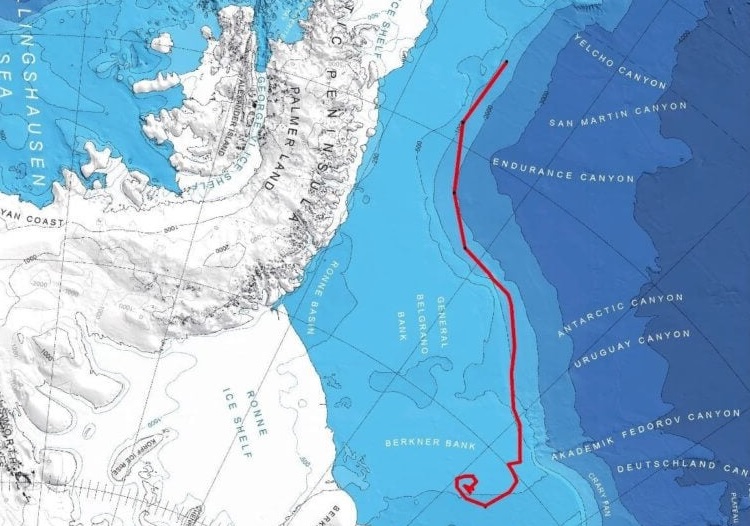
In early December of this year, ice monitoring services near Antarctica reported that the iceberg with the A23a index began to actively move towards the open ocean. The giant ice block is considered to be the largest on the planet: according to some estimates, its surface area is now about 4,170 km², which is one and a half times the size of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
The iceberg broke off from the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in the West Antarctic back in 1986 (this forced the Soviet Union to shut down the Druzhnaya-1 research station located there). However, it could not move far from the Antarctic coast: the thickness of the ice floe was very uneven, and its “deepest” point rested on the bottom of the Weddell Sea, preventing further progress.

Over time, the global warming began to gradually deteriorate the iceberg, reducing its thickness by about 2.5 meters per year. As a result, it finally broke away from the bottom and began to float, getting more and more submissive to winds and sea currents. Active movements were noticed in 2021, which made scientists take a closer look at the ice mountain. To study it, specialized satellites were used, including the European CryoSat-2, equipped with a radar altimeter, which can measure the profile of not only the surface of the iceberg but also its underwater part.
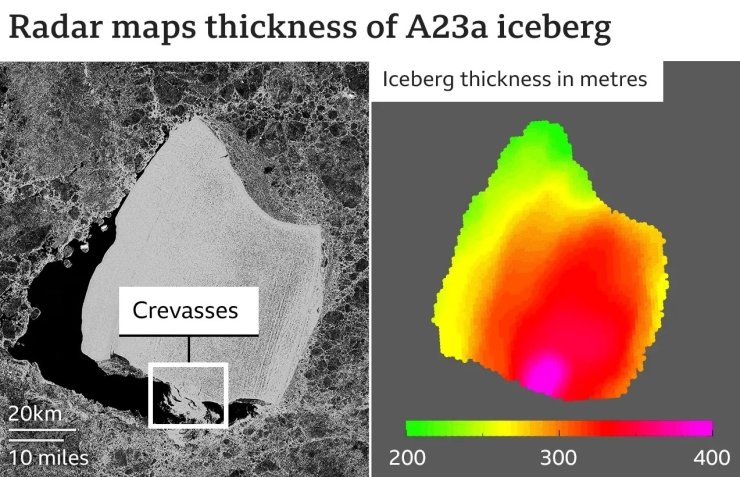
The results show that the average thickness of A23a is more than 280 meters, but its ice “keel” goes underwater by 350 meters, which is slightly less than the height of the Kyiv TV tower. Using this data, the researchers calculated the volume of the iceberg to be almost 1,100 cubic kilometers. This means that its mass reaches a trillion tons.
Now, with a better understanding of the shape of the underwater part of the ice giant, scientists will be able to more accurately predict its behavior. For now, they continue to monitor it. According to most experts, it has already reached a critical point in its journey north and will very soon go beyond the Weddell Sea, where it will be “picked up” by the powerful currents of the Southern Ocean.
Earlier we wrote about how scientists are trying to reduce the impact of global warming on the Antarctic ice sheet.
Based on the materials: www.ndtv.com

