Astronomers have obtained images of a star different from the Sun for the first time with enough detail to trace the movement of gas on its surface. They were taken using ALMA.

Stars produce energy in their cores by nuclear fusion. This energy can be carried to the surface of the star in huge hot bubbles of gas, which then cool and sink — like a lava lamp. Such mixing motion, known as convection, distributes heavy elements formed in the core, such as carbon and nitrogen, throughout the star. It is also thought to be responsible for the stellar winds that carry these elements across the space where they then become part of new stars and planets.
Until recently, convective motions had never been tracked in detail in stars other than the Sun. But everything has changed thanks to ALMA. The capabilities of the complex allowed astronomers to obtain detailed images of the star R Doradus, where convective granules on its surface can be seen.
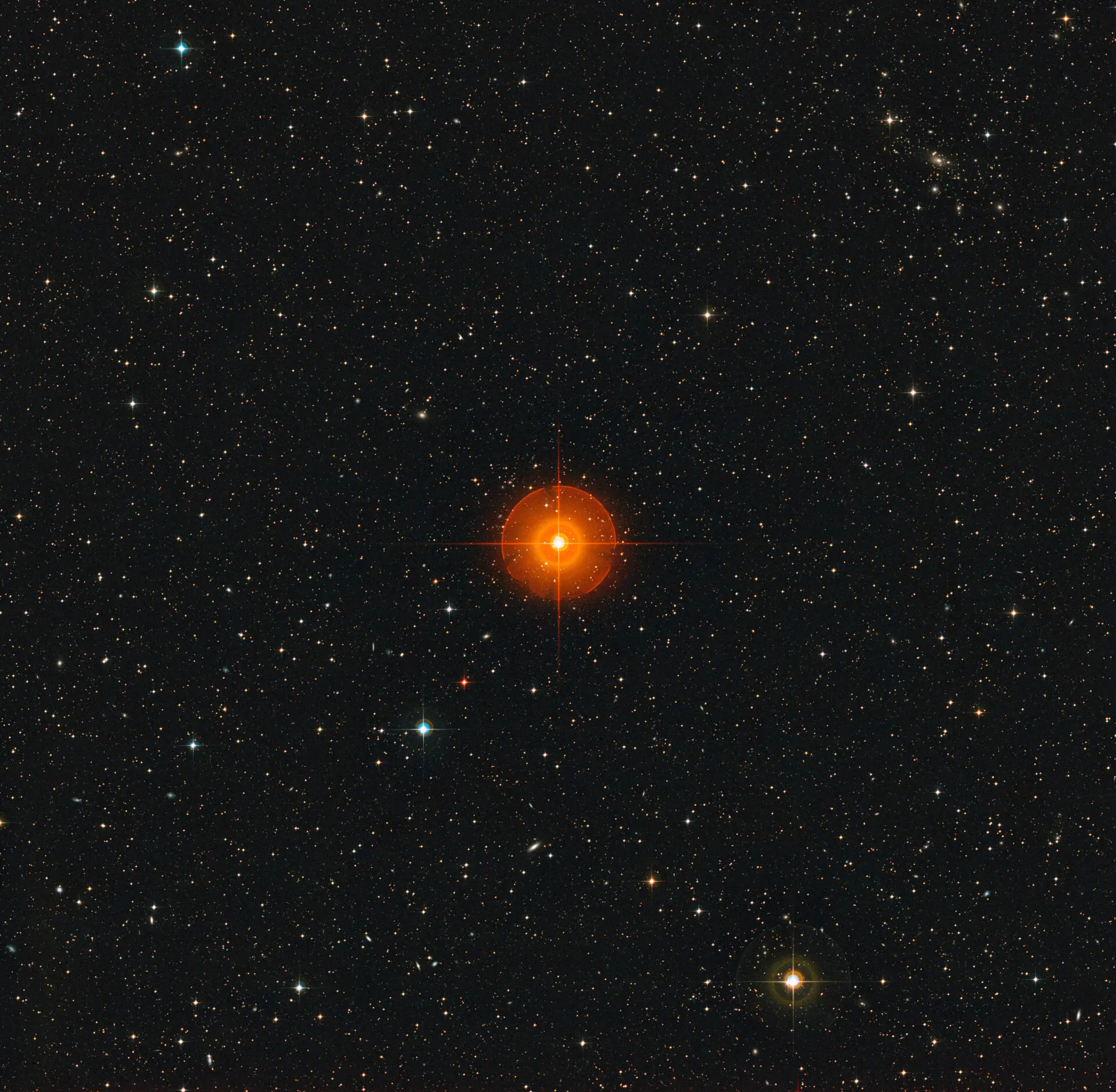

R Doradus is a pulsating red giant located about 180 light-years away from Earth. Its diameter is about 350 times that of the Sun. Its large size and proximity to Earth make it an ideal target for detailed observations. In addition, its mass is similar to that of the Sun. This means that R Doradus is probably very similar to what our Sun will look like five billion years from now, when it will also be a red giant.
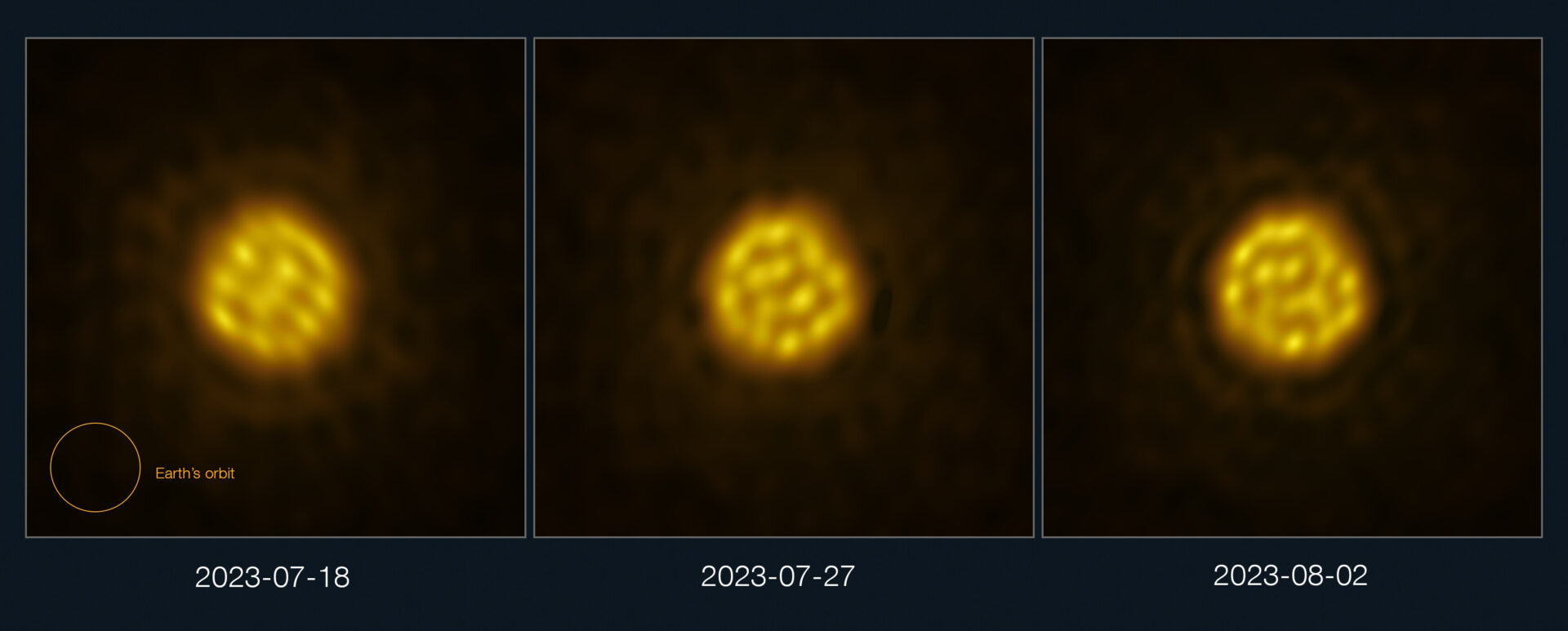
ALMA studied R Doradus in July and August 2023. The resulting images show how giant hot bubbles of gas, 75 times the size of the Sun, appear on the surface and then sink back into the interior of the star. The granules of R Doradus move on a monthly cycle. This is faster than scientists expected based on how convection works on the Sun.
So far, the researchers don’t know what the reason for this difference is. It is possible that convection changes as the star ages. Additional observations of R Doradus and other red giants may provide the answer.
You can also read our selection of interesting facts about the red giant Betelgeuse, which gave its name to the movie Beetlejuice.
According to Almaobservatory


