The InSight probe, which is on the surface of Mars, has missed a communication session. This may indicate that the device’s solar cells have stopped generating enough energy to continue operation.
Energy problems
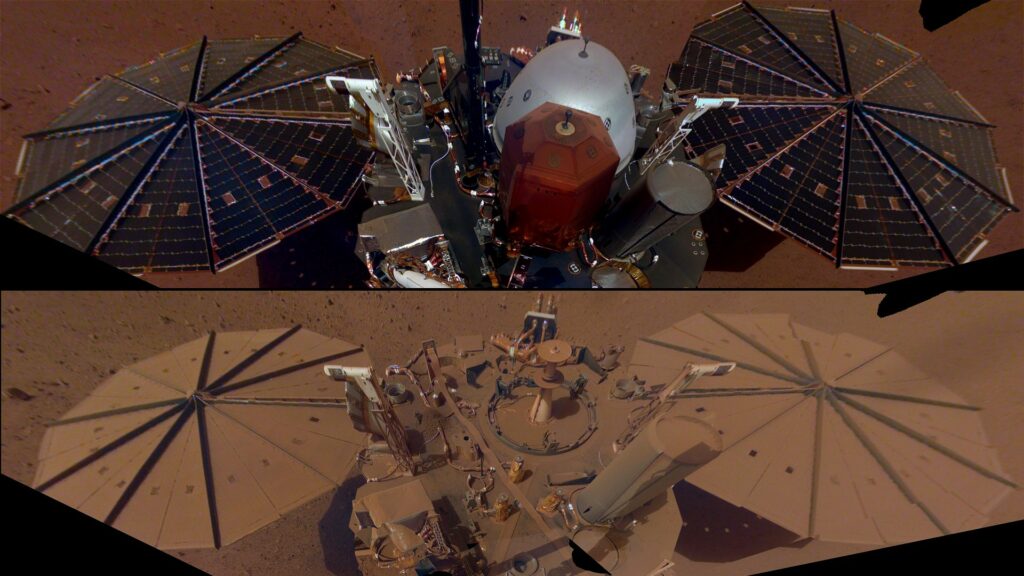
InSight landed on Mars in November 2018. The main task of the mission was to study the internal structure and tectonic activity of the Red Planet. To do this, InSight landed the SEIS seismometer on the surface, which has since registered many Martian earthquakes.
I
The nominal service life of the mission was two years. In fact, the device worked twice as long. InSight could have continued to collect data, but unfortunately ran out of power. The fact is that a thick layer of dust has accumulated on the surface of its solar panels. If at the time of landing they generated about 5,000 W of energy per hour, then by 2022 this figure has decreased to 500 W.
Engineers took steps to knock down some of the dust, but it only delayed the inevitable. Back in May 2022, NASA published a forecast that by December, InSight would no longer receive enough energy to maintain communication with Earth.
Silence of InSight
The last communication session with InSight took place on December 15. The next contact was scheduled for December 18. However, the device never responded to the signal from Earth.
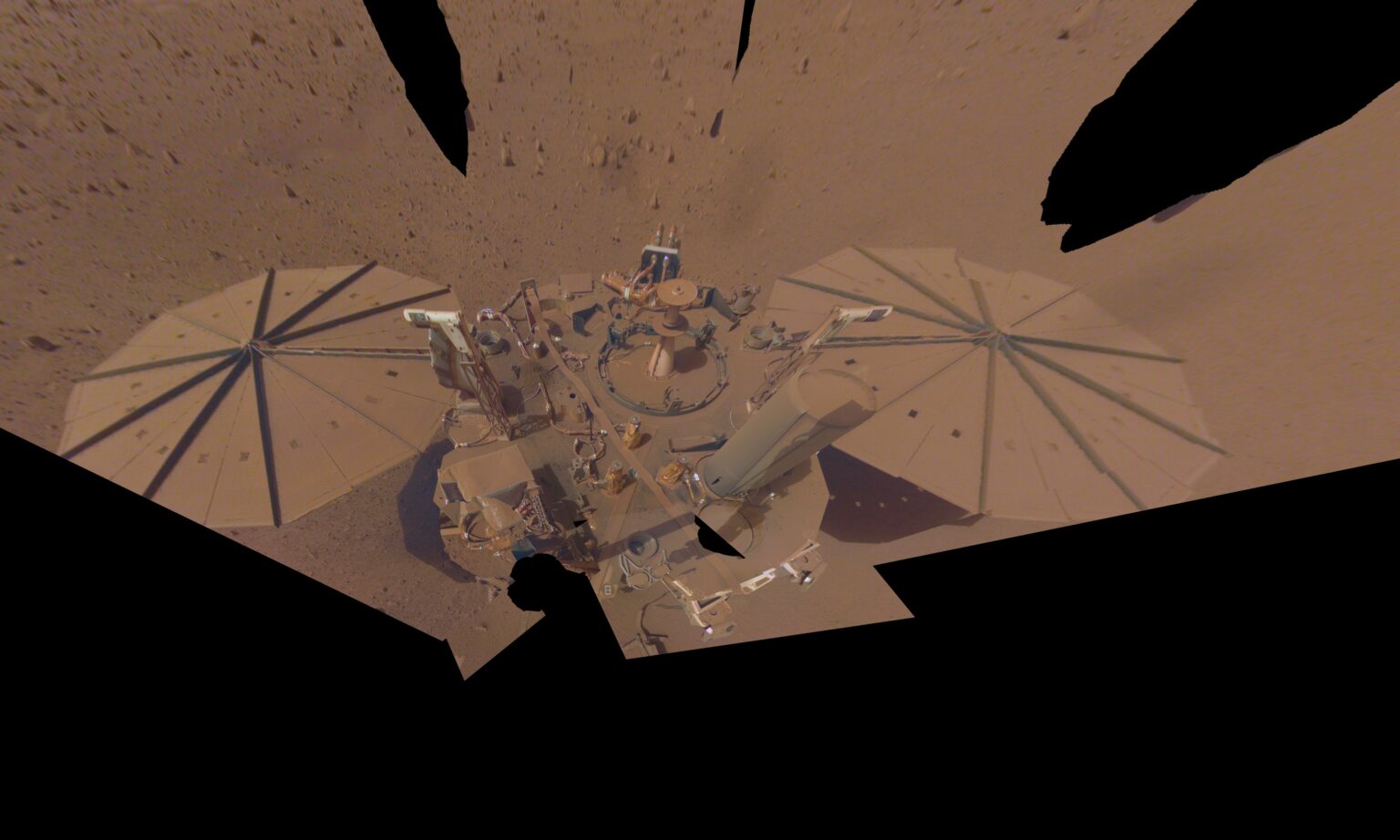
So far, NASA has not released an official announcement about the end of the mission. Most likely, specialists will make several more attempts to contact the device in the coming days. But even if InSight does manage to respond, it’s unlikely to change anything in the big picture. Without an opportunity to clean the solar cells from dust, the device is doomed not to survive one of the cold Martian nights.
Based on https://blogs.nasa.gov/

