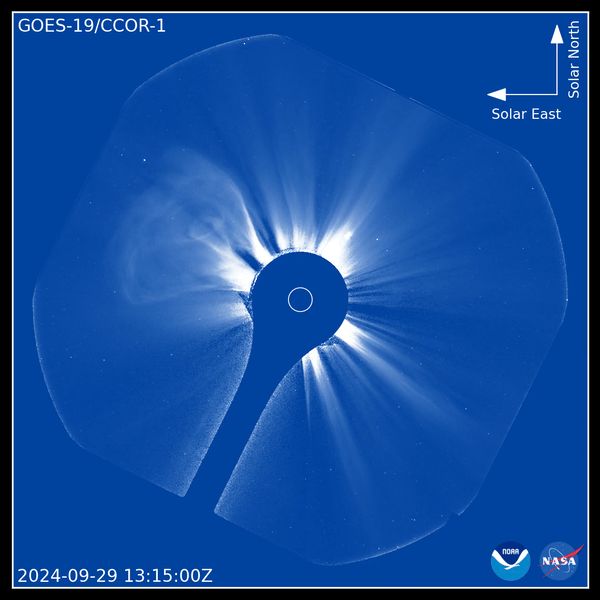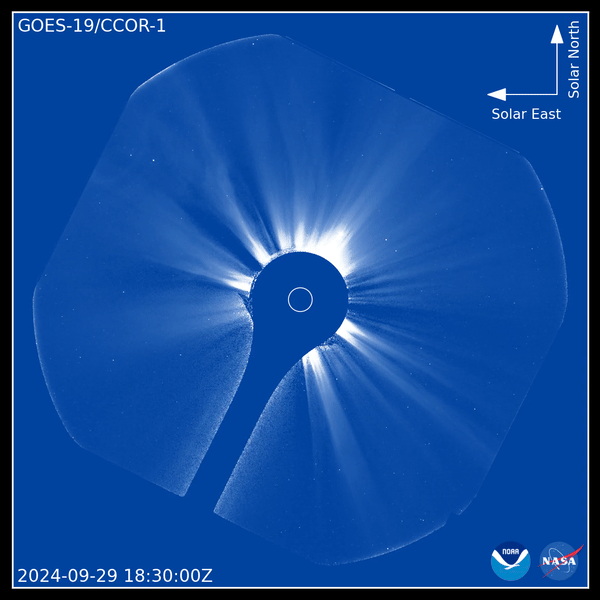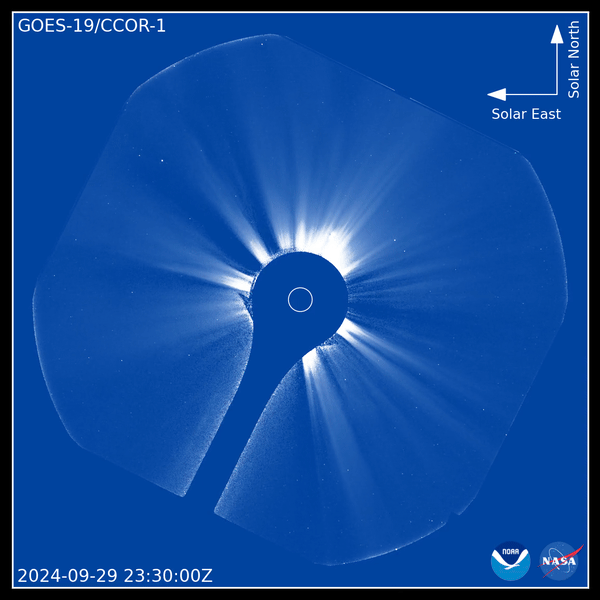
Coronagraph is a telescope designed to observe the corona, the outer layer of the solar atmosphere. It is much more heated than other regions of the Sun and various structures often form in it: coronal holes, arches, loops, etc. In addition, the corona is a source of mass ejections. When they reach Earth, they produce geomagnetic storms accompanied by auroras. They can impact satellites, navigation systems, astronaut safety, aviation communications and power grids.
The main problem in studying the corona arises from the fact that it is much dimmer than the Sun’s disk. It can only be seen with the naked eye during a total solar eclipse. That’s why astronomers use coronagraphs. These devices block out sunlight with special disks that act as an artificial moon.
The CCOR-1 coronagraph is aboard the GOES-19 geostationary satellite, launched in June 2024. It provides continuous corona coverage with imaging every 15 minutes. The coronagraph uses a disk (the dark blue circle in the center of the video) to eclipse the Sun (shown by the smaller white circle), allowing us to see the extremely faint corona.

The images published by NOAA are dated September 29, 2024. They clearly show a coronal ejection coming out of the eastern limb (left side) of the Sun. The images also show streamers, the bright radial structures along which solar plasma travels to the outside. Coronal ejections bend and sometimes destroy plasma streams, rushing past them at speeds of hundreds to thousands of kilometers per second.
CCOR-1 is the first in a series of NOAA coronagraphs. Similar instruments will be installed on satellites that are planned to be placed at the L1 and L5 Lagrange points of the Sun-Earth system.
Provided by NOAA


