The Japanese company iSpace published the results of the investigation of the accident of the Hakuto-R spacecraft, which crashed during the moon landing. The reason for the failure was an error in the probe’s software.
Hakuto-R was built by a team of engineers who once participated in the Google Lunar X PRIZE competition. The Japanese spacecraft went into space on December 11, 2022. Together with it, the first ever Arab rover “Rashid” flew to the Moon. The 10-kilogram spacecraft was built by the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Center (UAE).

In March 2023, Hakuto-R entered a permanent orbit around the Moon, after which experts began to prepare it for landing. It took place on April 25 and initially was held in the normal mode. However, just a few minutes before contact with the surface, communication with the spacecraft was lost. Later, the American LRO probe photographed the wreckage left after the crash of the Hakuto-R.
Reason for the accident Hakuto-R
On May 26, iSpace published a report on the results of the investigation of the Hakuto-R accident. The engineers came to the conclusion that it occurred due to a software glitch. During the descent, the Japanese spacecraft flew over a high cliff, which is part of the shaft of a large impact crater. There was a larger than planned discrepancy between the measured altitude value and the calculated one, which was why the probe’s onboard computer mistakenly decided that the device’s altimeter had given out incorrect data, after which it began to “filter” them.
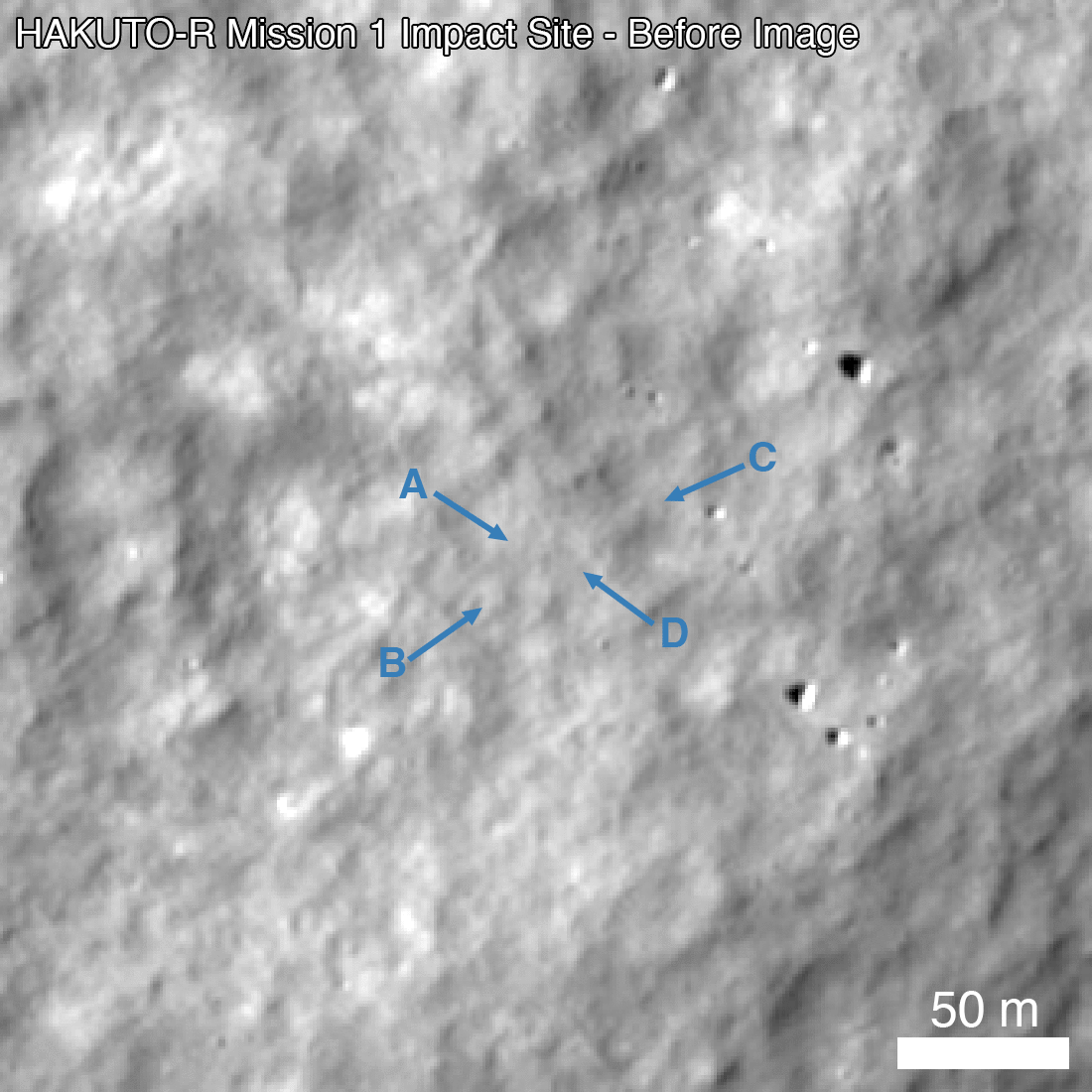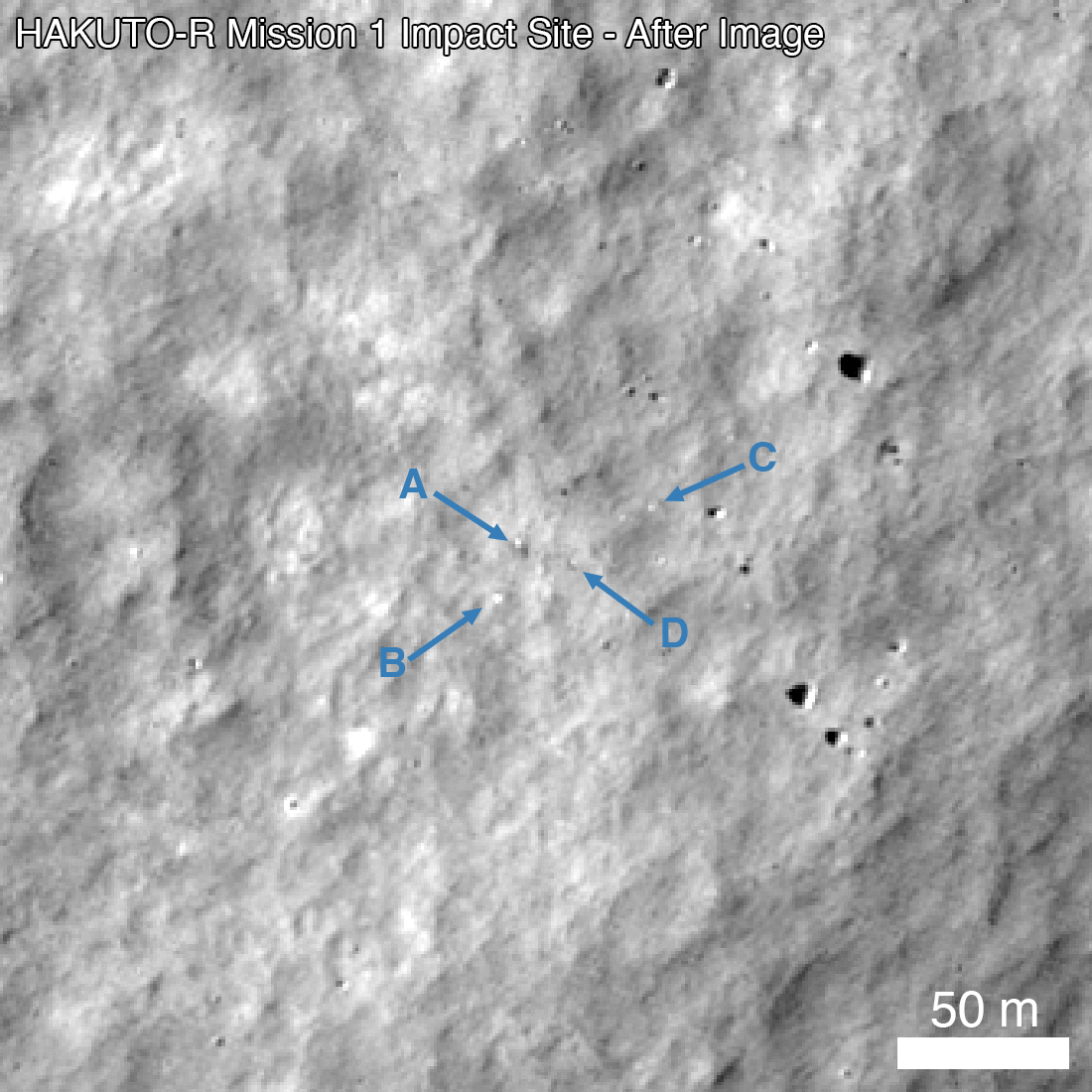
This led to the fact that when the Hakuto-R was at an altitude of 5 km above the lunar surface, the system decided that it had already landed. After that, the spacecraft’s engines continued to operate in low-thrust mode until it ran out of fuel and fell to the Moon.
iSpace also noted that one of the indirect causes of the accident was a rather late decision to change the landing site of the mission. After that, iSpace specialists conducted a number of additional landing simulations, but they did not take into account the changed terrain. As a result, a fatal mistake was made in the software.
According to the company’s statement, it will take into account the lessons of the Hakuto-R landing and make appropriate changes to the software and landing procedure for future lunar missions. Their implementation is planned for 2024-2025.
According to https://ispace-inc.com
Follow us on Twitter to get the most interesting space news in time
https://twitter.com/ust_magazine

