Scientists are studying the distribution of stars and dark matter in galaxies. They seek to find out how the ratio of these two components affects the evolution of stellar systems.
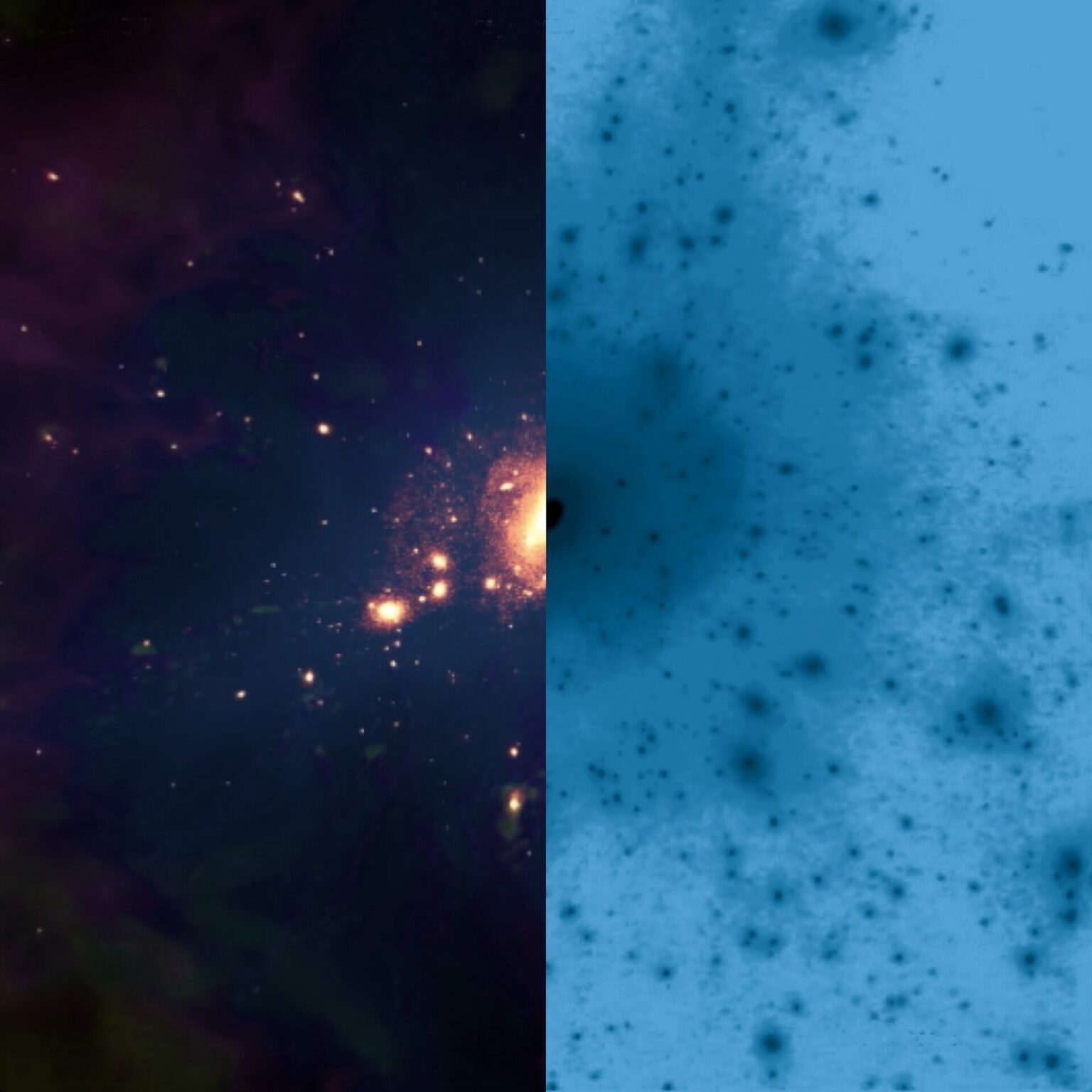
Dark matter in galaxies
A study conducted by a group of scientists from IAC, for the first time confirmed, using observations, the influence of dark matter on the evolution of galaxies. The work was published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Dark matter makes up about 85% of all matter in the universe. Unlike ordinary matter, it cannot be seen directly, which makes it difficult to detect. Its existence can be judged by its gravitational effect on visible objects — stars, planets and other celestial bodies.
Galaxies are made up of these two types of matter. Dark matter is distributed in the halo — huge structures surrounding galaxies, whereas ordinary matter is predominantly present in the central regions where most stars are located.
Traditionally, observational studies of galactic evolution have focused on the role of ordinary matter, even if it makes up a fairly small fraction of the mass of the galaxy. A lot of assumptions have also been made about the hidden part of the mass in recent decades. However, despite numerous efforts, there is no clear consensus on its role.
What the astronomers’ study showed
To study the influence of dark matter, the team of astronomers focused on the difference between the cluster of stars in the galaxy and the mass that can be calculated from its rotation, called the total dynamic mass.
The study shows that the age, metal content, morphology, angular momentum and rate of star formation depend not only on their mass, but also on the total amount of matter, which means that it must contain a dark matter component that corresponds to estimates of the mass of the halo.
“We have seen that in galaxies with equal masses of stars, their stellar populations behave differently depending on whether the halo has more, or less dark matter, in other words, the evolution of a galaxy, from its formation until the present time is modified by the halo in which it is contained. If it has a more or a less massive halo, the evolution of the galaxy over time will be different, and this will be reflected in the properties of the stars which it contains,” adds Ignacio Martín Navarro, an IAC researcher who is a co-author of the article.
Dark matter and the large-scale structure of the Universe
In the future, the team plans to measure stellar populations at different distances from the center of the galaxy and show whether this dependence of the properties of stars on the halo of dark matter persists at all radii. The next step in the study will explore the relationship between the dark matter halo and the large-scale structure of the universe.
Dark matter halos are not created by themselves, they are connected by filaments that are part of a large-scale structure called the cosmic web. It seems that the mass of the halo changes the properties of its galaxy, but this may be the result of the position that each halo occupies in the cosmic web. “In the coming years we want to see the effect of this large scale structure in the context we are studying,” the scientists explain.
According to phys.org
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.comne/ust_magazine


