Our website readers and social media followers regularly ask us various space-related questions. The Universe Space Tech editorial team decided to answer the most interesting ones. Today we will talk about why satellites do not fall to Earth, whether it is possible to build a FTL ship, and whether there are odors in space.

Why doesn’t a geostationary satellite fall to Earth?
Oleg.
Geostationary satellites do not fall to Earth for the same reason as all other satellites. They move at such a high speed that the centrifugal force becomes equal to gravity at the height of their orbit and prevents them from falling onto our planet. This, by the way, is a common misconception. In fact, on the ISS, the force of Earth’s gravity is 90% of the value we are used to. The astronauts are in a state of weightlessness not because there is no gravity, but because they are constantly in a state of free fall.
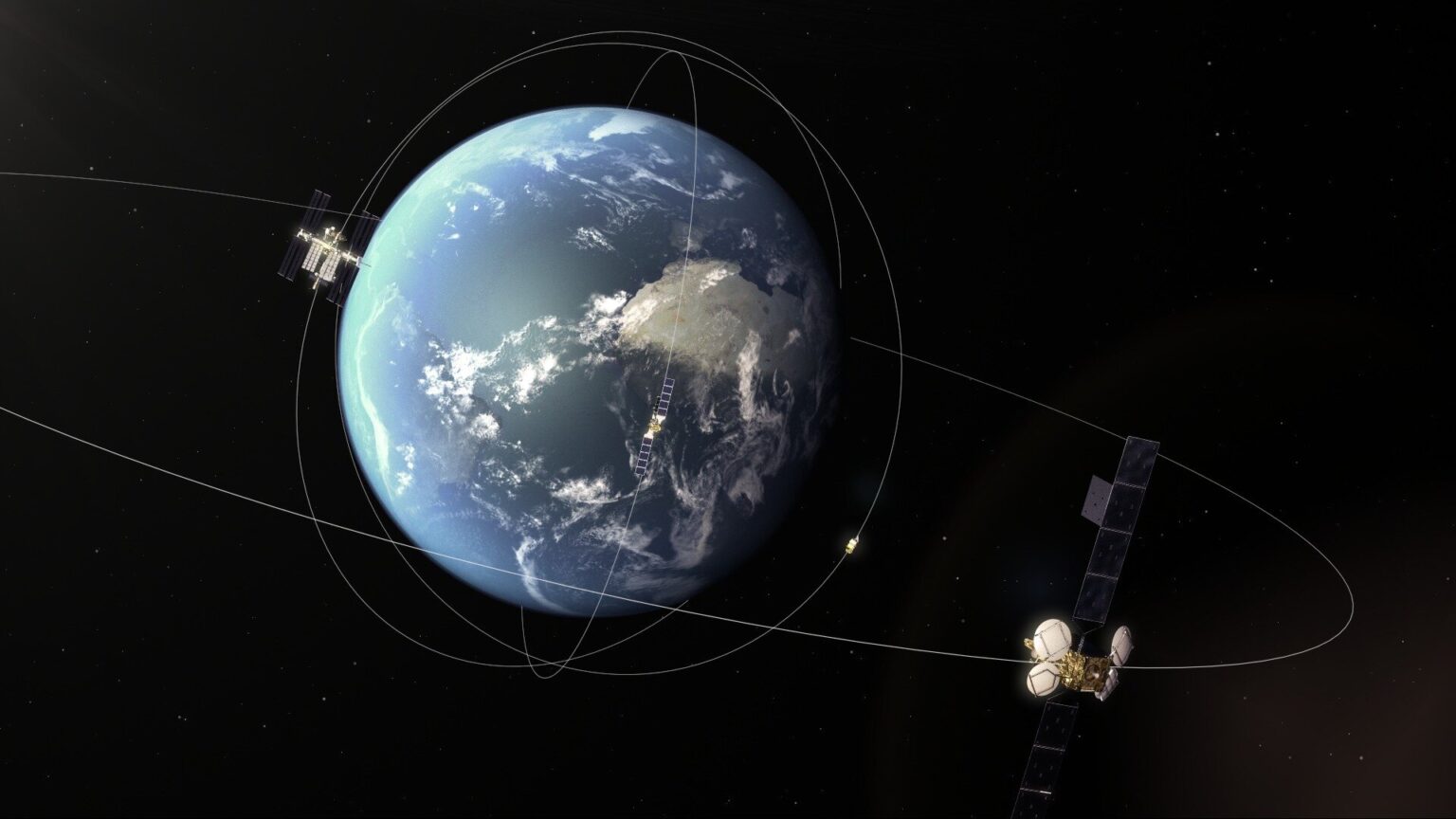

Another important detail should be noted. Due to the inhibiting effect of the upper layers of the Earth’s atmosphere, the orbital altitude of satellites decreases over time until they eventually de-orbited. However, this mechanism does not work in the case of the geostationary orbit. It is located at an altitude of 36 thousand kilometers, where atmospheric braking is really weak. Therefore, vehicles in geostationary orbit will remain in space for many millions of years.
Why does Mercury have such a large core? What are the hypotheses?
Maria.
Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System. Its radius is only 2440 km. At the same time, according to the latest data, the radius of Mercury’s core is 2020 km and it occupies 57% of the planet’s internal volume. For comparison, this figure for the Earth is only 17%.
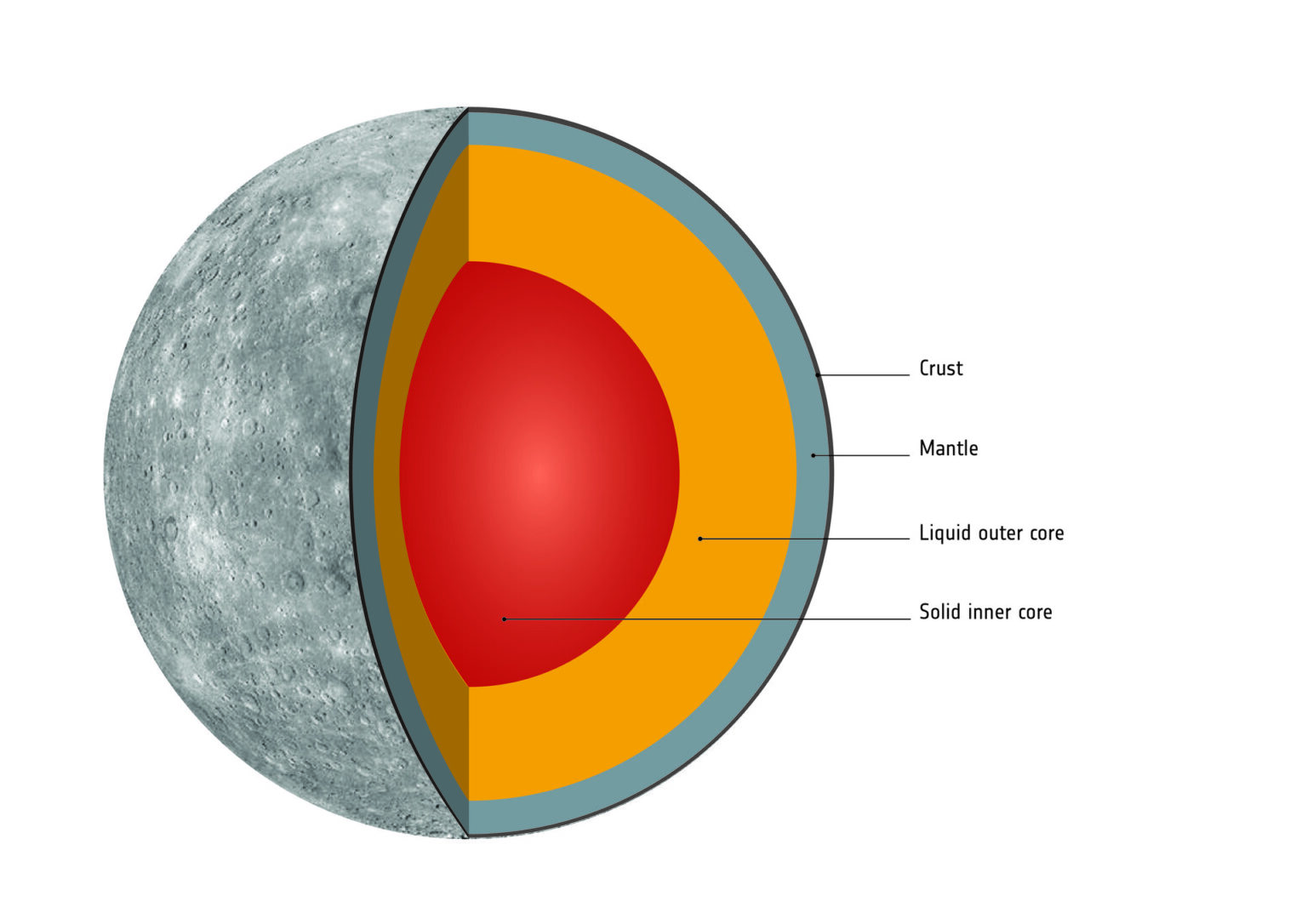
According to the most popular theory, immediately after its formation, Mercury had a typical rocky planet structure. But then it collided with some large object. This tremendous impact literally tore off its crust and most of its mantle.
According to another version, at the time of the planet’s formation, its mass was about twice as large as it is today, but due to the powerful radiation of the newborn Sun, most of the surface rocks evaporated. According to the third hypothesis, the planet was formed from the heaviest particles of the protoplanetary disk, while lighter particles were pushed to its outer part.
The BepiColombo mission may help determine which of these hypotheses is correct. One of its main tasks is to reveal the secret of Mercury’s core. BepiColombo will arrive to the planet in December 2025.
Will it be possible to invent a ship that fly faster than light (or travel through “wormholes” or use some similar method) and visit distant planets?
Oksana Duldier.
The theory of relativity states that no object in the universe can move at a speed that exceeds the speed of light. And no matter how much some fans of alternative physics would like it, all the experiments conducted by scientists confirm the correctness of Einstein’s conclusions.
At the same time, the theory of relativity can be circumvented by creating a device that would compress the space in front of the spacecraft and expand it behind. This concept is also called an Alcubierre bubble. Another option is to travel through a wormhole — a space-time tunnel, the existence of which also does not contradict the postulates of relativity.
However, both the Alcubierre bubble and wormholes are still purely imaginary concepts. Currently, scientists do not have a consensus on whether they can actually exist, let alone any technology that would allow them to create something like this.
How far away is the planet where life might exist?
Svitlana Matus.
If we talk about our solar system, the most promising places to search for extraterrestrial life are now considered to be the satellites of giant planets with subsurface oceans — Europa, Enceladus, Titan, and Triton. Also, the possibility of life on Mars (under the planet’s surface) and even Venus (in the form of microbes in the upper layers of its atmosphere) is still not excluded.
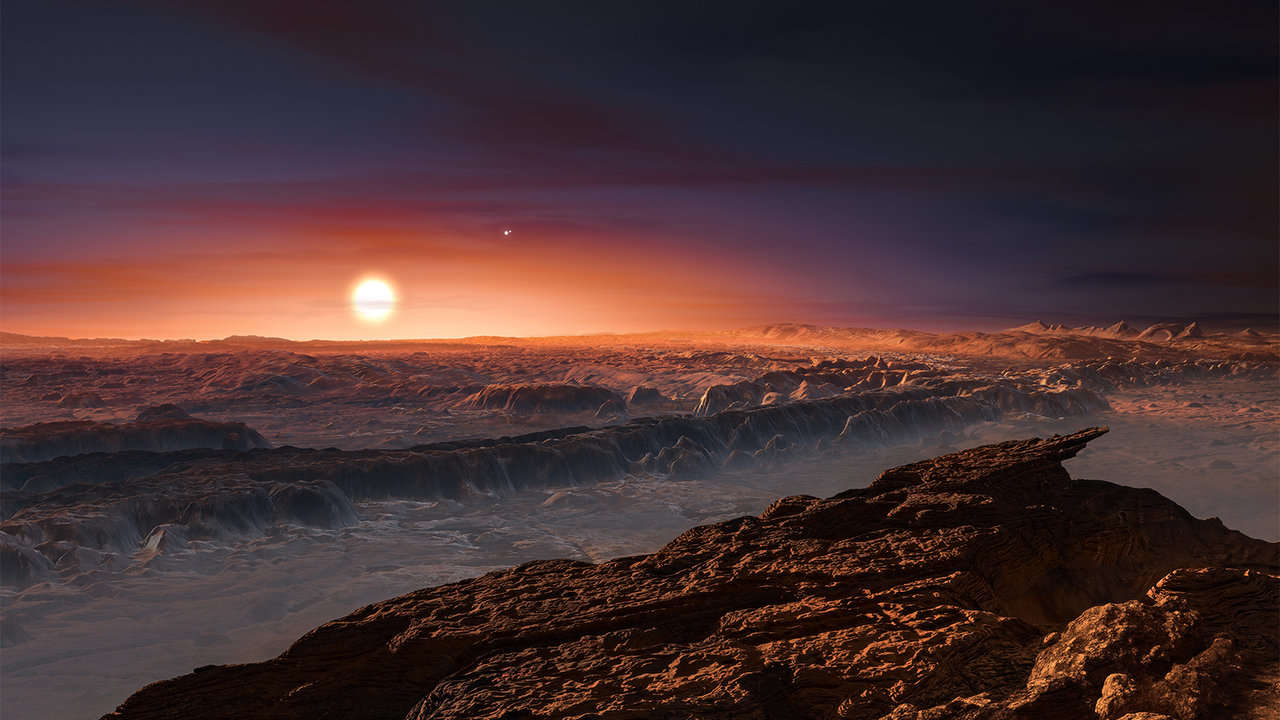

Speaking of planets near other stars, a very promising world can be found right next to the star closest to the Sun, Proxima Centauri. Astronomers have found that at least two exoplanets orbit around it. One of them is a so-called super-Earth, whose orbit passes through the habitable zone. This means that its surface receives enough energy from the star to allow water to exist in liquid form if it has an atmosphere.
Of course, finding a planet in a habitable zone does not guarantee the presence of life there. However, it does give hope that planets with suitable conditions for life may be quite common in the Universe.
Is there a smell in space?
Anna Korsakova.
We smell when the receptors in our nose perceive enough molecules of a substance to trigger a nerve impulse, which then travels to the brain. For obvious reasons, it’s impossible to smell something in space itself, as astronauts are separated from it by a spacesuit. And we hardly need to explain what will happen if you find yourself in a vacuum without a spacesuit or take off your helmet.

However, many astronauts say that space does have its own characteristic smell. When they take off their spacesuits after spacewalking, they smell an aroma that is unlike anything on Earth. It has been compared to the smell of welding, ozone, gunpowder, fried steak, and even burnt almond cookies.
Astronauts who landed on the Moon also noted the characteristic smell they felt as soon as they returned to the ship and took off their helmets. It was often compared to the smell of burnt gunpowder.
***
Friends! Send us your questions about space and we will definitely try to answer them.

