On the occasion of the upcoming winter holidays, the support team of the Mars Express mission has released a new series of images. They show a section of the surface in the south polar region of Mars.
Spring at the south pole of Mars
It may seem like a typical Martian winter. But in fact, the picture was taken when spring had already arrived in this region. This is indicated by dark dunes peeking through the hoarfrost and ice-free peaks. The eye is also riveted by two large craters, at the bottom of which layers of water ice and small sedimentary rocks alternate. Similar layered deposits are also visible on the rust-red ridge connecting the two impact formations.
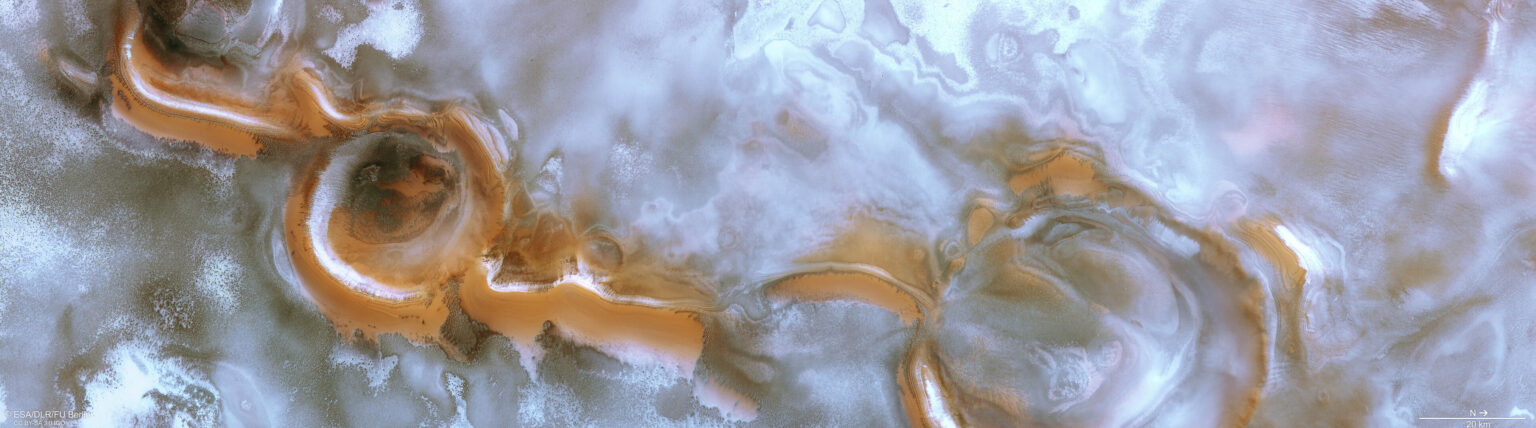
It should be borne in mind that the ice and hoarfrost visible in the pictures are mostly composed not of frozen water, but of frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice). During winter, 12% to 16% of the Martian atmosphere is stored at the poles. When the dry ice begins to sublimate in the spring, this leads to the formation of strong winds that are an integral part of the Martian climate cycle.
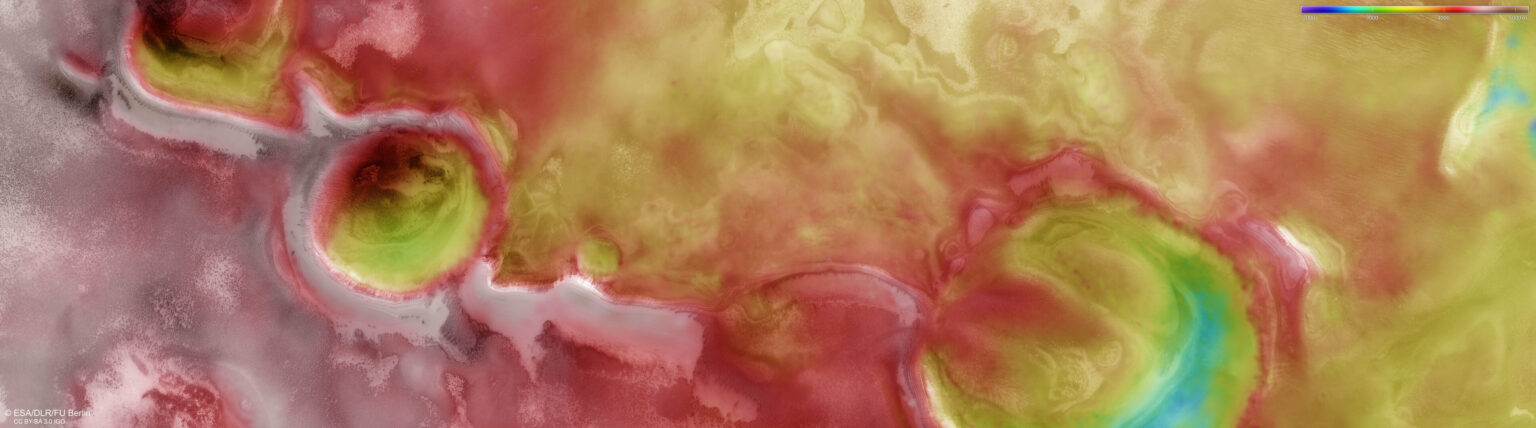
As for the water ice we are used to, the main mass of it is not on the surface, but hidden under it. Its deposits, alternating with layers of dust and sand, go hundreds of meters deep into Mars.
Volcanic dunes, geysers and clouds
The characteristic dark dunes consist of sand of volcanic origin. Its source is giant sediments left behind by ancient eruptions. They are easily eroded and then blown by the wind all over Mars.
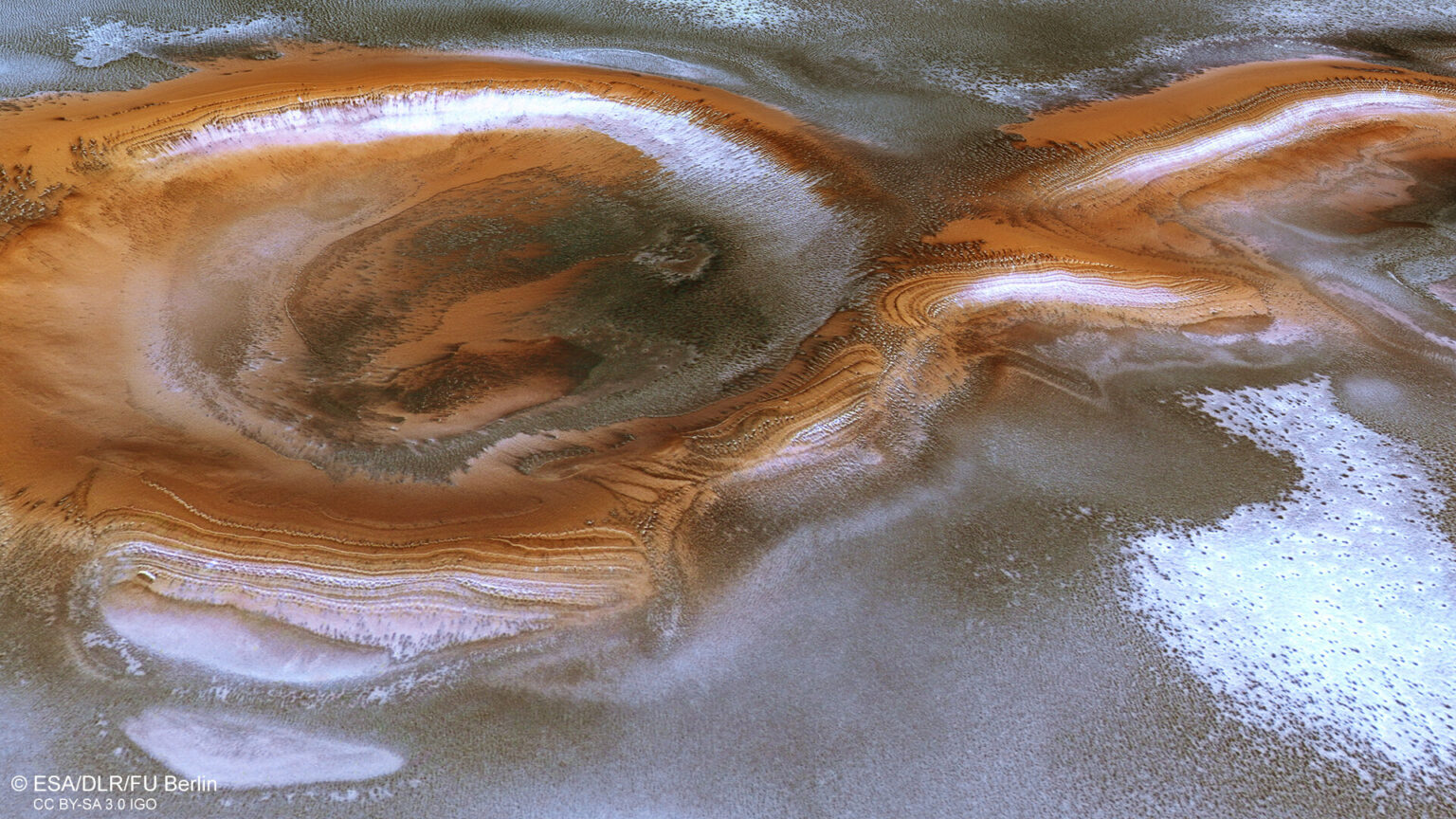
We can also see individual dark spots. They occur when jets of carbon dioxide, formed as a result of the sublimation of dry ice, burst upwards in the form of geyser-like fountains of dark dust. It then settles in round pits created by similar eruptions. These processes change the appearance of the polar regions of Mars.
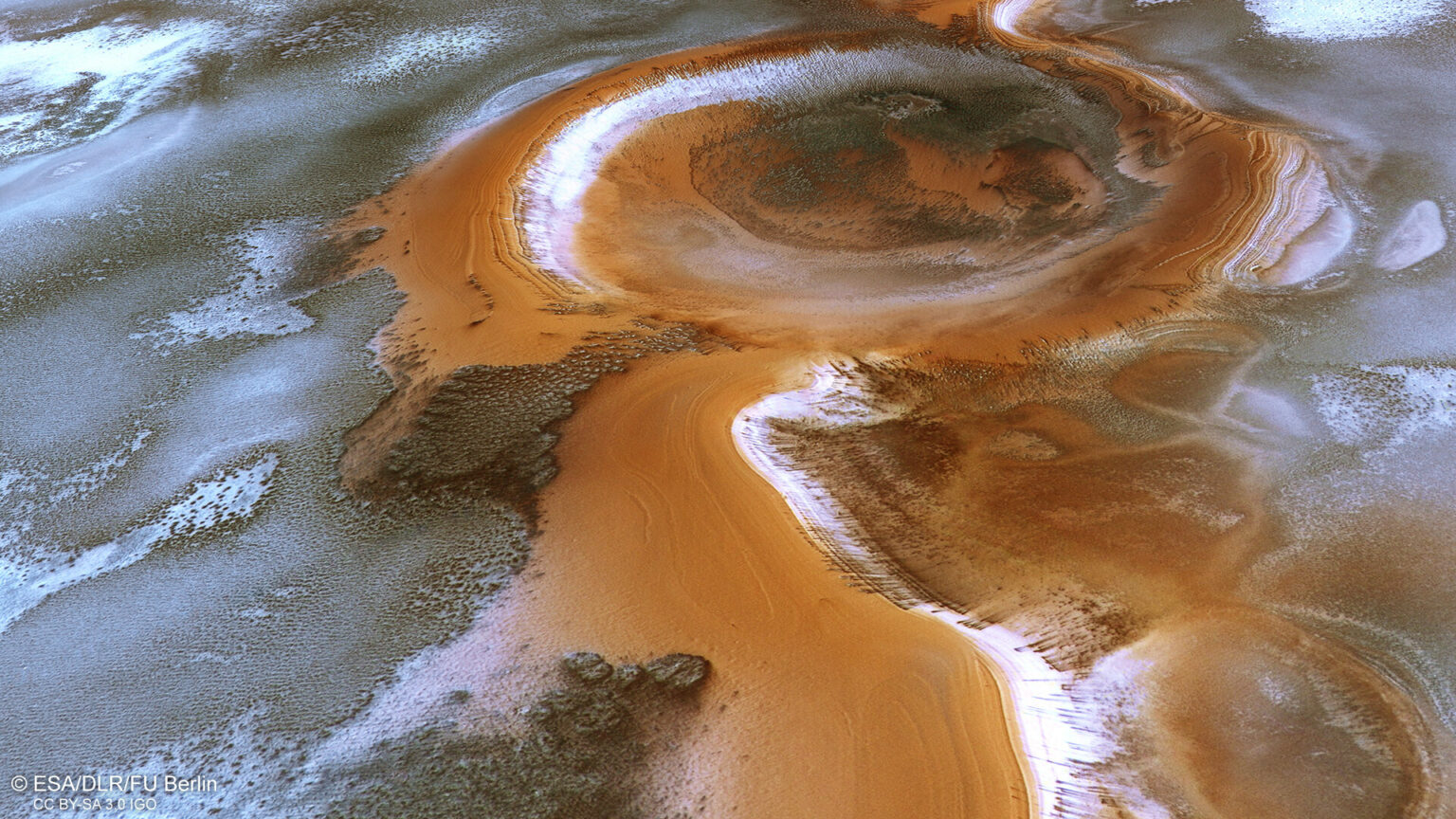

Clouds are also seen in the Mars Express photo, giving the landscape additional atmosphere. Clouds in the South Polar Region often contain water ice, and their trajectory is influenced by the topography of the area.
Earlier we talked about how Mars Express filmed the orbital dance between Phobos and Deimos.
Based on materials from https://www.esa.int

