Selection of the most interesting space news for breakfast: Scientists have found a disinfectant in the center of the galaxy. Virgin Orbit has received a license to launch in Brazil, and Airbus will create a new Earth exploration satellite for ESA.
CAPSTONE went to the Moon
Rocket Lab has successfully launched an Electron rocket with a NASA-owned CAPSTONE (Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment) satellite. In the coming days, the spacecraft will have to perform a series of maneuvers that will send it to the Moon.
Cygnus departs ISS after reboost test
A Cygnus cargo spacecraft departed the International Space Station June 28, three days after it demonstrated its ability to raise the station’s orbit. The spacecraft, loaded with garbage for disposal, is scheduled to reenter after a June 29 deorbit burn by the spacecraft. “This reboost of the ISS using Cygnus adds a critical capability to help maintain and support the space station,” Steve Krein, vice president of civil and commercial space at Northrop Grumman, said in a company statement. Maintenance of the station’s orbit is usually handled by thrusters on the Russian segment of the station or Progress spacecraft docked to it.
Airbus to create new Earth Exploration satellite for ESA
ESA has awarded a contract worth €160 million to Airbus in the UK to build the Earth Explorer FORUM satellite. This exciting new mission will yield unique insight into the planet’s radiation budget and how it is controlled – thereby filling in a critical missing piece of the climate jigsaw. FORUM is ESA’s ninth Earth exploration mission.
Implemented as part of the ESA FutureEO program, Earth Explorers are innovative research satellites. Each of these unusual missions carries innovative space technologies, and all, without exception, have surpassed their original scientific goals.
Market News

China’s newest EO satellite carried aloft by a Long March 4C rocket
China sent a new Earth Observation (EO) satellite into space from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwest China. The satellite, Gaofen-12 03, was launched by a Long March-4C carrier rocket at 11:46 p.m. (Beijing Time) and has successfully entered its planned orbit. The satellite will be used in a variety of fields, including land surveys, urban planning, road network design, crop yield estimation and disaster relief. The launch marked the 425th flight mission of the Long March series carrier rockets.
Space Software Startup Leanspace Raises $6M Seed Round
French startup Leanspace raised a 6 million euro ($6.35 million) seed round to further its mission to simplify space software. European VC firm Karista led the round, along with 42CAP. French innovation agency Bpifrance participated as well, bringing Leanspace’s total funding to 8.5 million euros ($9 million).
Leanspace offers a collection of space-specific cloud services that can be used via API. Customers can use Leanspace as an integration platform. It is easily configurable and scales ground segments, and also makes it possible to develop your own systems for individual use. The company calls it “platform as a service.”
Virgin Orbit is Now Licensed to Launch in Brazil With New Subsidiary
Virgin Orbit is now licensed to launch from Brazil through its new subsidiary, Virgin Orbit Brasil Ltda, and could potentially conduct the first domestic orbital launch from Brazil as early as next year.
This is a step toward domestic launch capability in Brazil after last year, the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB) and Brazilian Air Force (FAB) signed a contract with Virgin Orbit to establish commercial launch services at the 39-year-old Alcântara Launch Center on Brazil’s northern coast. The Alcântara Launch Center has hosted several launches of suborbital rockets, but the facility has not yet been used to reach Earth orbit.
House appropriators partially restore funding for planetary defense mission
House appropriators partially restored funding for a planetary defense mission as part of a spending bill while also raising concerns about NASA’s closure of an airborne observatory and plans to return samples from Mars.
The House Appropriations Committee released June 27 the report accompanying its commerce, justice and science (CJS) spending bill for fiscal year 2023, due to be marked up by the full committee June 28. The CJS appropriations subcommittee approved the bill without debate June 22.
Interesting
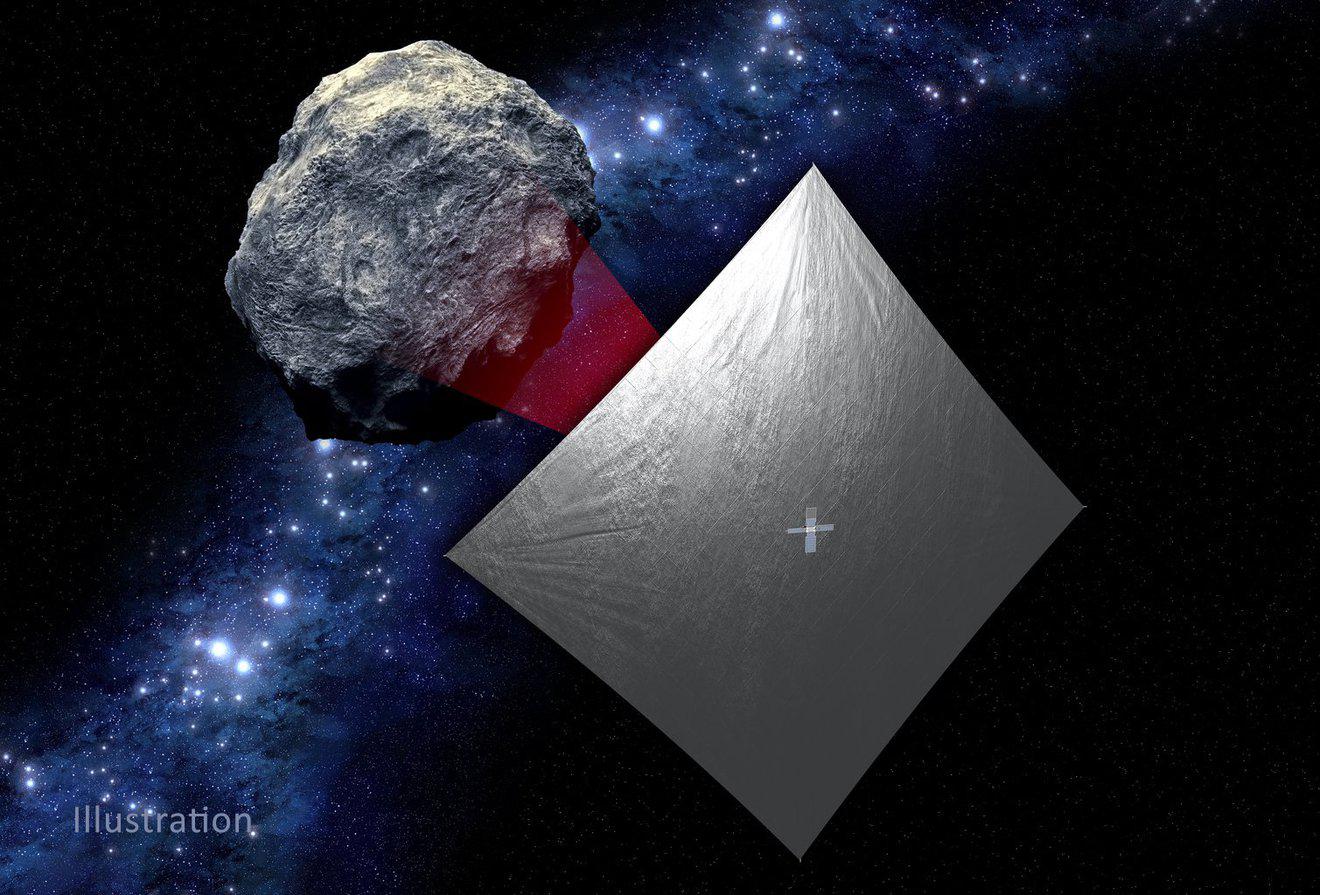
NASA prepares to launch a solar sail
NASA is completing preparations for the launch of the NEA Scout. It will be the first solar sail probe in history to visit an asteroid. In terms of its dimensions, the NEA Scout is comparable to a shoe box. Its dimensions are 30 × 20 × 10 cm (6U), weight — 14 kg. The scientific load of the probe is represented by a 14-megapixel monochrome camera developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. NEA Scout will have to make a close flyby of one of the near-Earth asteroids. Initially, the device was planned to be sent to the stone under the designation 1991 VG, but due to the postponement of the SLS launch, the mission goal changed to asteroid 2020 GE. Its diameter is only 18 meters. If successful, 2020 GE will become the smallest celestial body explored by the Earth device.
A sanitizer in the galactic center region
An international group of researchers led by Arnaud Belloche (MPIfR, Bonn, Germany) reports the first identification of iso-propanol in interstellar space, a substance which is used as a sanitizer on Earth. Iso-propanol is the largest alcohol detected so far, demonstrating the increasing complexity of members of one of the most abundant classes of molecule that can be found in space. The identification was made possible thanks to observations of the star forming region Sagittarius B2 (Sgr B2) close to the center of our galaxy where many molecules have already been detected. It is the target of an extended investigation of its chemical composition with the ALMA telescope in Chile.
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

