On January 28, the Voyager 1 probe passed the symbolic mark, moving 25 billion kilometers away from Earth. This is evidenced by tracker data on NASA’s website, which indicates the position and speed of the vehicle.
The most distant spacecraft in history
Voyager 1 was launched in 1977 to study the giant planets of the Solar System. In 1979, the spacecraft visited Jupiter, and in 1981 it made a flyby of Saturn. The gravity of the gas giants accelerated it, speeding it up enough to leave the Solar System forever.
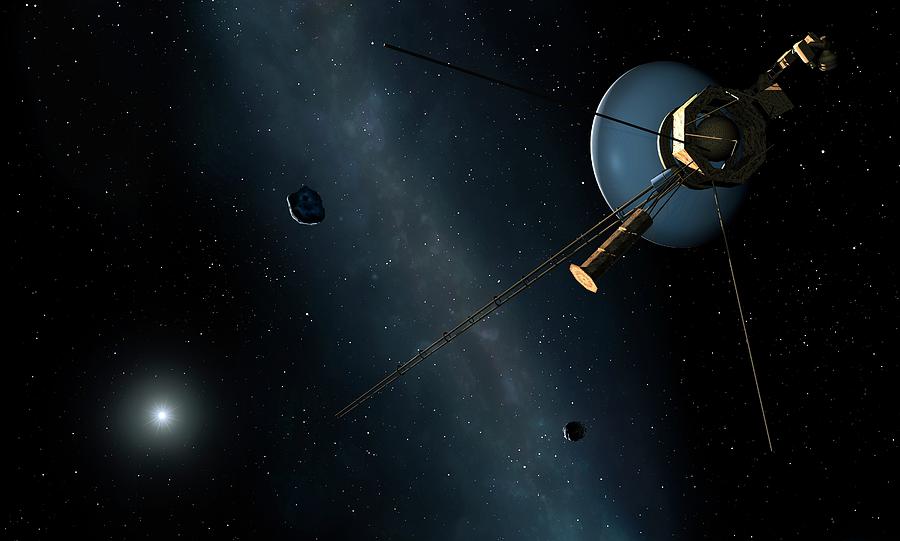

Despite the fact that it has been over 47 years since the launch of Voyager 1, it still remains operational. It has four operational scientific instruments on board that transmit measurements back to Earth. Admittedly, Voyager 1’s venerable age is increasingly making itself felt. There have been a number of incidents with the spacecraft in recent years. During the last one, NASA lost contact with it for some time.
In any case, none of this stopped Voyager 1 from setting another nice achievement. On January 28, it became the first spacecraft in history to travel 25 billion kilometers away from our planet. It now takes 23 hours and 9 minutes for a signal emitted from Earth to reach Voyager 1. It takes the same amount of time to get a response from the spacecraft.
It is important to note that since the Earth orbits the Sun, because of this, at some moments the distance between our planet and Voyager 1 does not increase, but decreases. As for the Sun, Voyager 1 is now at a distance of 24.84 billion kilometers from it. The spacecraft will move away from our star at a distance of 25 billion kilometers in mid-May 2025.
When will Voyager 1 move one light day away from the Sun?
The next milestone for Voyager 1 will be a distance of one light day (25,902,068,371.2 kilometers). The vehicle will move to such a distance from the Sun in January 2027 — i.e. in the year of the fiftieth anniversary of its launch. It is expected that Voyager 1 will still be functional by this point, although engineers will probably have to shut down some of its remaining science instruments due to the depletion of its radioisotope generators.
From a human perspective, the distance of one light day is unimaginably vast. But that’s not much by astronomical standards. The closest star to the Sun, Proxima Centauri, is 4.24 light-years away. It would take Voyager 1 74,000 years to travel that distance.


