Selection of the most interesting space news for the week: China will launch two missions with one rocket; scientists have discovered a flaw in the work of James Webb, and we are telling how to become a space tourist.

“Nothing in life is to be feared, it is only to be understood. Now is the time to understand more, so that we may fear less.”
― Marie Curie
Hilton will provide the Starlab Space Hotel with luxury rooms
Hilton, known for its luxury hotels, has officially signed a contract for the construction of crew accommodation and luxury rooms on the commercial space station Starlab to make a long stay in orbit more comfortable. But Hilton and Voyager Space did not share details of how the luxury rooms will be equipped. What will be included in the additional luxe package: will there be a choice of pillows or a free breakfast? It is known that visitors to the orbit will be able to receive freshly baked treats. The company Doubletree by Hilton previously sponsored a successful experiment on making cookies on the ISS.
First license for direct communication between a mobile phone and a satellite
Lynk Global has received the first commercial license for direct communication between a satellite and a mobile phone without the intermediate station. Permission to deploy 10 satellites in orbit, each the size of a pizza box, contains restrictions that make it impossible to cross the ranges of the company’s customers with other operators. The license also does not allow the company to monopolize the entire range allocated to it. A real battle has now unfolded in the United States over which company will better provide mobile phone users with communication beyond the reach of ground towers.
NASA successfully refueled SLS
NASA has successfully completed the test refueling of the SLS lunar rocket. During it, small hydrogen leaks were detected, but they remained within acceptable limits. The next launch opportunity will appear on September 27. However, the problem with the supply of liquid hydrogen is not the only one that can prevent the launch this time. First of all, this concerns the emergency flight termination system, the certificate of conformity of which expired during the previous launch attempt. The weather can also make its own adjustments. Now forecasters are watching the atmospheric disturbance Invest 98L flying over the Caribbean. In a few days it may turn into a storm.
China to launch probes to Uranus and Jupiter
China is preparing to launch two scientific missions with one rocket in 2030. The first of the probes will be directed to Jupiter and will study its moons. The second one will fly to Uranus. Both devices will operate under a single program called “Tianwen-4”. They will also launch them together, for which they use a giant Long March 5 rocket. First, the two spacecraft will fly together, and then they will separate and each will head towards its goal.
The scientific goals and the final design of both devices are still under development. Apparently, the mass of the main vehicle, which will be sent to Jupiter, will exceed a ton. Its main goal will be to enter the orbit of the most distant of the four major moons of Jupiter, Callisto. The smaller of the two spacecraft, which will be sent to Uranus, will have a mass of hundreds of kilograms. The program of its flights, perhaps, will provide for a rendezvous with an asteroid similar to the flight of the asteroid Lutetia, made by the Rosetta apparatus.
Not to distinguish Venus from Earth: James Webb found a flaw
Astronomers have expressed concern that JWST data on exoplanets may be interpreted incorrectly. To confirm their concerns, the researchers created a set of artificial spectra obtained from the telescope. Then, using existing models, they tried to determine what chemical composition these spectra correspond to. It turned out that their accuracy is very limited. They do not always allow you to distinguish the temperature of the atmosphere at 26 °C from 326 °C, and also to identify the difference between 5% or 25% of the content of a certain gas, in particular water vapor. Due to such an error in the data obtained from James Webb, for example, it will be difficult for scientists to distinguish the “living” Earth from the incandescent Venus. Thus, the boundary between the suitability of the planet for life and unsuitability becomes barely noticeable.
Photo of the week
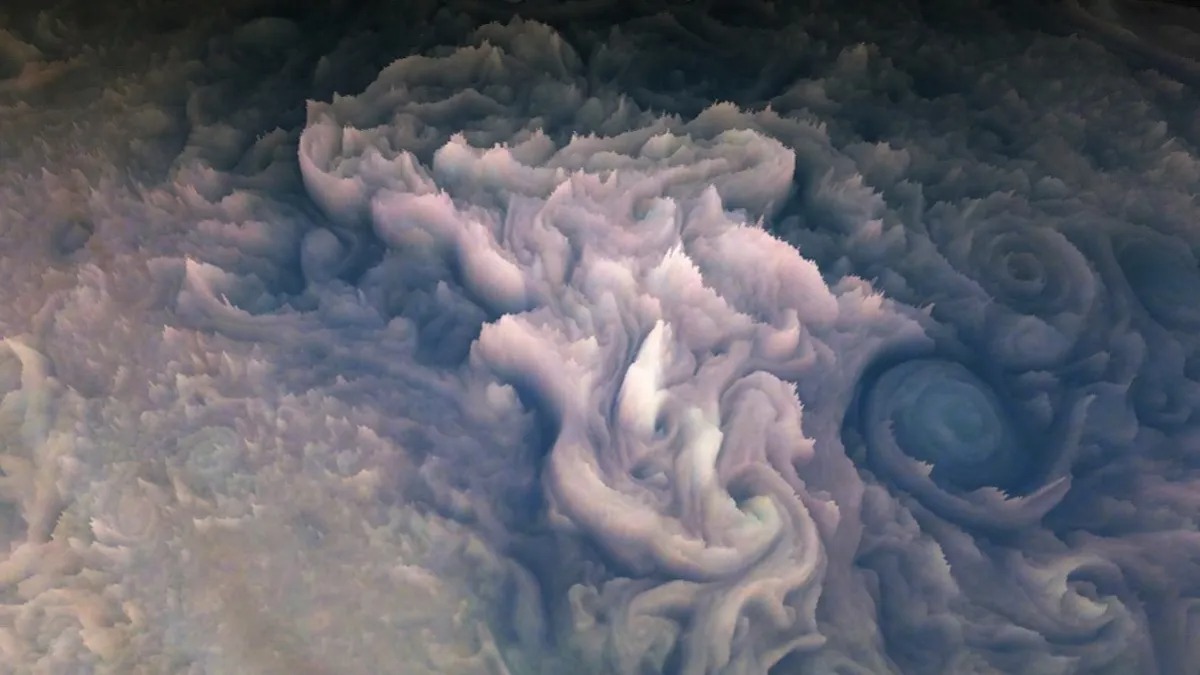

A team of scientists wanted to find out what Jupiter’s clouds would look like with a sense of depth. Therefore, they created excellent 3D renderers using NASA’s Juno spacecraft. For ordinary citizens, these are spectacular shots, but for science they are more than just good photos in 3D. The team says digital models can help scientists improve their understanding of the chemical composition of clouds.
Interesting figure — 587 million km
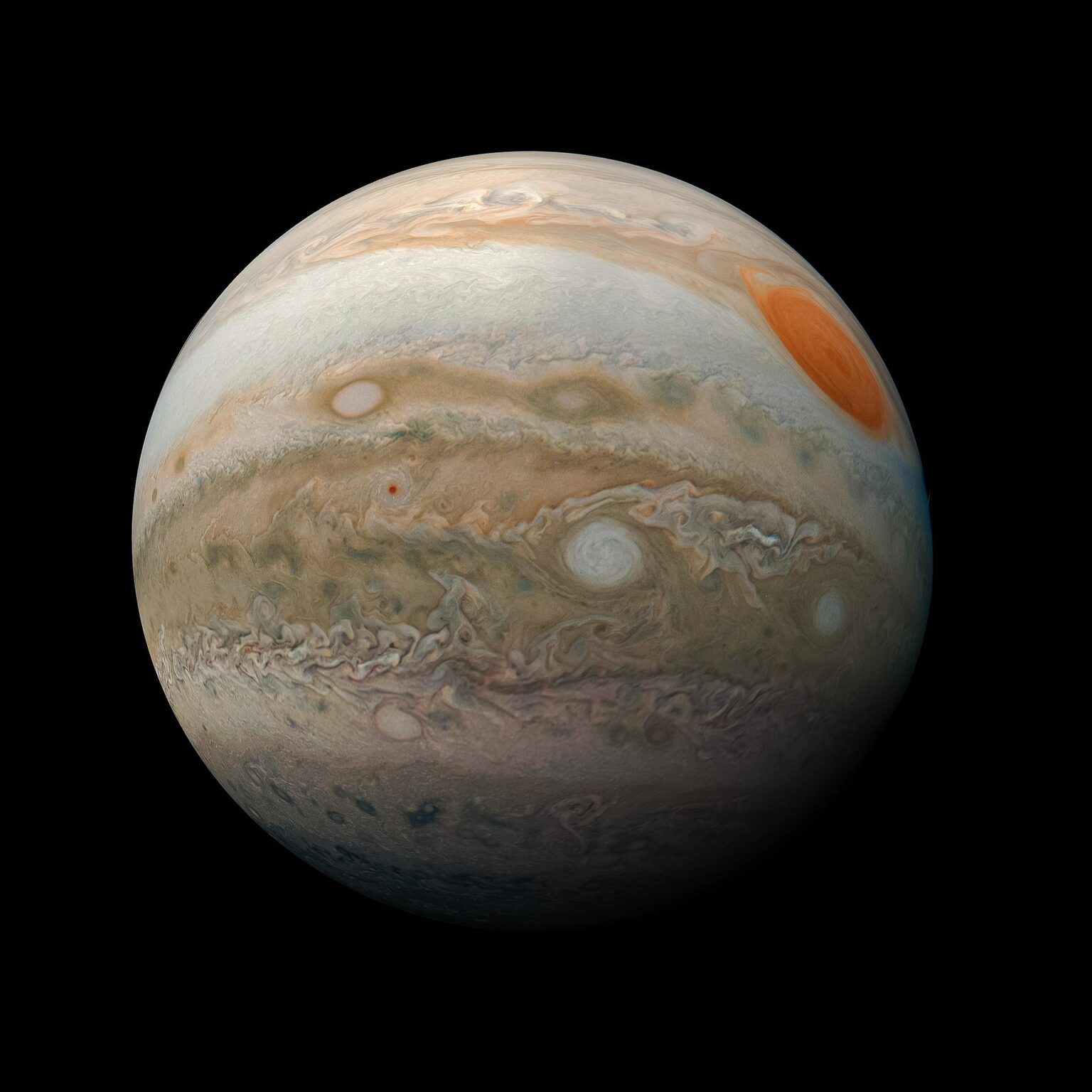
Jupiter’s opposition occurs every 13 months. But in September 2022, the planet will come as close as possible to the Earth at a distance of 587 million km — as opposed to 965 million km at the farthest point. Such a rapprochement will happen for the first time in 70 years.
Something to read on the weekend
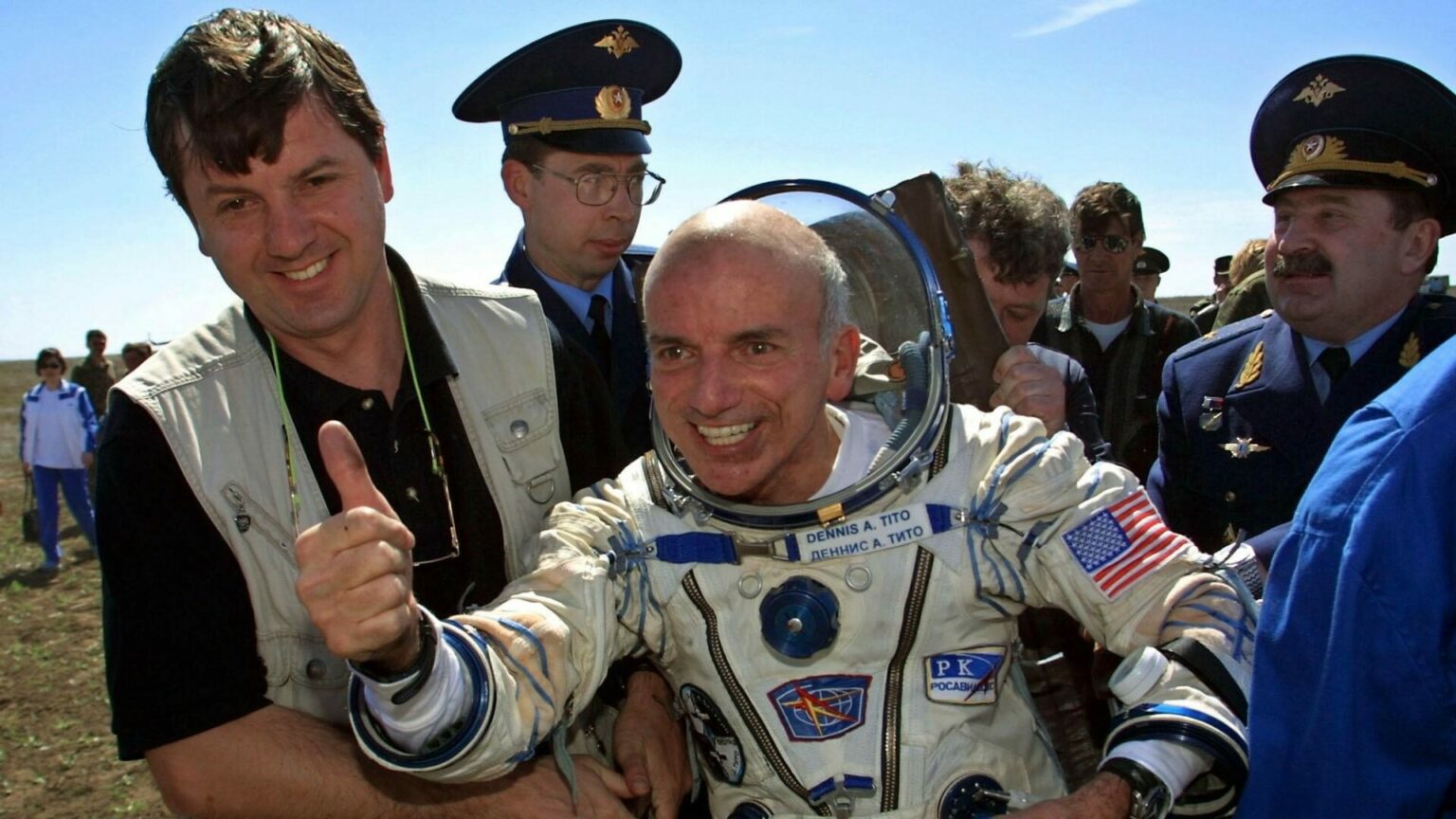

In April 2001, the first tourist flew into space. Thus began a new era in space travel. How much did the first flight cost? Who has already flown on a tour to orbit, as well as what are the main offers on the market today? Read the article “How to become a space tourist“.
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

